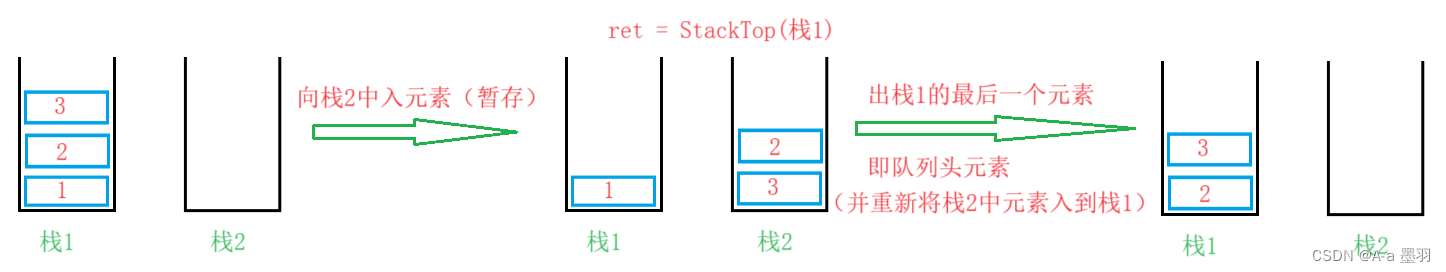
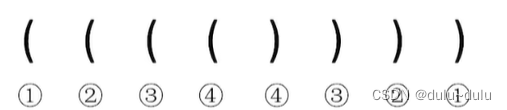2.1.1-2.1.2
定义顺序存储的栈(数组实现)
基于上述定义,实现出栈、入栈、判空、判满
#include <iostream>
#define size 10
using namespace std;
typedef struct stack{
int*data= (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) *size);
int pointer;
}stack;
void init(stack* st)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) st->data[i]=0;
st->pointer=0;
}
void print(stack* st)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
printf("%3d",st->data[i]);
}
cout<<endl;
}
bool is_full(stack *st)
{
if(st->pointer==size) return true;
else return false;
}
bool isEmpty(stack *st)
{
if(st->pointer==0) return true;
else return false;
}
void push(stack* st,int x)
{
if(is_full(st)) {
cout<<"the stack is full!"<<endl;
return;
}else{
st->data[st->pointer++]=x;
}
}
int pop(stack *st)
{
if(isEmpty(st)){
cout<<"the stack is empty"<<endl;
return -1;
}else{
return st->data[--st->pointer];
}
}
void test1()
{
stack stack1;
init(&stack1);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) push(&stack1,i);
print(&stack1);
int tmp;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) tmp=pop(&stack1), printf("%3d",tmp);
cout<<endl;
print(&stack1);
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
2.1.3-2.1.4
定义链式存储的栈(单链表表示)
栈顶在链头,实现出栈、入栈、判空、判满四个操作
#include <iostream>
#define number 10
using namespace std;
typedef struct node{
int data;
node* next;
}node;
node* buyNewnode(int x)
{
node *n1=(node*) malloc(sizeof (node));
n1->data=x;
n1->next= nullptr;
return n1;
}
typedef struct link{
node* head;
int size;
};
void init(link* l)
{
l->head=buyNewnode(-1);
l->size=0;
}
bool full(link* l)
{
return (l->size>=number);
}
void push(link* l,int x)
{
if (full(l)) cout<<"the stack is full"<<endl;
else{
node* tmp=buyNewnode(x);
tmp->next=l->head->next;
l->head->next=tmp;
l->size++;
}
}
bool empty(link* l)
{
return (l->size==0);
}
int pop(link* l)
{
if(empty(l)) cout<<"the link is empty"<<endl;
else{
int tmp=l->head->next->data;
node* p=l->head->next;
l->head->next=l->head->next->next;
free(p);
l->size--;
return tmp;
}
}
void print(link* l)
{
node* tmp=l->head->next;
while(tmp) printf("%3d",tmp->data),tmp=tmp->next;
cout<<endl;
}
void test1()
{
link l;
init(&l);
for(int i=0;i<11;i++) push(&l,i);
print(&l);
int tmp=-1;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) tmp= pop(&l), printf("%3d",tmp);
print(&l);
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
2.1.5-2.1.6
定义链式存储的栈(双向链表实现
基于上述定义,栈顶在链尾,实现“出栈、入栈、判空、判满”四个基本操作
#include <iostream>
#define number 10
using namespace std;
typedef struct node{
int data;
node* next;
node* prev;
}node;
node* buyNewnode(int x)
{
node *n1=(node*) malloc(sizeof (node));
n1->data=x;
n1->next= nullptr;
n1->prev= nullptr;
return n1;
}
typedef struct link{
node* head;
int size;
node* pointer;//队尾指针
};
void init(link* l)
{
l->head=buyNewnode(-1);
l->size=0;
l->pointer=l->head;
}
bool full(link* l)
{
return (l->size>=number);
}
void push(link* l,int x)
{
if (full(l)) cout<<"the stack is full"<<endl;
else{
node* tmp=buyNewnode(x);
l->pointer->next=tmp;
tmp->prev=l->pointer;
l->pointer=tmp;
l->size++;
}
}
bool empty(link* l)
{
return (l->size==0);
}
int pop(link* l)
{
if(empty(l)) cout<<"the link is empty"<<endl;
else{
int tmp=l->pointer->data;
node* p=l->pointer;
l->pointer=l->pointer->prev;
l->pointer->next= nullptr;
free(p);
l->size--;
return tmp;
}
}
void print(link* l)
{
node* tmp=l->head->next;
while(tmp) printf("%3d",tmp->data),tmp=tmp->next;
cout<<endl;
}
void test1()
{
link l;
init(&l);
for(int i=0;i<11;i++) push(&l,i);
print(&l);
int tmp=-1;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) tmp= pop(&l), printf("%3d",tmp);
print(&l);
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
2.2.1-2.2.2
定义顺序存储的队列(数组实现),要求数组空间可以循环使用
基于上述定义实现“出队、入队、判空、判满四个操作
#include <iostream>
#define size 10
using namespace std;
typedef struct queue{
int* data;
int head,rear;
};
void init(queue* q)
{
q->data=(int *) malloc(sizeof (int)*size);
q->head=0,q->rear=0;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) q->data[i]=-1;
}
void print(queue* q)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) printf("%3d",q->data[i]);
puts("");
}
bool full(queue* q)
{
return (q->rear+1)%size ==q->head;
}
bool empty(queue* q)
{
return q->rear==q->head;
}
void push(queue* q,int x)
{
if(full(q)) cout<<"the queue is full"<<endl;
else{
q->data[q->rear]=x;
q->rear=(++q->rear)%size;
}
}
int pop(queue*q)
{
if(empty(q)) cout<<"the queue is empty"<<endl;
else {
int tmp= q->data[q->head];
q->head=(++q->head)%size;
return tmp;
}
}
void test1()
{
queue q;
queue* pq=&q;
init(pq);
int tmp;
for(int i=0;i<size&&!full(pq);i++) push(pq,i);
for(int i=0;i<size&&!empty(pq);i++) tmp=pop(pq), printf("%3d",tmp);
puts("");
for(int i=0;i<size&&!full(pq);i++) push(pq,i);
for(int i=0;i<size&&!empty(pq);i++) tmp=pop(pq), printf("%3d",tmp);
puts("");
for(int i=0;i<5&&!full(pq);i++) push(pq,i);
for(int i=0;i<5&&!empty(pq);i++) tmp=pop(pq), printf("%3d",tmp);
puts("");
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
2.2.3-2.2.4
基于链式存储的队列(单链表实现)
基于上述定义,实现出队、入队、判空、判满四个基本操作
#include <iostream>
#define number 10
using namespace std;
typedef struct node{
int data;
node*next;
};
typedef struct queue{
node* head;
node*rear;
int size;
};
node * buynewnode(int x)
{
node *n1=(node*) malloc(sizeof (node));
n1->data=x;
n1->next= nullptr;
}
void init(queue * q)
{
q->head= buynewnode(-1);
q->rear=q->head;
q->size=0;
}
bool empty(queue* q)
{
return q->rear==q->head;
}
bool full(queue* q)
{
return q->size>=number;
}
void push(queue* q,int x)
{
if(full(q)) cout<<"the queue is full"<<endl;
else{
node* n1= buynewnode(x);
q->rear->next=n1;
q->rear=n1;
q->size++;
}
}
int pop(queue*q)
{
if(empty(q)) cout<<"the queue is empty"<<endl;
else{
node* tmp=q->head->next;
q->head->next=q->head->next->next;
int res=tmp->data;
free(tmp);
if(--q->size==0) q->rear=q->head;
return res;
}
}
void test1()
{
queue q;
queue* pq=&q;
init(pq);
for(int i=0;i<number&&!full(pq);i++) push(pq,i);
int tmp;
for(int i=0;i<number&&!empty(pq);i++) tmp=pop(pq), printf("%3d",tmp);
for(int i=10;i<21&&!full(pq);i++) push(pq,i);
for(int i=0;i<number&&!empty(pq);i++) tmp=pop(pq), printf("%3d",tmp);
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}