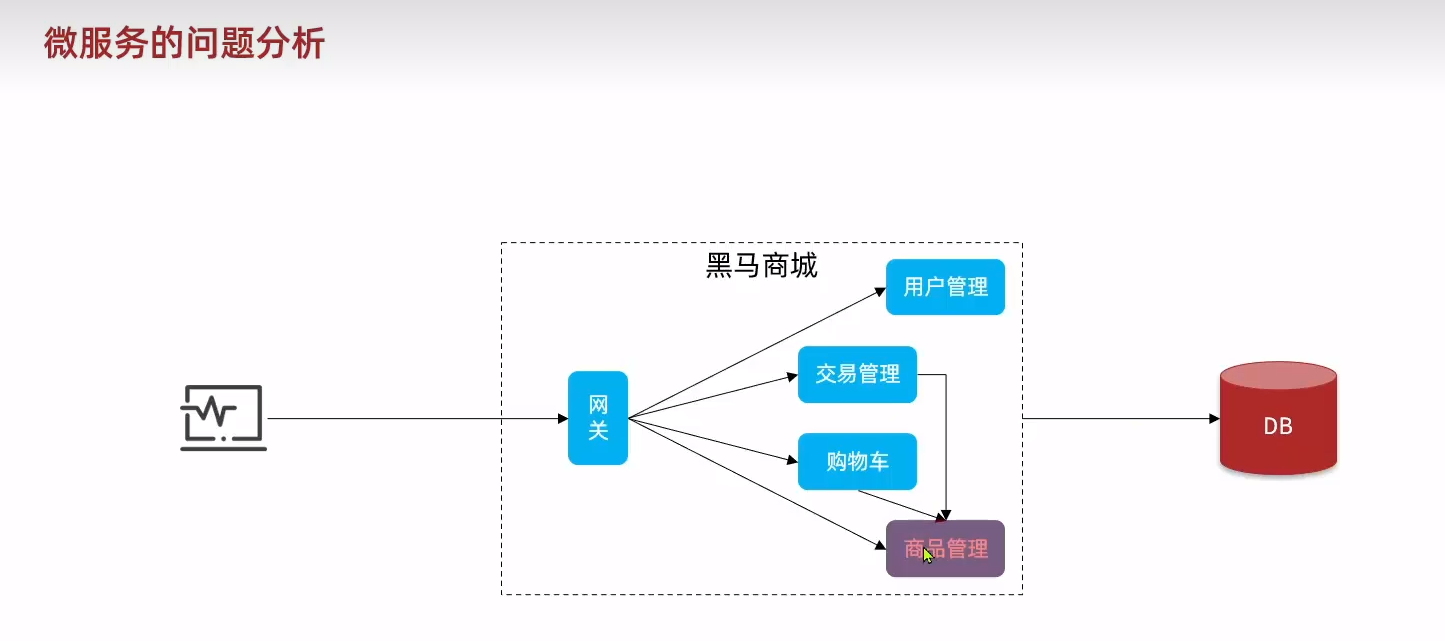
14-1、IO流
lO流打开和关闭
通过构造函数打开I/O流
其中filename表示文件路径,mode表示打开模式
- 打开输入流
ifstream (const char* filename ,openmode mode) - 打开输出流
ofstream(const char* filename , openmode mode); - 打开输入输出流
fstream (const char* filename , openmode mode);
lO流打开模式
- ios::out
打开文件用于写入,不存在则创建,存在则清空
适用于ofstream(缺省)/fstream - ios::app
打开文件用于追加,不存在则创建,存在不清空
适用于ofstream/fstream - ios::trunc
打开时清空原内容
适用于ofstream/fstream - ios:in
打开文件用于读取,不存在则失败,存在不清空
适用于ifstream(缺省)/fstream - ios::ate
打开时定位文件尾
适用于ifstream/fstream - ios.:binary
以二进制模式读写
适用于ifstream/ofstream/fstream
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ofstream(文件输出流)类
int main( void ){
ofstream ofs1("./file",ios::out);
if(!ofs1){ // !(ofs1.operator bool())
cout << "ofs1流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
}
ofs1 << 1234 << ' ' << 56.78 << ' ' << "Hello" << '\n';
if(!ofs1){
cout << "ofs1流对象状态错误 -- 写文件失败" << endl;
}
ofs1.close();
ofstream ofs2("./file",ios::app);
if(!ofs2){ // !(ofs2.operator bool())
cout << "ofs2流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
}
ofs2 << "World" << endl;;
if(!ofs2){
cout << "ofs2流对象状态错误 -- 写文件失败" << endl;
}
ofs2.close();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ifstream ifs1("./file",ios::in);
if(!ifs1){ // !(ifs1.operator bool())
cout << "ifs1流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
}
int i; double d; string s1,s2;
ifs1 >> i >> d >> s1 >> s2;
if(!ifs1){
cout << "ifs1流对象状态错误 -- 读文件失败" << endl;
}
cout << i << ' ' << d << ' ' << s1 << ' ' << s2 << endl;
ifs1.close();
ifstream ifs2("./file",ios::ate);
if(!ifs2){ // !(ifs2.operator bool())
cout << "ifs2流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
}
ifs2.seekg(0,ios::beg);
int ii; double dd; string ss1,ss2;
ifs2 >> ii >> dd >> ss1 >> ss2;
if(!ifs2){
cout << "ifs2流对象状态错误 -- 读文件失败" << endl;
}
cout << ii << ' ' << dd << ' ' << ss1 << ' ' << ss2 << endl;
ifs2.close();
return 0;
}
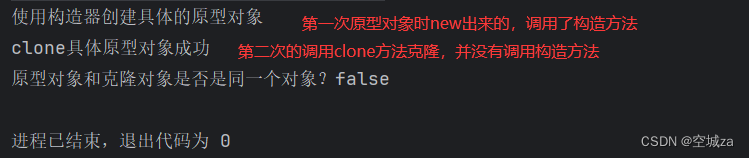
lO流对象的状态
I/O流类对象内部保存当前状态,其值为以下常量的位或
- ios:goodbit: 0,一切正常
- ios::badbit: 1,发生致命错误
- ios::eofbit: 2,遇到文件尾
- ios::failbit: 4,打开文件失败或实际读写字节数未达预期
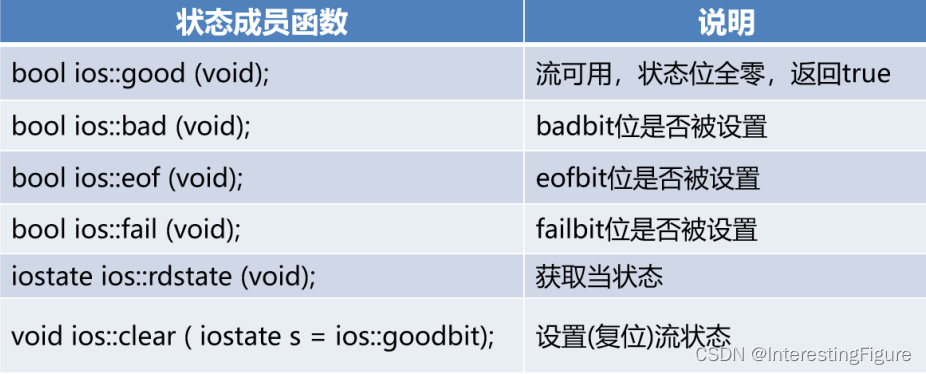
l/O流类对象支持到bool类型的隐式转换
- 发生1,2,4等情况,返回false,否则返回true
- 将I/O流对象直接应用到布尔上下文中,即可实现转换
处于1或4状态的流,在复位前无法工作
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ifstream ifs2("./file",ios::ate);
if(!ifs2){ // !(ifs2.operator bool())
cout << "ifs2流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
}
int ii; double dd; string ss1,ss2;
cout << "--------------------第一次读数据-----------------------" << endl;
ifs2 >> ii >> dd >> ss1 >> ss2;// ifs2.operator>>(ii).operator>>(dd)>>operator>>(ss1)>>operator>>(ss2)
if(!ifs2){
cout << "ifs2流对象状态错误 -- 读文件失败" << endl;
cout << "ifs2是0状态吗?" << ifs2.good() << ", ifs2是1状态吗?" << ifs2.bad()
<< ", ifs2是2状态吗?" << ifs2.eof() << ", ifs2是4状态吗?" << ifs2.fail() << endl;
cout << "ifs2的具体状态:" << ifs2.rdstate() << endl;
}
cout << ii << ' ' << dd << ' ' << ss1 << ' ' << ss2 << endl;
ifs2.clear();
ifs2.seekg(0,ios::beg);
cout << "--------------------第二次读数据-----------------------" << endl;
ifs2 >> ii >> dd >> ss1 >> ss2;// ifs2.operator>>(ii).operator>>(dd)>>operator>>(ss1)>>operator>>(ss2)
if(!ifs2){
cout << "ifs2流对象状态错误 -- 读文件失败" << endl;
cout << "ifs2是0状态吗?" << ifs2.good() << ", ifs2是1状态吗?" << ifs2.bad()
<< ", ifs2是2状态吗?" << ifs2.eof() << ", ifs2是4状态吗?" << ifs2.fail() << endl;
cout << "ifs2的具体状态:" << ifs2.rdstate() << endl;
}
cout << ii << ' ' << dd << ' ' << ss1 << ' ' << ss2 << endl;
ifs2.close();
return 0;
}
非格式化IO
- 写入字符
ostream& ostream::put (char ch);一次向输出流写入一个字符,返回流本身 - 刷输出流
ostream& ostream::flush (void);将输出流缓冲区中的数据刷到设备上,返回流本身 - 读取字符
int istream::get (void);成功返回读到的字符,失败或遇到文件尾返回EOF
istream& istream::get (char& ch);返回输入流本身,其在布尔上下文中的值,成功为true,失败或遇到文件尾为false - 读取行
istream& istream::getline (char* buffer,streamsize num, char delim = ‘\ n’);- 读取字符 (至定界符)到buffer中。
- 一旦读取了num个字符还未读取定界符,第num个字符设置为 ‘\0’,返回 (输入流对象状态为4)。
- 如果因为遇到定界符 (缺省为 ‘\n’ ) 返回 (输入流对象状态为0)定界符被读取并丢弃,追加结尾空字符 ‘\0’,读指针停在该定界符的下一个位置
- 遇到文件尾,返回 (输入流对象状态为6)
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ofstream(文件输出流)、ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ofstream ofs("./noformat",ios::out);
if(!ofs)
cout << "ofs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
for( char c = ' '; c <= '~';c++)
ofs.put(c).flush();
ofs.close();
ifstream ifs("./noformat",ios::in);
if(!ifs)
cout << "ifs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
char c;
// 单參get
while(1){
ifs.get(c);
if(!ifs)
break;
else
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;
ifs.clear();
ifs.seekg(0,ios::beg);
// 无參get
while(1){
c = ifs.get();
if( c == EOF )
break;
else
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;
ifs.close();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ofstream(文件输出流)、ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ifstream ifs("./getline",ios::in);
if(!ifs)
cout << "ifs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
char buf[256];
while(1){
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n');
if(!ifs)
break;
else{
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
}
}
/*
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); // aa\n
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); // bbbb\n
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); // cccccc\n
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); // dddddddd\n
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); // 0123456789\n
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
ifs.getline(buf,256,'\n'); //
cout << buf << endl;
cout << "ifs流对象状态值:" << ifs.rdstate() << endl;
*/
ifs.close();
return 0;
}
二进制IO
读取二进制数据
istream& istream::read (char* buffer,streamsize num)
- 从输入流中读取num个字节到缓冲区buffer中
- 返回流对象本身,其在布尔上下文中的值,成功(读满)为true,失败(没读满)为false
- 如果没读满num个字节,函数就返回了,比如遇到文件尾,最后一次读到缓冲区,buffer中的字节数可以通过istream::gcount()函数获得
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ofstream(文件输出流)、ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ofstream ofs("./binary",ios::out);
if(!ofs)
cout << "ofs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
ifstream ifs("./getline",ios::in);
if(!ifs)
cout << "ifs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
char buf[3];
while(1){
ifs.read(buf,3);
if(ifs){
ofs.write(buf,3);
// cout << buf; // 读满3个字符
}
else{
// 没有读满3个字符
int len = ifs.gcount();
ofs.write(buf,len);
// buf[len]='\0';
// cout << buf;
break;
}
}
ifs.close();
ofs.close();
return 0;
}
获取读长度
streamsize istream::gcount (void)
返回最后一次从输入流中读取的字节数
写入二进制数据
ostream& ostream::write (const char* buffer,streamsize num);
- 将缓冲区buffer中的num个字节写入到输出流中
- 返回流本身,其在布尔上下文中的值,成功(写满)为true,失败(没写满)为false
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
// C++标准库已经设计好的类ofstream(文件输出流)、ifstream(文件输入流)类
int main( void ){
ofstream ofs("./binary",ios::out);
if(!ofs)
cout << "ofs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
ifstream ifs("./getline",ios::ate);
if(!ifs)
cout << "ifs流对象状态错误 -- 打开文件失败" << endl;
int size = ifs.tellg();
char buf[size];
ifs.seekg(0,ios::beg);
ifs.read(buf,size);
ofs.write(buf,size);
ifs.close();
ofs.close();
return 0;
}
读写指针 和 随机访问
设置读/写指针位置
istream& istream::seekg (off_type offset,ios::seekdir origin);
ostream& ostream::seekg (off_type offset,ios::seekdir origin);
origin表示偏移量offset的起点:
ios::beg从文件的第一个字节ios::cur从文件的当前位置ios::end从文件最后一个字节的下一个位置
offset为负/正表示向文件头/尾的方向偏移
读/写指针被移到文件头之前或文件尾之后,则失败
获取读/写指针位置
返回读/写指针当前位置相对于文件头的字节偏移量
pos type istream::tellg (void);
pos type ostream::tellp (void):
字符串流
输出字符串流
#include <sstream>
ostringstream oss ;
oss << 1234 << ' ' << 56.78 <<' '<< "ABCD";
string os = oss.str();
输入字符串流
#include <sstream>
string is ("1234 56.78 ABCD") ;
istringstream iss (is);
int i;
double d;
string s;
iss >> i >> d >> s;