前言
本篇文章接上一篇【Linux取经路】网络套接字编程——UDP篇,所以目录号从十开始。
十、Tcp Server 端代码
10.1 socket、bind
listensockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listensockfd_ < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket creat successful, listensockfd_: %d", listensockfd_);
// 2. bind
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(port_);
// inet_aton(ip_.c_str(), &(local.sin_addr)); // 将 ip 地址转化成网络序列
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
socklen_t len = sizeof(local);
int ret = bind(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&local, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket bind successful");
TCP 这里的创建套接字、绑定代码和 UDP 中的一样。
10.1 listen——监听一个套接字
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
绑定完之后需要将监听套接字设为监听状态。
// 3. listen
// TCP 是面向连接的,服务器一般是比较“被动的”,在没有客户端访问的时候就只能干等,不能退出,服务器需要一直处于一种,一直在等待连接到来的状态
int n = listen(listensockfd_, backlog);
if (n < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket listen successful");
10.2 accept——获取一个新连接
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
该函数参数和 recvfrom 函数的参数一样,后面俩输出型参数用来获取 client 端的套接字信息。该函数的返回值是一个文件描述符,它和 socket 函数返回的文件描述符有什么区别呢?socket 函数返回的这个套接字用来绑定、监听和获取新的连接,一般把这个套接字叫做监听套接字,它的主要任务就是用来获取新连接,可以把它看成拉客的。accept 函数返回的套接字才是后面进行网络通信时使用的套接字,一个服务器进程,它的监听套接字一般就只有一个,而用来通信的套接字可能会存在多个。
for (;;)
{
// 4. 获取新连接
lg(Info, "server is running...");
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
int sockfd = accept(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port);
char client_ip[32];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(client.sin_addr), client_ip, sizeof(client_ip));
lg(Info, "get a new link, sockfd: %d, clientip: %s, clientport: %d", sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// 5. 根据新连接来进行通信
// version 1
Server(sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
sleep(1);
}
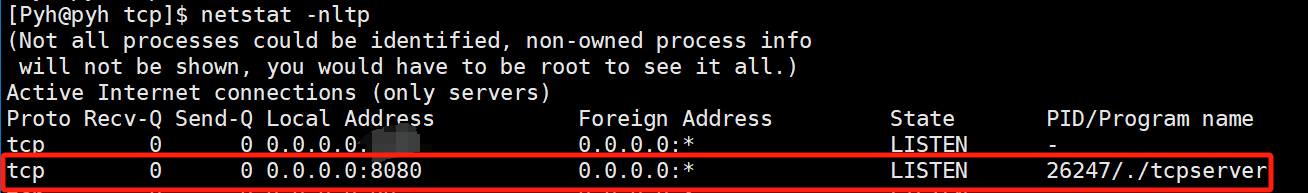
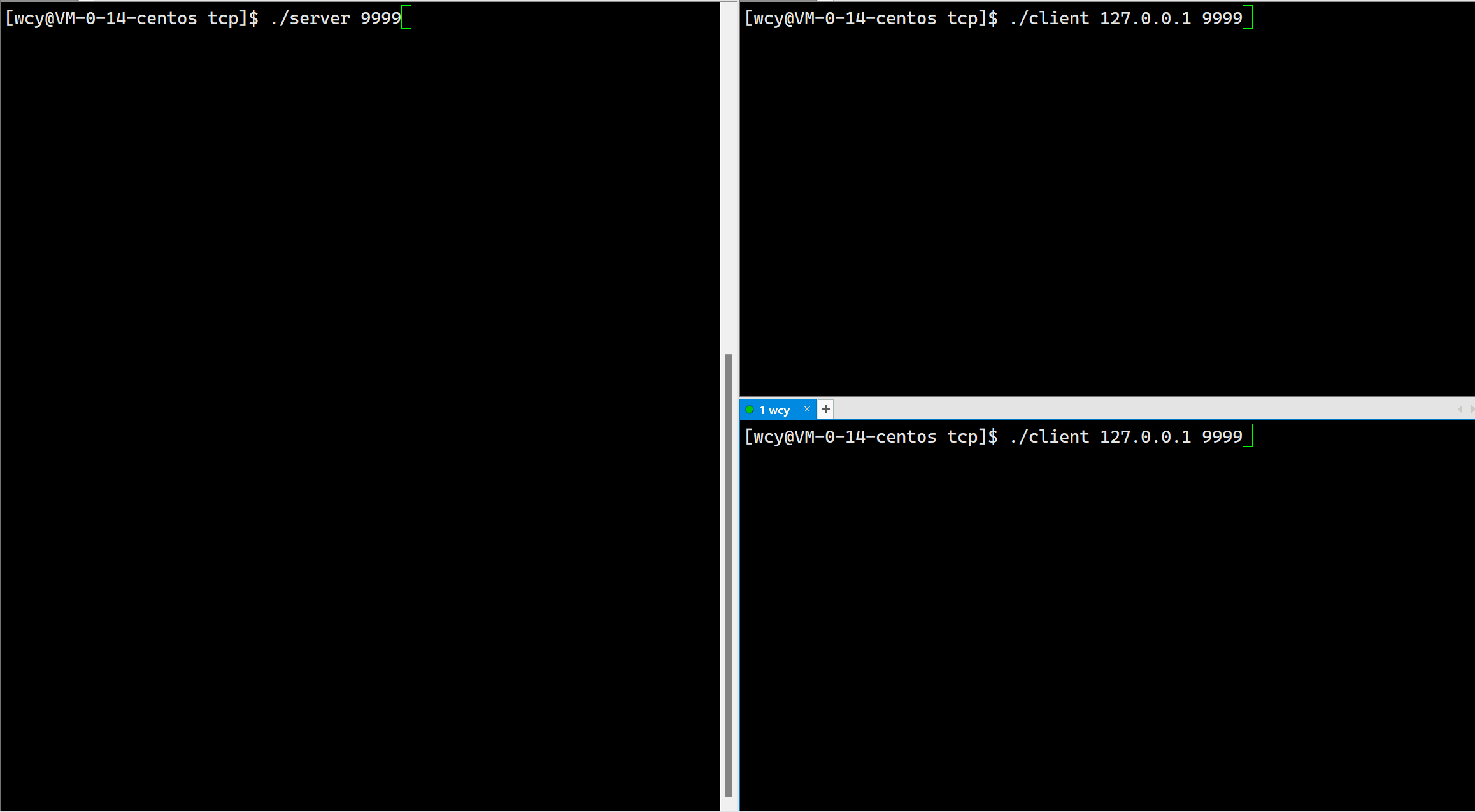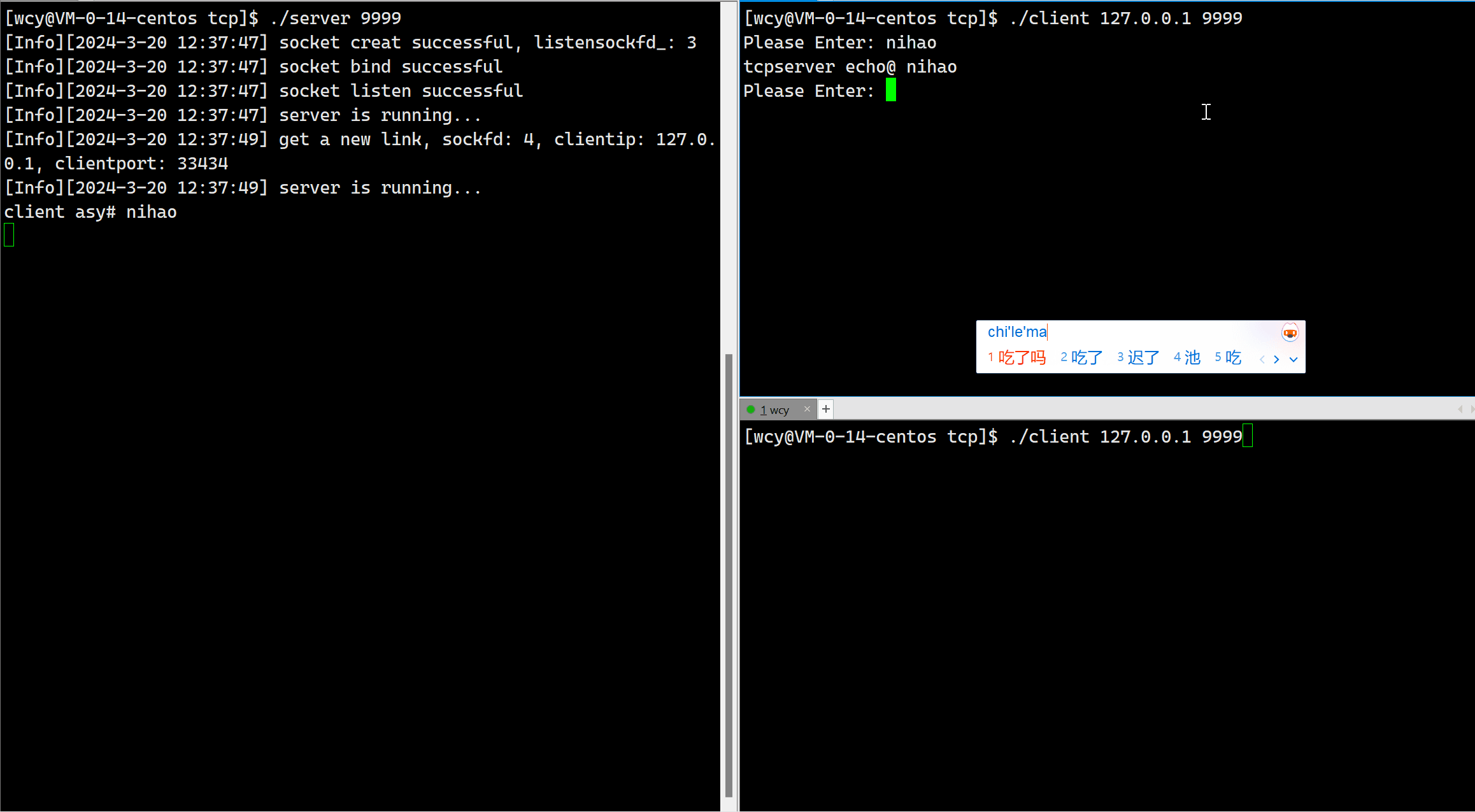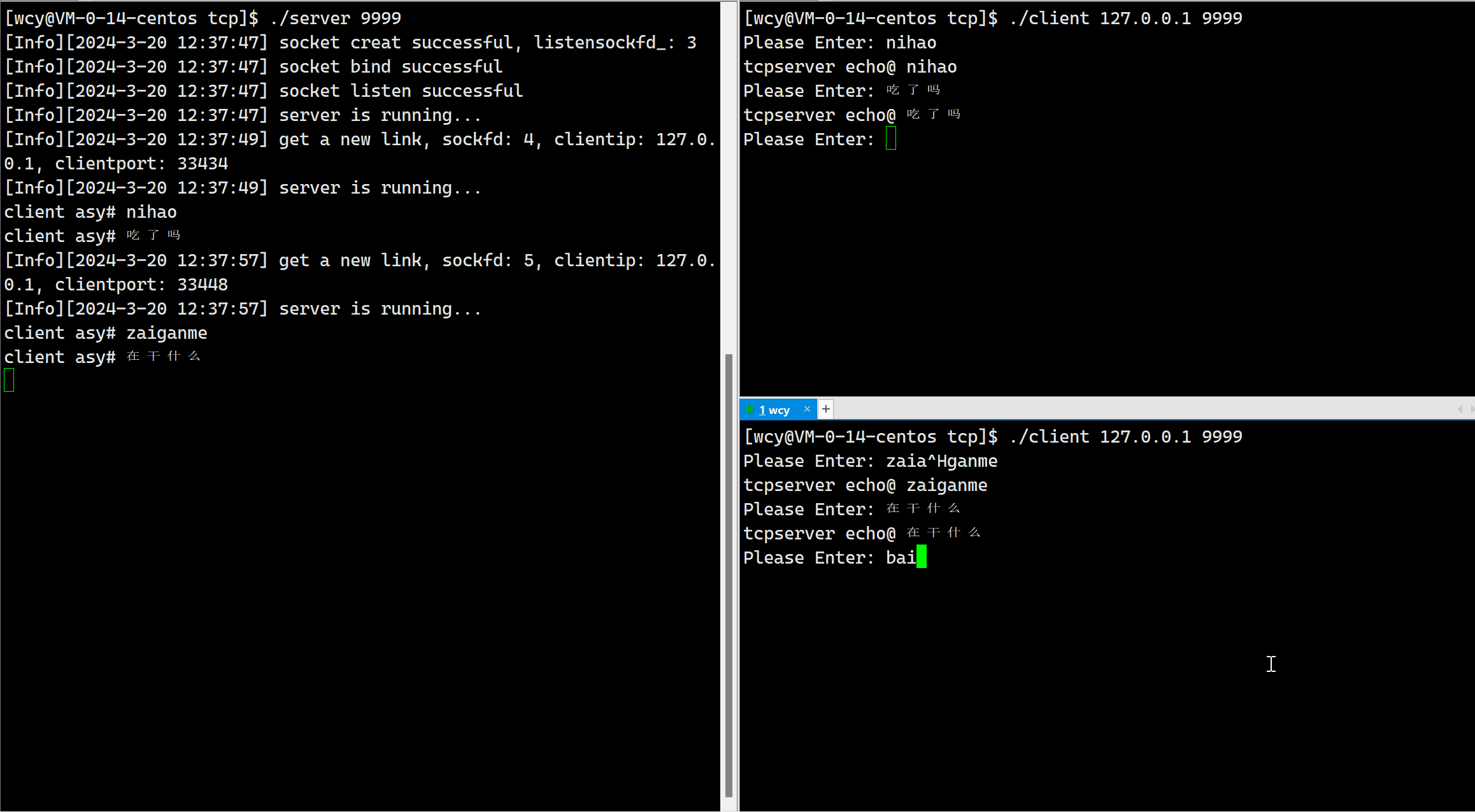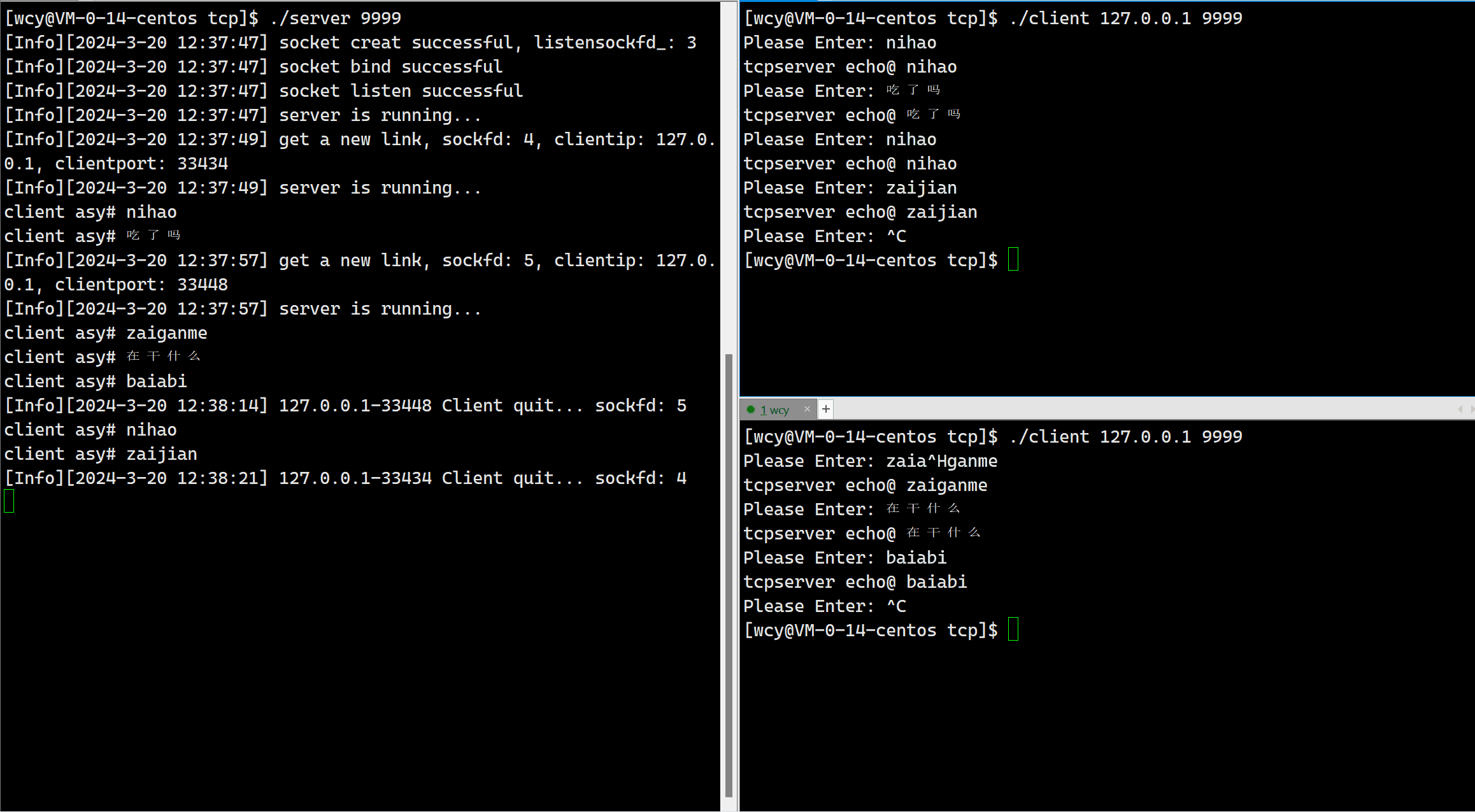
可以在本本机使用 telnet 127.0.0.1 9999 (其中 9999 是端口号,是自定义的)指令来验证服务器是否能成功获取一个连接。
10.3 read——从套接字中读取数据
因为 TCP 是面向字节流的,所以可以直接使用 read 系统调用去读取数据。
void Server(int sockfd, const std::string &client_ip, const uint16_t &client_port)
{
char buffer[num];
while(true)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
ssize_t n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
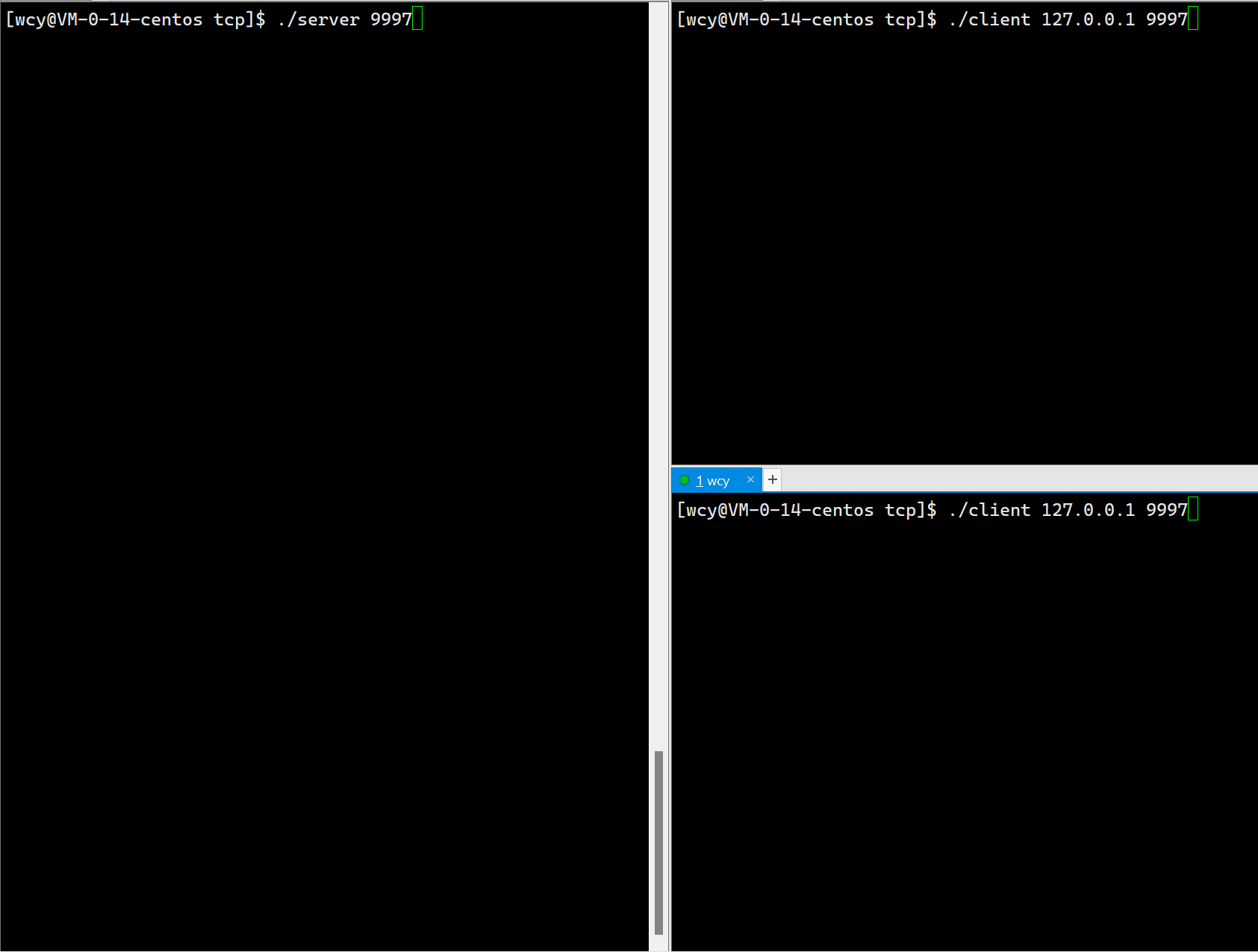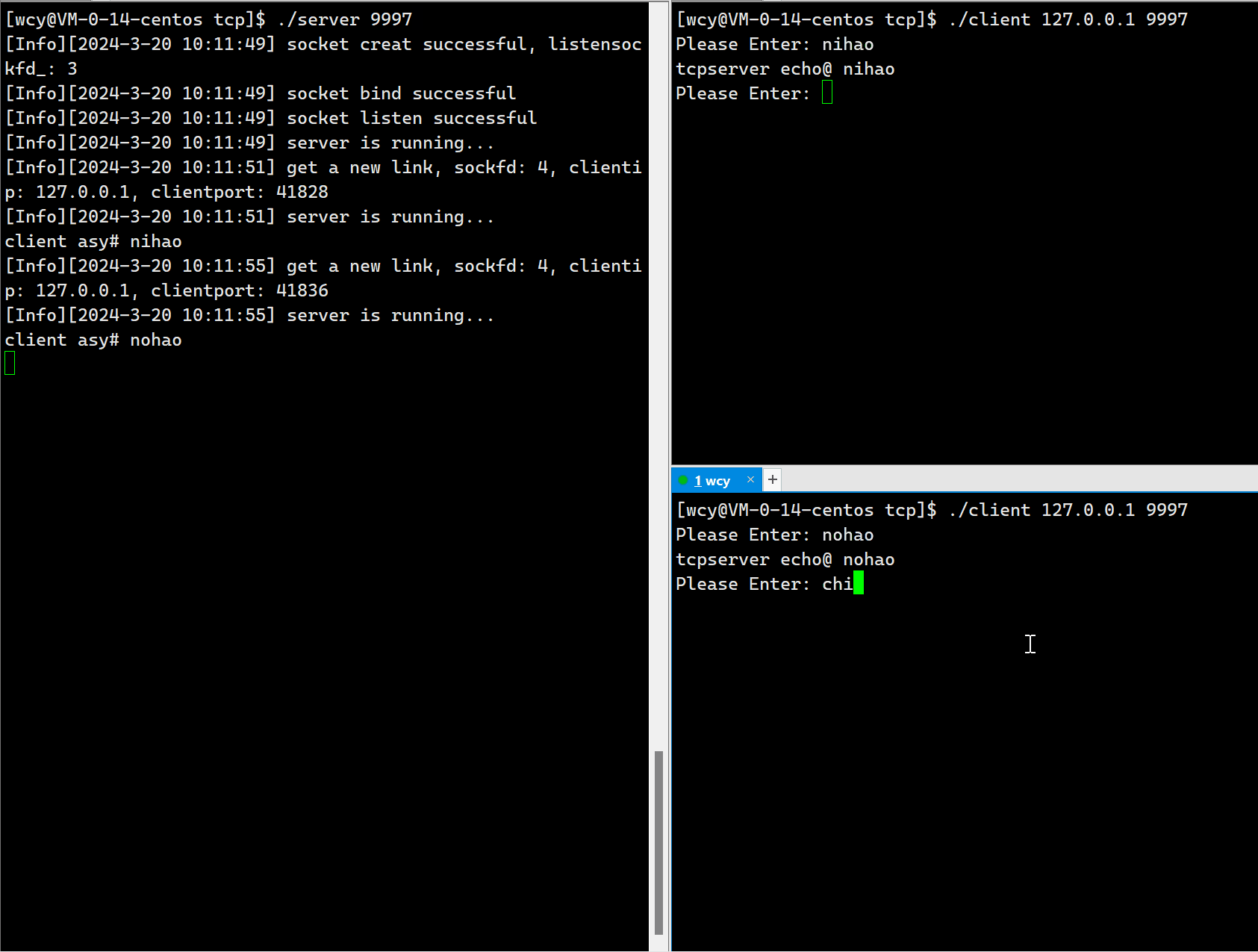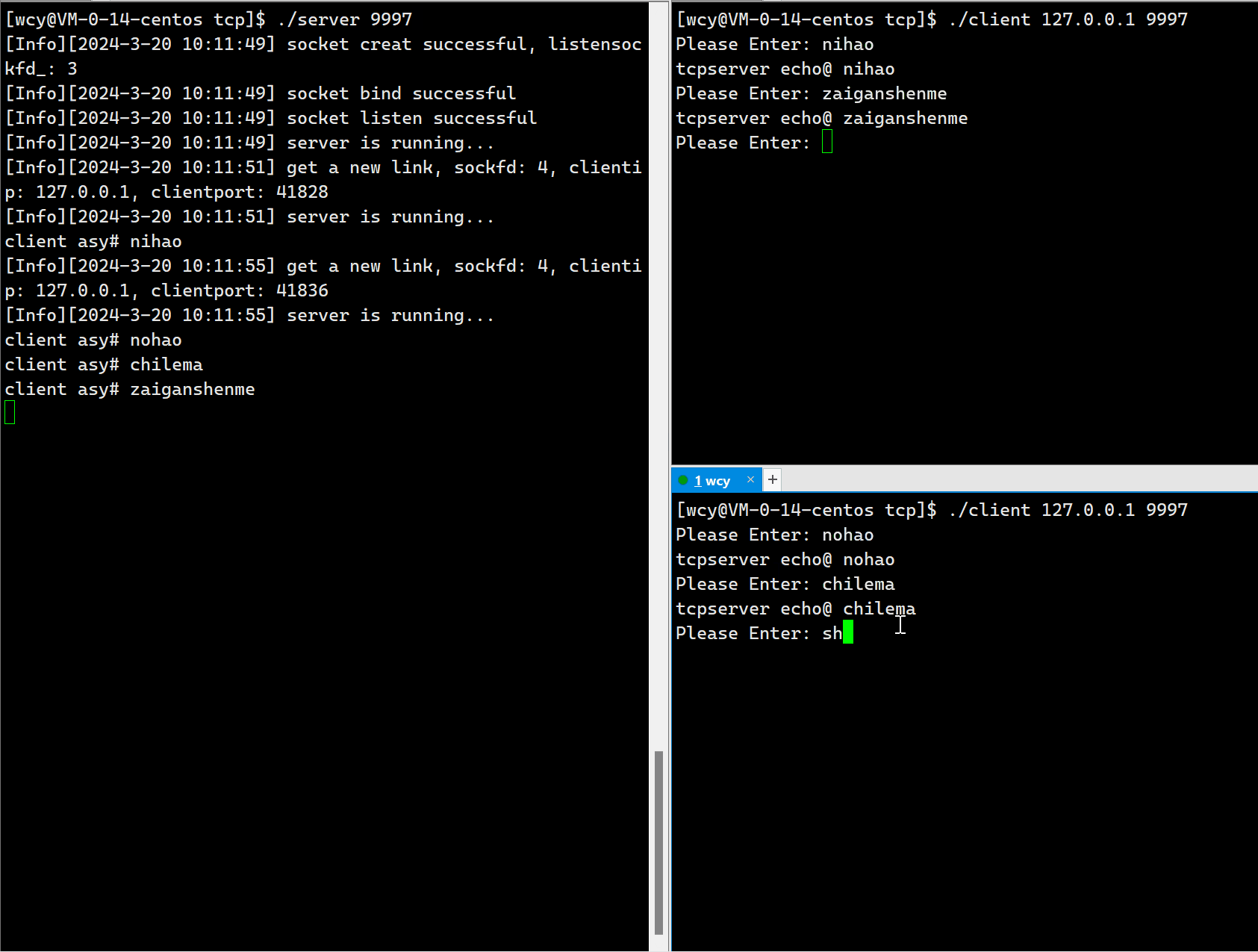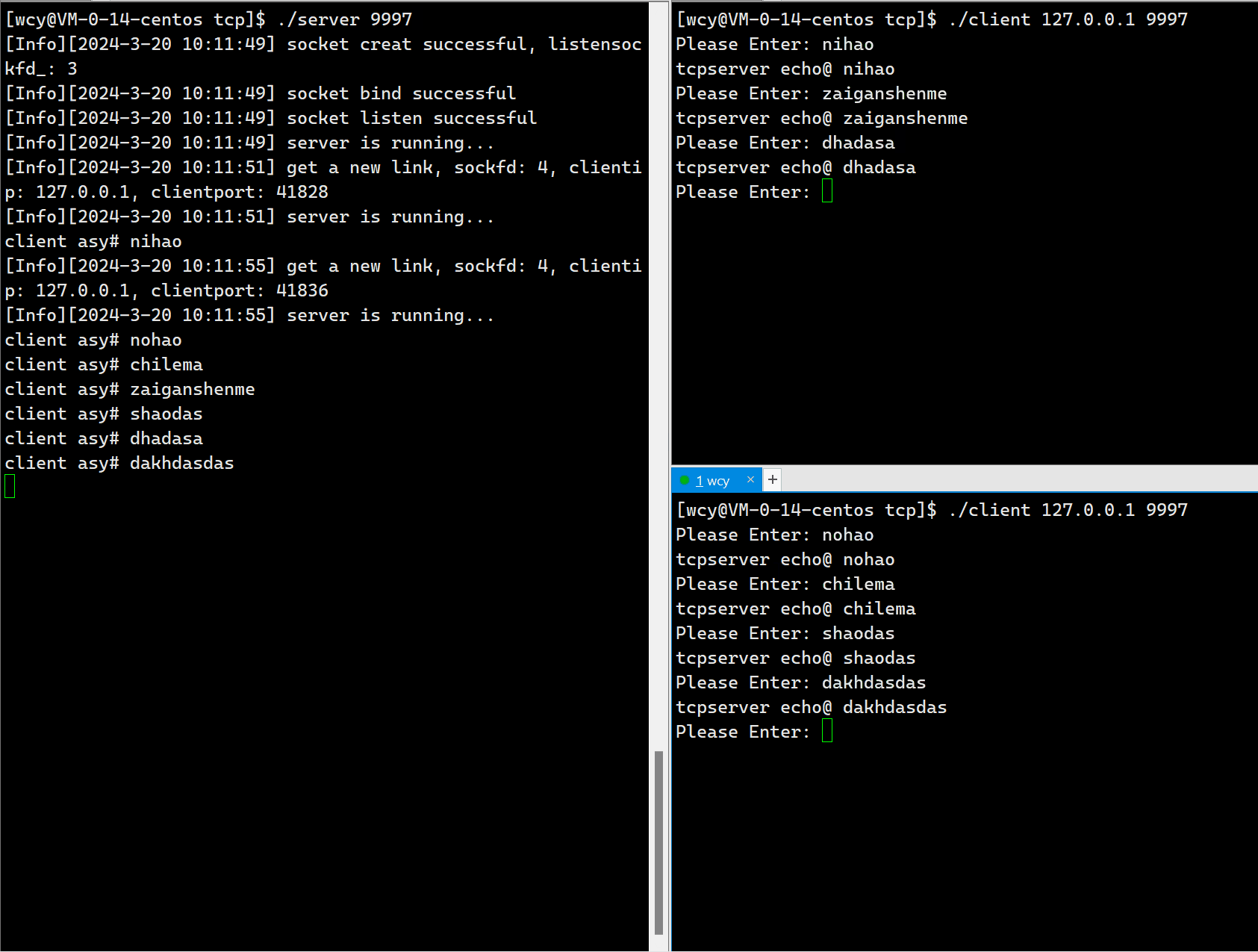
std::cout << "client asy# <b>" << buffer << std::endl;
std::string echo_string = "tcpserver echo@ ";
echo_string += buffer;
int n = write(sockfd_, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size());
if (n < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "write error, errno: %d, strerror: %d", errno, strerror(errno));
}
}
else if(n == 0)
{
lg(Info, "%s-%d Client quit... sockfd: %d", client_ip.c_str(), client_port, sockfd);
break;
}
else
{
lg(Warning, "read err:, errno: %d, errstr: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
break;
}
}
}
如果客户端退出了,那么 read 会读到0,此时需要把之前 accept 返回的 sockfd 关闭,防止误操作,造成意想不到的结果。
10.4 write——向套接字中进行写入
同理,向套接字中进行写入时,直接使用 write 系统调用即可。服务端在收到客户端的数据后,先进行加工处理,然后再进行写入,上面 if(n > 0) 后面就是写入的代码。唯一需要注意的就是,如果在写入前或者正在写入的过程中,client 端退出了,此时客户端与服务器之间的连接就断了,此时客户端如果进行写入操作可能会导致整个服务端崩掉。这和管道类似,读端关闭,写端继续写,操作系统会给写端发送 13 号信号,将写端 kill 调,为了避免这种情况,我们需要在服务器启动的时候将 13 号新号进行捕捉。
10.5 Tcp Service 端完整代码(单进程版)
#pragma once
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include "log.hpp"
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
extern Log lg;
#define num 1024
const int defaultfd = -1;
const std::string defaultip = "0.0.0.0";
const int backlog = 10; // 一般不要设置的太大
enum
{
SOCKET_ERR = 1,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR
};
class TcpServer
{
private:
void Server(int sockfd, const std::string &client_ip, const uint16_t &client_port)
{
char buffer[num];
while(true)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
ssize_t n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
std::cout << "client asy# <b>" << buffer << std::endl;
std::string echo_string = "tcpserver echo@ ";
echo_string += buffer;
write(sockfd, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size());
}
else if(n == 0)
{
lg(Info, "%s-%d Client quit... sockfd: %d", client_ip.c_str(), client_port, sockfd);
break;
}
else
{
lg(Warning, "read err:, errno: %d, errstr: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
break;
}
}
}
public:
TcpServer(const uint16_t &port, const std::string &ip = defaultip)
: listensockfd_(defaultfd), port_(port), ip_(ip)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1. 创建套接字
listensockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listensockfd_ < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket creat successful, listensockfd_: %d", listensockfd_);
// 2. bind
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(port_);
// inet_aton(ip_.c_str(), &(local.sin_addr)); // 将 ip 地址转化成网络序列
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
socklen_t len = sizeof(local);
int ret = bind(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&local, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket bind successful");
// 3. listen
// TCP 是面向连接的,服务器一般是比较“被动的”,在没有客户端访问的时候就只能干等,不能退出,服务器需要一直处于一种,一直在等待连接到来的状态
int n = listen(listensockfd_, backlog);
if (n < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket listen successful");
}
void Start()
{
for (;;)
{
// 4. 获取新连接
lg(Info, "server is running...");
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
int sockfd = accept(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port);
char client_ip[32];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(client.sin_addr), client_ip, sizeof(client_ip));
lg(Info, "get a new link, sockfd: %d, clientip: %s, clientport: %d", sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// 5. 根据新连接来进行通信
// version 1
Server(sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
close(sockfd);
sleep(1);
}
}
~TcpServer()
{
close(listensockfd_);
}
private:
int listensockfd_; //
uint16_t port_; // 端口号
std::string ip_; // ip
};
因为服务端是单进程版,所以一但一个 client 与 服务端建立了连接,那么其它的客户端在前一个 client 退出之前就无法再与客户端建立连接,这意味着,服务端同时只能服务一个 client 端。这显然是不符合实际应用场景的。
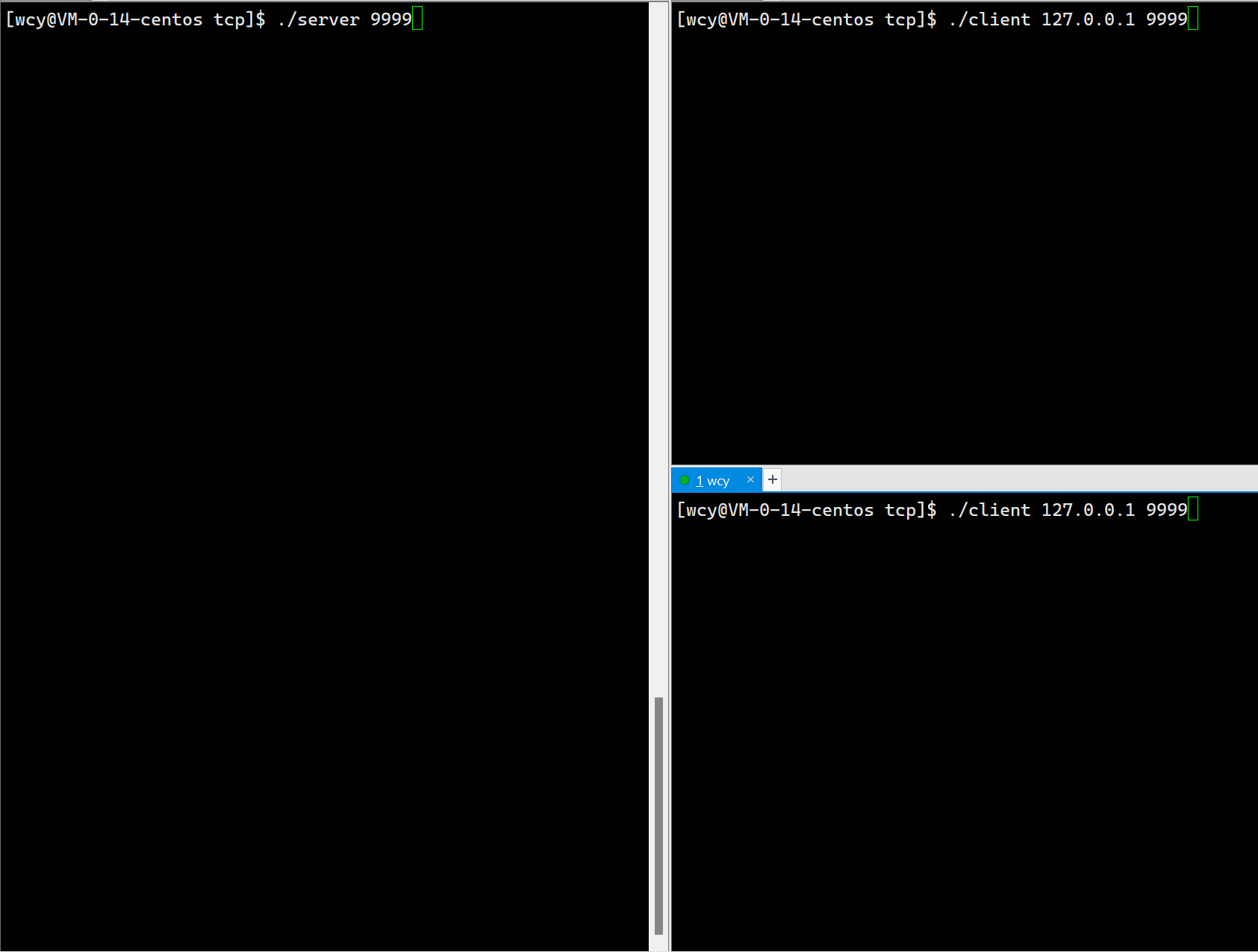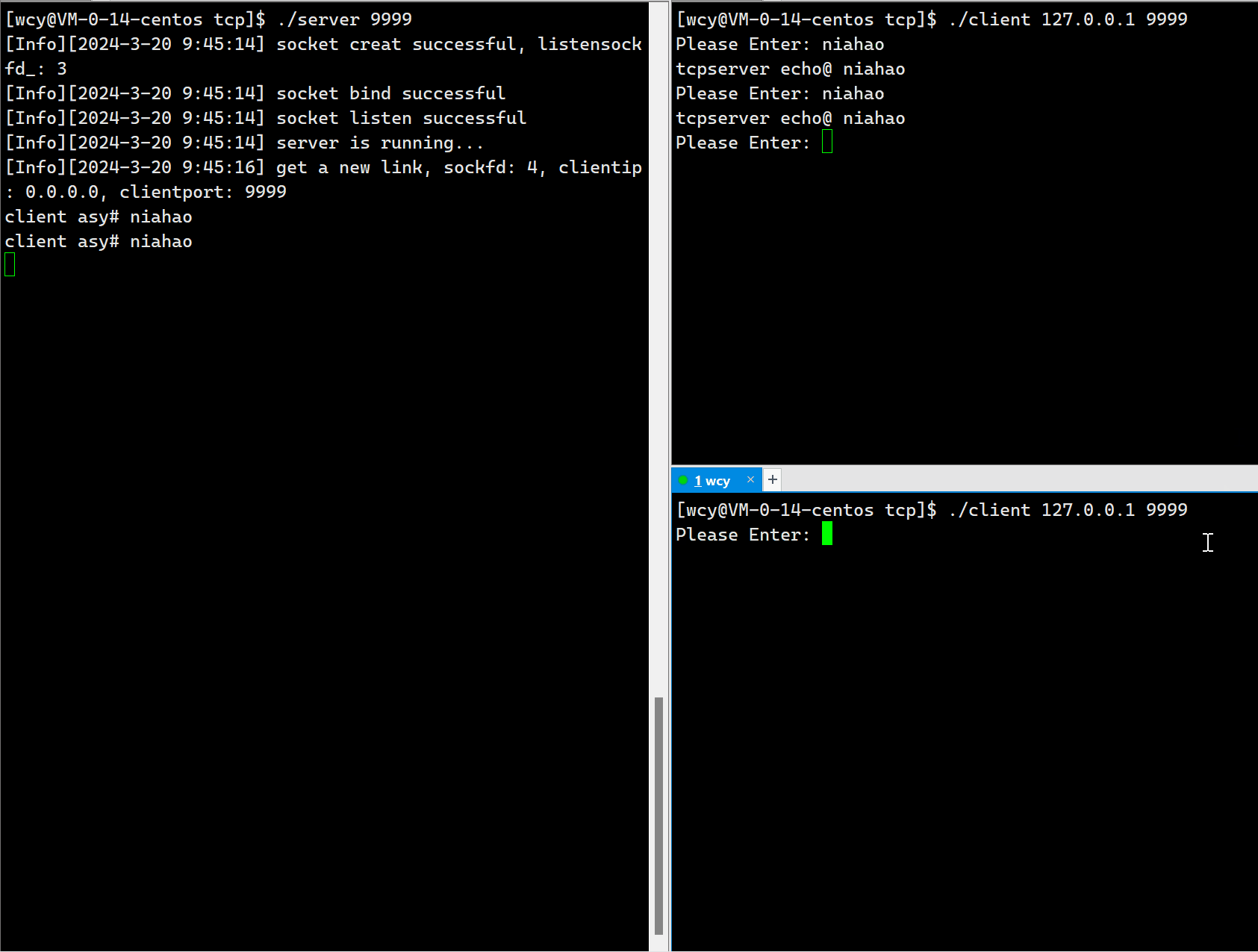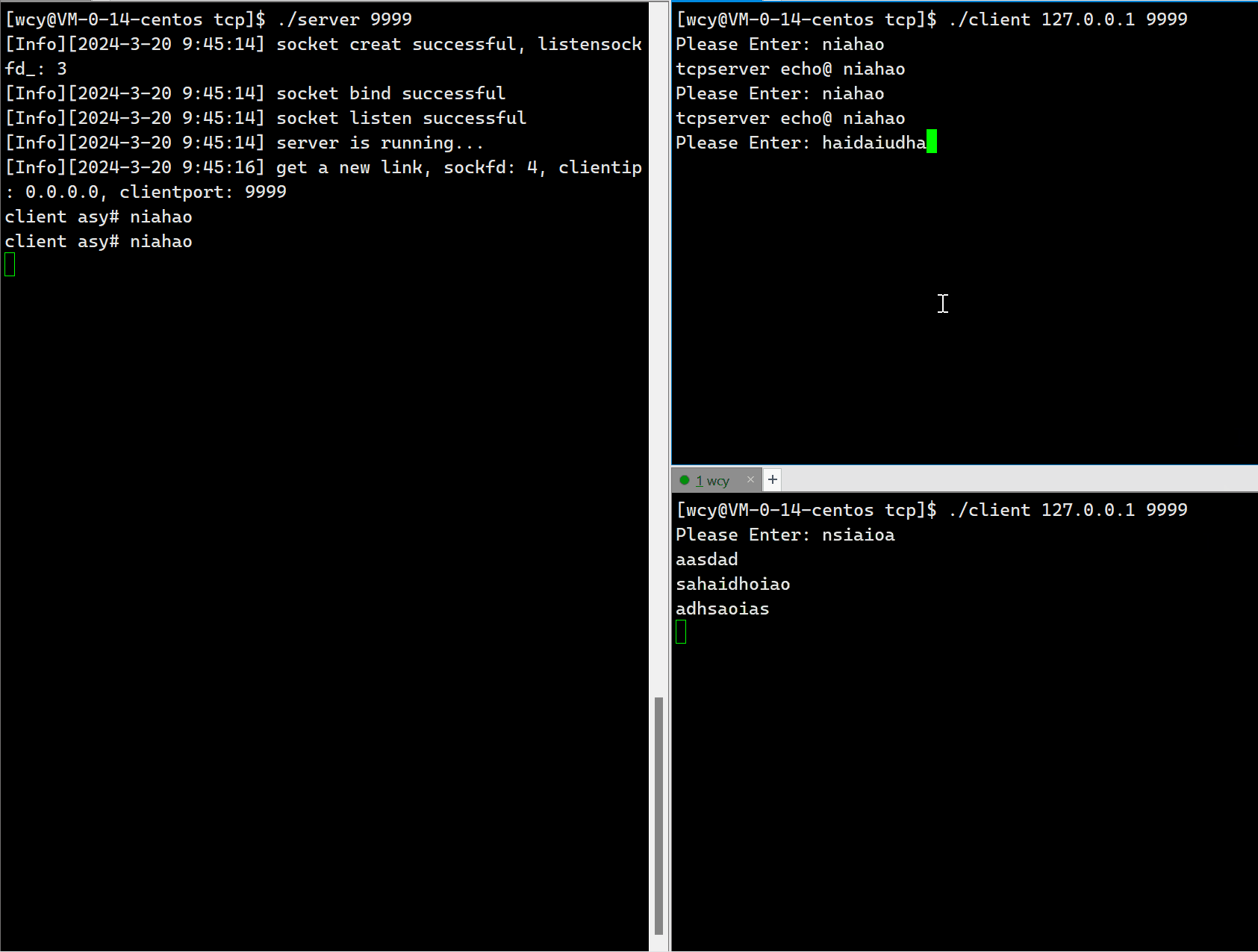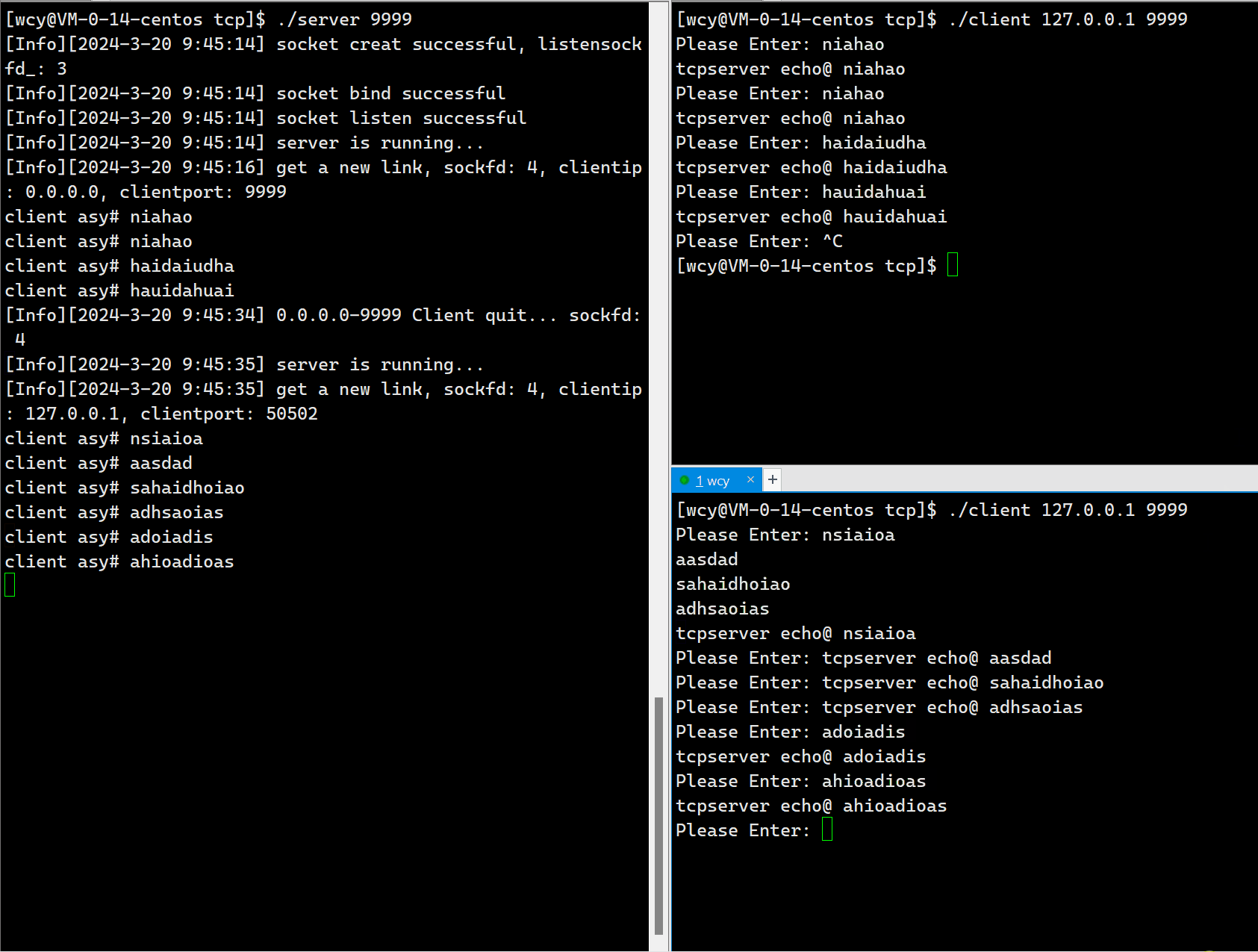
10.6 Tcp Server 端代码(多进程版)
void Start()
{
for (;;)
{
// 4. 获取新连接
lg(Info, "server is running...");
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
int sockfd = accept(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port);
char client_ip[32];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(client.sin_addr), client_ip, sizeof(client_ip));
lg(Info, "get a new link, sockfd: %d, clientip: %s, clientport: %d", sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// 5. 根据新连接来进行通信
// version 1——单进程版
// Server(sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// close(sockfd);
// sleep(1);
// version 2——多进程版
pid_t id = fork();
if (id == 0)
{
// 子进程
close(listensockfd_); // 子进程不关心这个 socket
if(fork() > 0) exit(0); // 子进程再创建子进程,然后让子进程直接退出,由孙子进程执行后续代码
Server(sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
close(sockfd); // 子进程处理完后将套接字信息关闭
exit(0); // 因为子进程退出了,所以孙子进程就会被系统领养,最终执行完毕,会被系统直接回收
}
close(sockfd); // 子进程已经把当前父进程中 accept 获得的文件描述符继承下去了,所以父进程已经不关心该文件描述符了,可以直接关闭掉,不然到时候父进程中存在大量被打开的文件
// 父进程
int rid = waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
}
}
相较于单进程版,多进程的变化是在 Start 中,来一个 client 连接请求,通过创建子进程,让该子进程去为这个 client 端进行服务(获取该 client 端的数据、对数据加工处理、将处理完的数据发送给 client 端),父进程继续去 accept 获取新连接。这里需要注意:子进程是会继承父进程中的所有文件描述符,对子进程来说 listensockfd_ 是没有用的,因为子进程不去拉客(获取新连接),因此子进程代码中第一件事就是将 listensockfd_ 这个文件描述符进行关闭。对父进程来说,获取到一个新连接后会为该连接创建一个新的文件描述符,这个文件描述符被子进程继承下去后父进程就不在关心了,因为父进程要去继续拉客(获取新连接),而不是为当前获取到的连接提供服务。其次父进程需要等待子进程,如果是 waitpid(id, nullptr, 0); 这种等待,那和单进程版的,没有任何区别,因为这是阻塞等待,只有等子进程退出了父进程才能继续执行。解决该问题的办法有很多:上面代码中,采用的是让子进程继续创建孙子进程,然后让孙子进程去提供服务,子进程直接退出,这时,父进程就立刻能将子进程回收,孙子进程会被操作系统领养,最终执行完毕,会被操作系统直接回收。这里再提供两种解决方案:
- 用一个数据将创建的子进程的 pid 管理起来,然后
waitpid(id, nullptr, WNOHANG);或者直接waitpid(-1, nullptr, WNOHANG);非阻塞等待任意子进程。 - 父进程中对
SIGCHLD进行捕捉,在捕捉方法里面对退出的子进程进行回收;或者父进程中直接对SIFCHLD信号进行SIG_IGN,此时子进程在退出时会自动被清理掉,不会产生僵尸进程。
10.7 Tcp Server 端代码(多线程版)
创建一个新进程相较于创建一个新线程是很“重”的,所以下面引入多线程版。一个进程打开的文件描述符是被所有子线程共享的,子线程可以根据文件描述符去对文件进行读写操作。
// 线程函数的参数
class ThreadData
{
public:
ThreadData(int sockfd, const std::string &client_ip, const uint16_t &client_port, TcpServer *tcpserver)
: sockfd_(sockfd), client_ip_(client_ip), client_port_(client_port), tcpserver_(tcpserver)
{
}
~ThreadData()
{
}
public:
int sockfd_; // 文件描述符
std::string client_ip_; // 客户端 ip
uint16_t client_port_; // 客户端 port
TcpServer *tcpserver_; // 一个 tcpserver 进程
};
static void *Rountine(void *args)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); // 让子线程分离,这样在主线程中不用进行 join 了
ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args);
td->tcpserver_->Server(td->sockfd_, td->client_ip_, td->client_port_);
close(td->sockfd_);
}
void Start()
{
for (;;)
{
// 4. 获取新连接
lg(Info, "server is running...");
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
int sockfd = accept(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port);
char client_ip[32];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(client.sin_addr), client_ip, sizeof(client_ip));
lg(Info, "get a new link, sockfd: %d, clientip: %s, clientport: %d", sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// 5. 根据新连接来进行通信
// version 3——多线程版
ThreadData *td = new ThreadData(sockfd, client_ip, client_port, this);
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, Rountine, td);
}
}
注意要把线程函数设置成 static。
10.8 Tcp Server 端完整代码(线程池版)——英汉字典
上面三个版本的服务端都提供的是常服务,什么事常服务呢?就是只要一个 client 发起了连接,服务端这边就一直 while 循环式的为该客户端提供服务,直到客户端退出,这样实际也是不合理的,正确做法是,服务端在收到一个连接请求后,一次处理完后就应该返回了。所以这里我们引入线程池,将一次客户端的连接当做一个任务,将该任务放到线程池里面去,让线程池里面的线程为这一次连接服务(获取客户端发来的数据、对数据加工处理、将结果返回给客户端)。
// TcpServer.hpp——服务端
#pragma once
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include "log.hpp"
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
#include "Task.h"
extern Log lg;
#define num 1024
const int defaultfd = -1;
const std::string defaultip = "0.0.0.0";
const int backlog = 10; // 一般不要设置的太大
enum
{
SOCKET_ERR = 1,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR
};
class TcpServer;
class ThreadData
{
public:
ThreadData(int sockfd, const std::string &client_ip, const uint16_t &client_port, TcpServer *tcpserver)
: sockfd_(sockfd), client_ip_(client_ip), client_port_(client_port), tcpserver_(tcpserver)
{
}
~ThreadData()
{
}
public:
int sockfd_; // 文件描述符
std::string client_ip_; // 客户端 ip
uint16_t client_port_; // 客户端 port
TcpServer *tcpserver_; // 一个 tcpserver 进程
};
class TcpServer
{
public:
TcpServer(const uint16_t &port, const std::string &ip = defaultip)
: listensockfd_(defaultfd), port_(port), ip_(ip)
{
}
void Init()
{
// 1. 创建套接字
listensockfd_ = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listensockfd_ < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "socket create error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket creat successful, listensockfd_: %d", listensockfd_);
// 2. bind
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local, 0, sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(port_);
// inet_aton(ip_.c_str(), &(local.sin_addr)); // 将 ip 地址转化成网络序列
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
socklen_t len = sizeof(local);
int ret = bind(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&local, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket bind successful");
// 3. listen
// TCP 是面向连接的,服务器一般是比较“被动的”,在没有客户端访问的时候就只能干等,不能退出,服务器需要一直处于一种,一直在等待连接到来的状态
int n = listen(listensockfd_, backlog);
if (n < 0)
{
lg(Fatal, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
lg(Info, "socket listen successful");
}
void Start()
{
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
ThreadPool<Task>::GetInstance()->start();
for (;;)
{
// 4. 获取新连接
lg(Info, "server is running...");
struct sockaddr_in client;
socklen_t len;
int sockfd = accept(listensockfd_, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &len);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
lg(Warning, "bind error, errno: %d, error message: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
continue;
}
uint16_t client_port = ntohs(client.sin_port);
char client_ip[32];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(client.sin_addr), client_ip, sizeof(client_ip));
lg(Info, "get a new link, sockfd: %d, clientip: %s, clientport: %d", sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
// 5. 根据新连接来进行通信
// version 4——线程池版本
Task t(sockfd, client_ip, client_port);
ThreadPool<Task>::GetInstance()->push(t);
}
}
~TcpServer()
{
close(listensockfd_);
}
private:
int listensockfd_; //
uint16_t port_; // 端口号
std::string ip_; // ip
};
// ThreadPool.hpp——线程池
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <unordered_map>
struct ThreadInfo
{
pthread_t tid_; // 线程 ID
std::string name_; // 线程的名字
};
template <class T>
class ThreadPool
{
static const int defaultnum = 5;
public:
void Lock()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
}
void Unlock()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
void Weakup()
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_);
}
void Sleep()
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_, &mutex_);
}
bool IsTaskQueueEmpty()
{
return tasks_.empty();
}
T PopTasks()
{
T task = tasks_.front();
tasks_.pop();
return task;
}
const std::string &GetThreadName(pthread_t tid)
{
return um_[tid];
}
public:
static void *Routine(void *args)
{
ThreadPool *tp = static_cast<ThreadPool *>(args);
std::string name = tp->GetThreadName(pthread_self());
while (true)
{
tp->Lock();
while (tp->IsTaskQueueEmpty())
{
tp->Sleep();
}
T task = tp->PopTasks();
tp->Unlock();
task(); // 此时这个任务已经属于该线程私有的了,所以对任务的处理工作可以在解锁之后进行
// printf("%s is running----%s\n", name.c_str(), task.result_to_string().c_str());
}
}
void start()
{
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num_; i++)
{
threads_[i].name_ = "Thread-" + std::to_string(i);
pthread_create(&(threads_[i].tid_), nullptr, Routine, this);
um_[threads_[i].tid_] = threads_[i].name_;
}
}
void push(const T &task)
{
Lock();
tasks_.push(task);
Weakup();
Unlock();
}
static ThreadPool<T> *GetInstance() // 指正通过该接口获取一个单例对象
{
if (ptp_ == nullptr)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&smutex_);
if (ptp_ == nullptr)
{
lg(Info, "singleton creat done first!");
ptp_ = new ThreadPool<T>();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&smutex_);
}
return ptp_;
}
private:
ThreadPool(int thread_num = defaultnum)
: threads_(thread_num), thread_num_(thread_num)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&cond_, nullptr);
}
~ThreadPool()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_);
}
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<T> &tp) = delete;
const ThreadPool<T> &operator=(const ThreadPool<T> &tp) = delete;
private:
std::vector<ThreadInfo> threads_; // 一批线程
int thread_num_; // 线程池中的线程的数量
std::queue<T> tasks_; // 任务
pthread_mutex_t mutex_; // 定义一把锁,让所有线程保持互斥
pthread_cond_t cond_; // 定义一个条件变量,让线程同步
std::unordered_map<pthread_t, std::string> um_; // 一个 map 用来快速查找一个线程的name
static ThreadPool<T> *ptp_; // 单例
static pthread_mutex_t smutex_; // 定义一把静态的锁
};
template <class T>
ThreadPool<T> *ThreadPool<T>::ptp_ = nullptr;
template <class T>
pthread_mutex_t ThreadPool<T>::smutex_ = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
// Task.hpp——任务
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "log.hpp"
#include "ECDictionary.hpp"
ECDictionary ecd;
extern Log lg;
#define num 1024
class Task
{
public:
Task(int sockfd, const std::string &client_ip, const uint16_t &client_port)
: sockfd_(sockfd), client_ip_(client_ip), client_port_(client_port)
{
}
void run()
{
char buffer[num];
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
ssize_t n = read(sockfd_, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
std::cout << "client asy# <b>" << buffer << std::endl;
std::string echo_string = "tcpserver echo@ ";
echo_string += ecd.GetTranslation(buffer);
write(sockfd_, echo_string.c_str(), echo_string.size());
}
else if (n == 0)
{
lg(Info, "%s-%d Client quit... sockfd: %d", client_ip_.c_str(), client_port_, sockfd_);
}
else
{
lg(Warning, "read err:, errno: %d, errstr: %s", errno, strerror(errno));
}
close(sockfd_);
}
void operator()()
{
run();
}
private:
int sockfd_;
std::string client_ip_;
uint16_t client_port_;
};
// ECDictionary.hpp——字典
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "log.hpp"
#define SEP ":"
extern Log lg;
const std::string path = "./dictionary.txt";
class ECDictionary
{
private:
static void Split(const std::string &line, std::string *english, std::string *chinese)
{
size_t pos = line.find(SEP);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return;
*english = line.substr(0, pos);
*chinese = line.substr(pos+1);
return;
}
public:
ECDictionary()
{
std::ifstream di(path.c_str());
if(!di.is_open())
{
lg(Fatal, "open %s Dictionary errror, errno: %d, errstr: %s", path.c_str(), errno, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
std::string line;
while(std::getline(di, line))
{
std::string english, chinese;
Split(line, &english, &chinese);
dir_.insert({english, chinese});
}
di.close();
}
std::string GetTranslation(const std::string &english)
{
auto it = dir_.find(english);
if(it == dir_.end()) return "There is no such word";
return it->second;
}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> dir_;
};
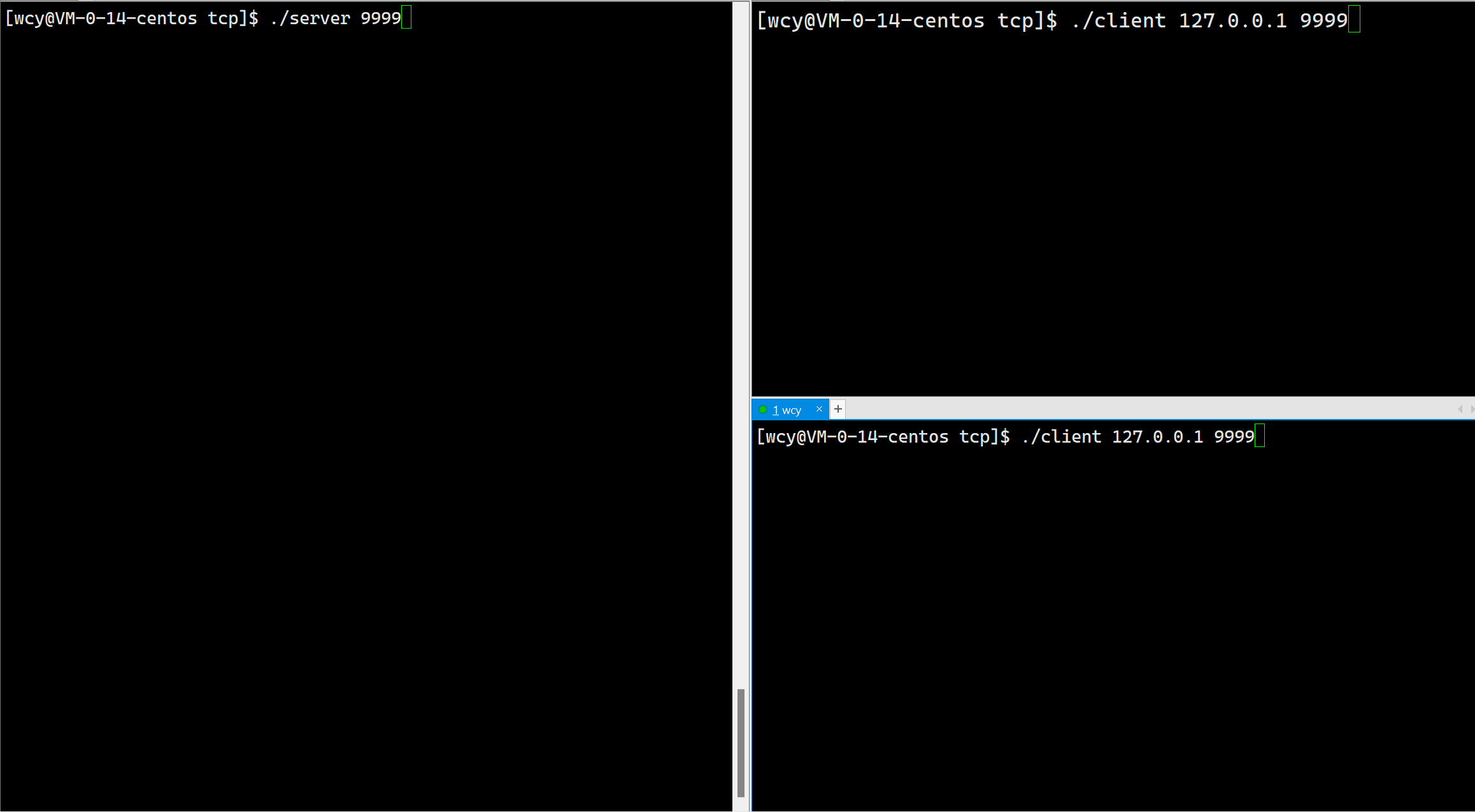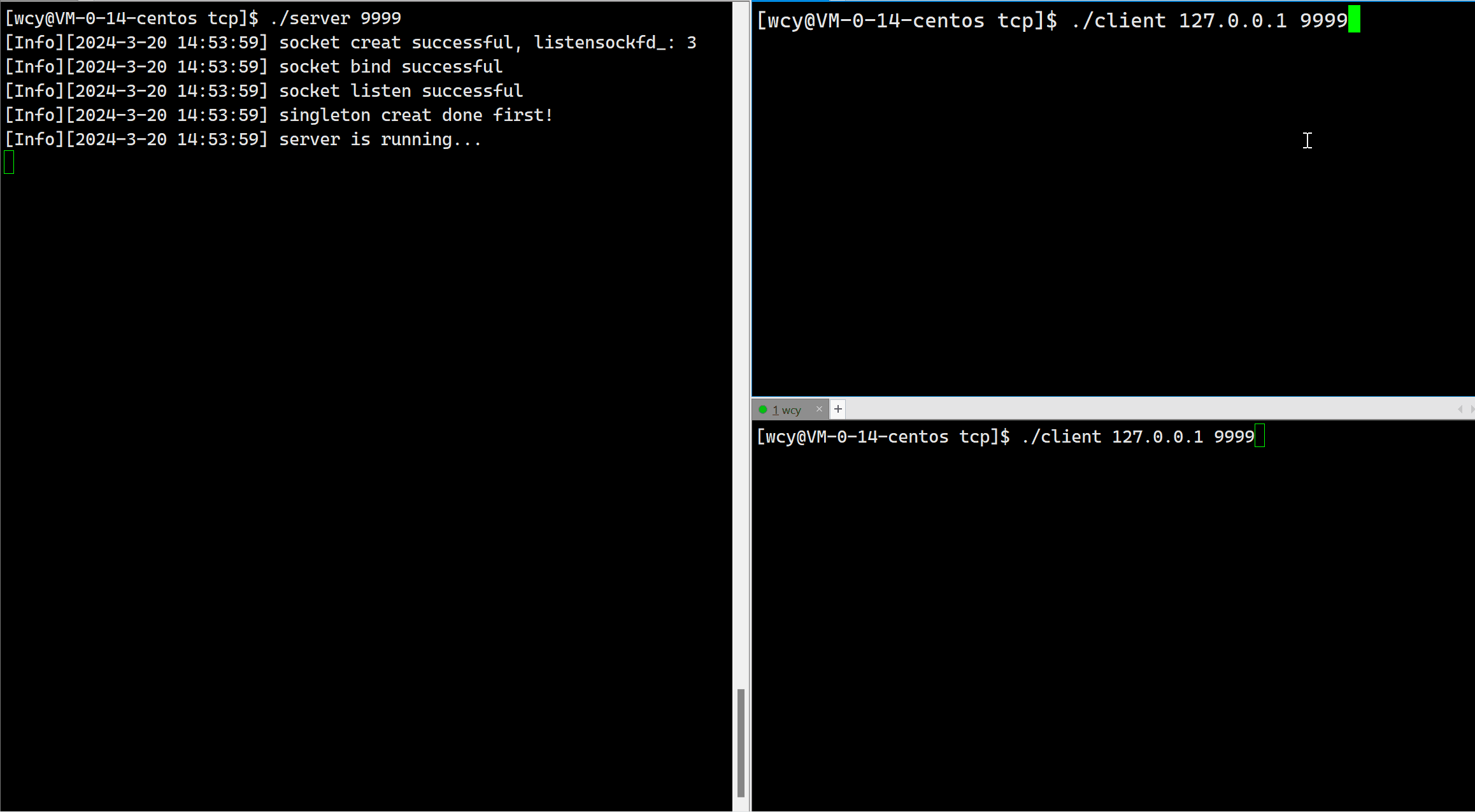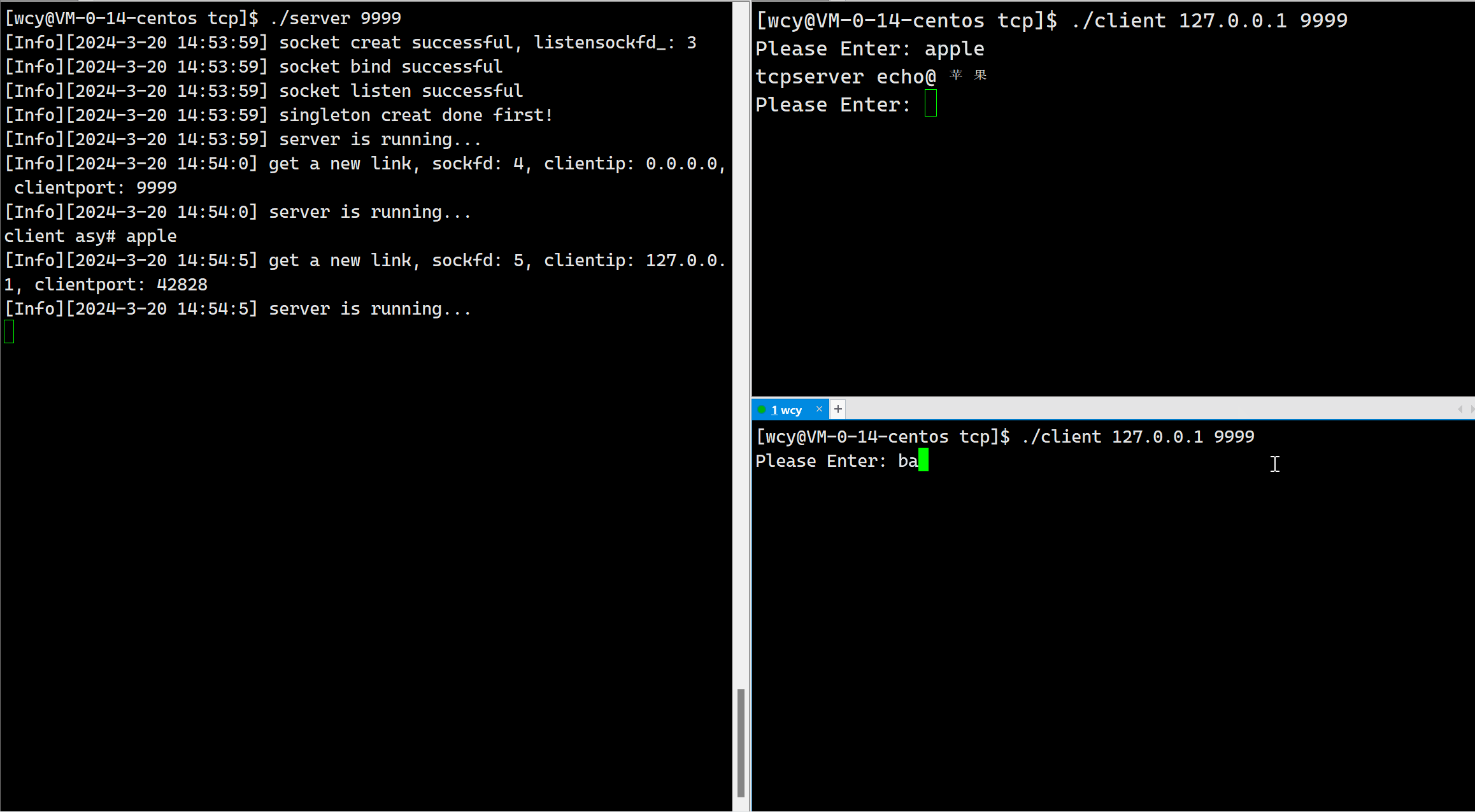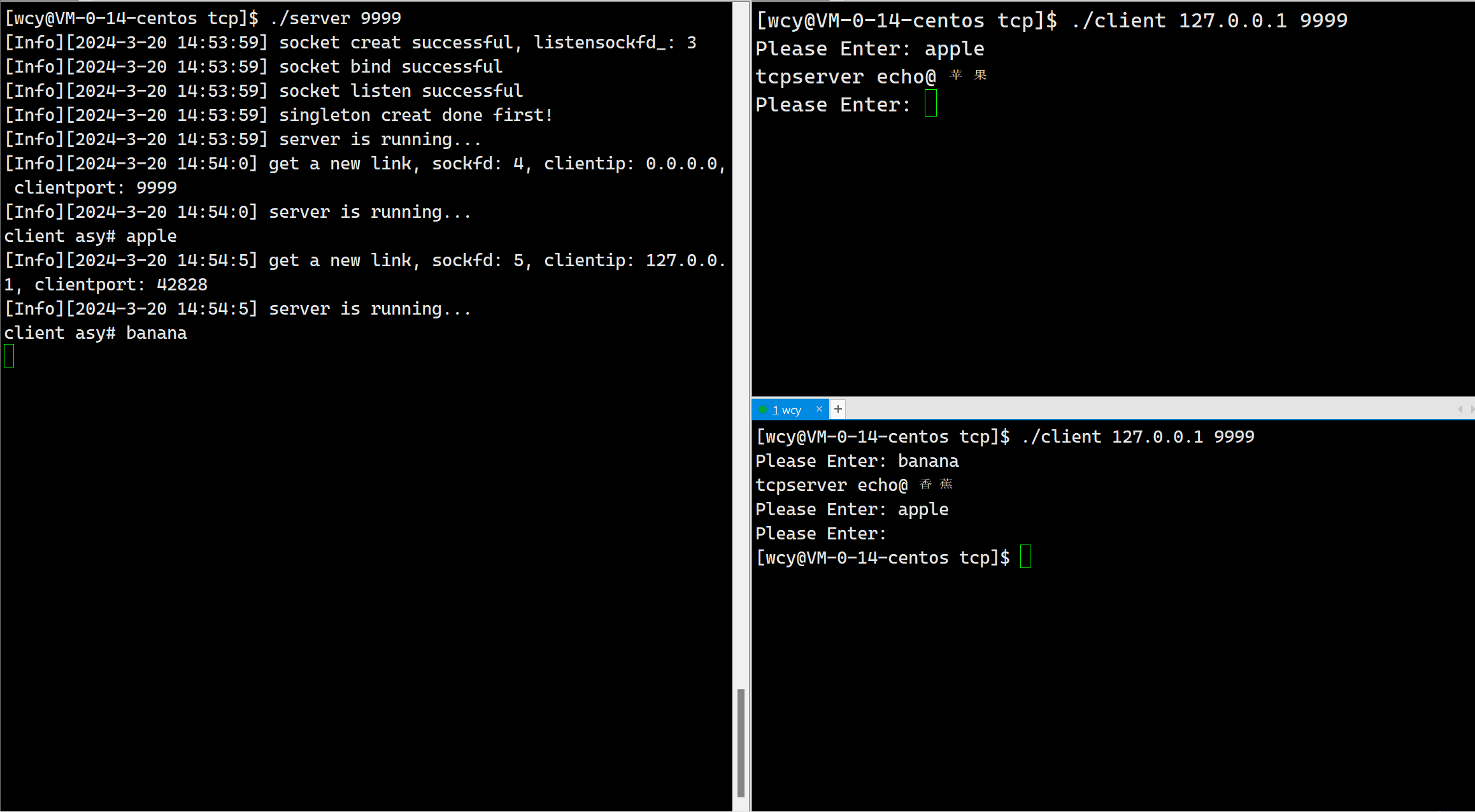
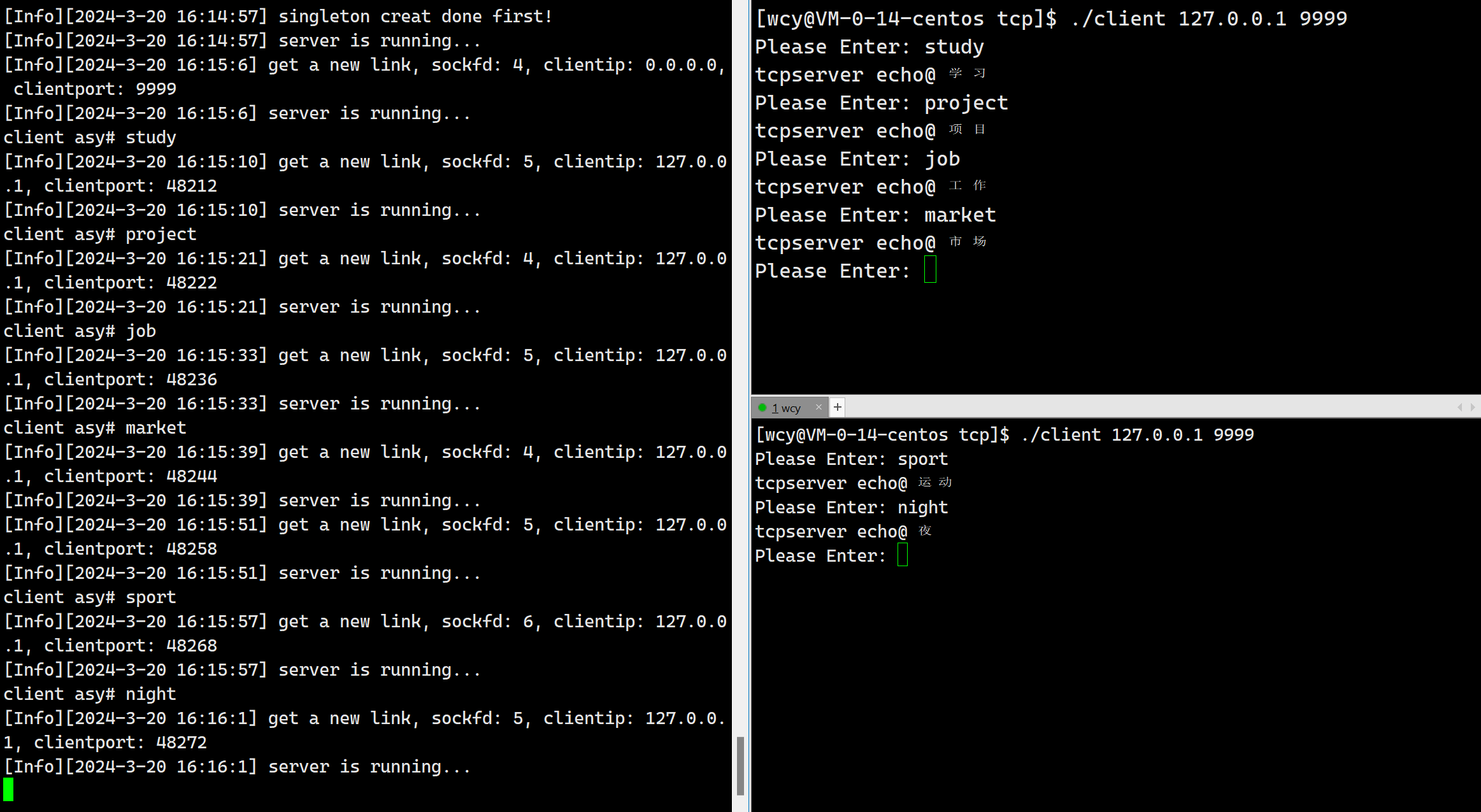
由于我们当前是短连接,即对于一个客户端发起的一次连接请求,服务器只处理一次,就把相应的文件描述符进行了关闭。所以一个客户端启动后只能翻译一次。
10.9 setsockopt——设置套接字描述符的属性
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int setsockopt(int sockfd, int level, int optname, const void *optval, socklen_t optlen);
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(listensockfd_, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR|SO_REUSEPORT, &opt, sizeof(opt)); // 防止偶发性的服务器无法进行立即重启
十一、Tcp Client 端代码
和 Udp Client 端一样,Tcp Client 在创建完套接字之后,不需要我们自己编写代码去显示的绑定 ip 地址和端口号,而是在 connect 的时候,由操作系统随机的为我们绑定端口号。
11.1 connect——向服务端发起连接
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
后两个参数用来标识要连接服务端的套接字信息。返回值:只要绑定成功并且获取连接成功,0被返回;失败-1被返回。
11.2 write、read——向服务器发送数据、从服务器接收数据
和服务端一样,客户端也是通过 write 和 read 接口来发送数据和读取数据。
11.3 Tcp Client 端完整代码
因为服务端对一个连接只会处理一次,然后就会把服务端对应的文件描述符给关闭了,此时相当于连接就断了,所以客户端需要循环去发起连接请求,并且每连接一次,得到服务器端的结果后需要把创建的套接字进行关闭,因为服务端已经关了,你不关还想干啥??所以客户端需要每次重新去创建套接字,发起连接。
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Usage(const char *command)
{
std::cout << "\n\tUsage: " << command << " port[1024+]" << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
string server_ip = argv[1];
uint16_t server_port = stoi(argv[2]);
sockaddr_in server;
memset(&server, 0, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(server_port);
inet_pton(AF_INET, server_ip.c_str(), &(server.sin_addr));
socklen_t len = sizeof(server);
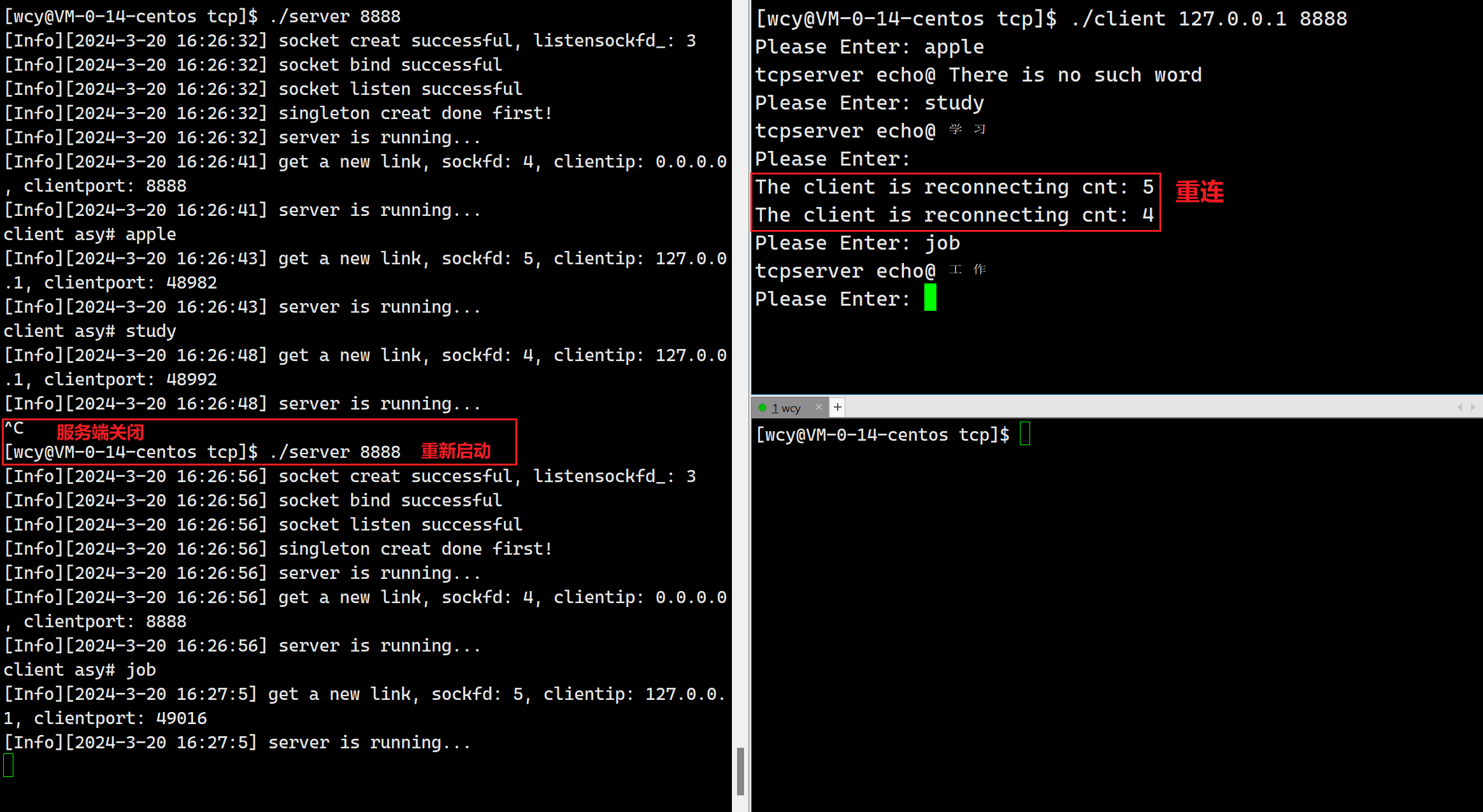
while (true)
{
int cnt = 5; // 重连次数
bool needreconnect = true;
// 1. 创建套接字
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0)
{
perror("sockfd");
exit(2);
}
do // 重连模块
{
// 2. bind —— 客户端不需要我们显示去 bind,是由操作系统帮我们进行绑定的
// 3. 发起连接
int result = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server, len);
if (result < 0)
{
needreconnect = true;
std::cerr << "The client is reconnecting cnt: " << cnt << std::endl;
cnt--;
sleep(2);
}
else
{
needreconnect = false; // 连接成功,不需要重连
break;
}
} while (cnt && needreconnect);
if (cnt == 0)
{
std::cerr << "The user is disconnected..." << std::endl;
break;
}
// 4. 向server发送消息
string message;
std::cout << "Please Enter: ";
getline(cin, message);
ssize_t n = write(sockfd, message.c_str(), message.size());
if (n < 0)
{
std::cerr << "write err, errno: " << errno << ", strerror: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
continue;
}
char buffer[4096];
int ret = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (ret > 0)
{
buffer[ret] = 0;
printf("%s\n", buffer);
}
close(sockfd);
}
return 0;
}
十二、基于 TCP 协议的客户端/服务器程序的一般流程
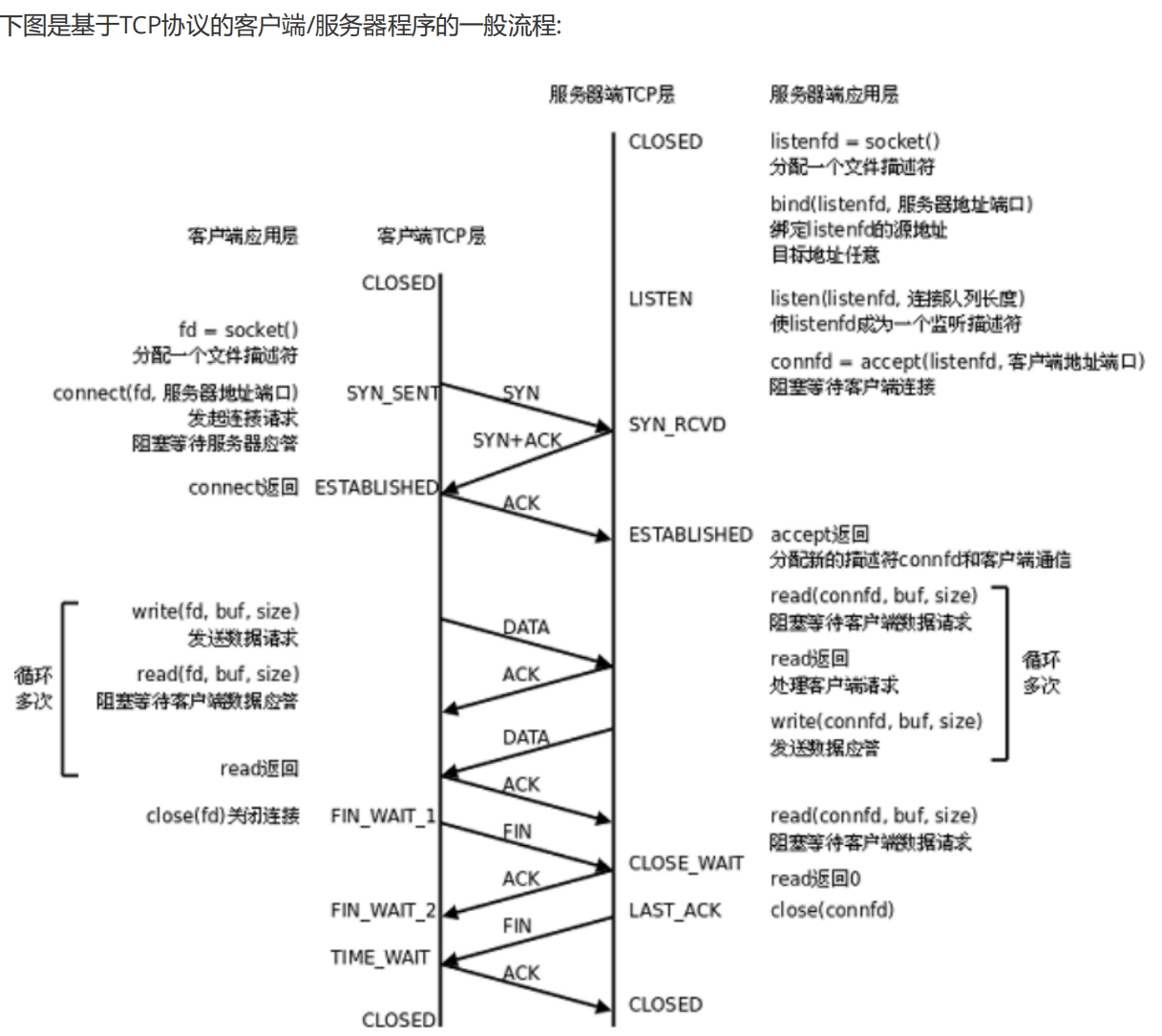
服务器初始化:
调用
socket,创建文件描述符调用
bind,将当前的文件描述符和 ip、port 绑定在一起;如果端口号被其他进程占用就会 bind 失败。调用
listen,声明当前这个文件描述符作为一个服务器的文件描述符,为后面的accept做好准备调用
accept,并阻塞,等待客户端连接过来。
建立连接的过程:
调用
socket,创建文件描述符调用
connect,向服务器发起连接请求connect会发出 SYN 段并阻塞,等待服务器应答(第一次)服务器收到客户端的 SYN ,会应答一个 SYN-ACK 段表示“同意建立连接”(第二次)
客户端收到 SYN-ACK后会从
connect()返回,同时应答一个 ACK 段(第三次)
这个建立连接的过程,通常成为三次握手。
数据传输的过程:
建立连接后,TCP 协议提供全双工的通信服务;所谓全双工,就是在同一条连接中,同一时刻,通信双方可以同时写数据。当创建一个 TCP 套接字的时候,我们虽然只获得了一个文件描述符,但是在底层操作系统会为给文件描述符创建两个缓冲区,一个是发送缓冲区,另一个接收缓冲区;相对的概念是半双工,同一条连接在同一时刻,只能由一方来写数据。
服务器从
accept返回后,立刻调用read()读socket就像读管道一样,如果没有数据到达就阻塞等待。这时客户端调用
write()发送请求给服务器,服务器收到后从read()返回,对客户端的请求进行处理,在此期间客户端调用read()阻塞等待服务器的应答。服务器调用
write()将处理结果发回给客户端,再次调用read()阻塞等待下一条请求。客户端收到后从
read()返回,发送下一条请求,如此循环下去。
断开连接的过程:
如果客户端没有更多的请求了,就调用
close()关闭连接,客户端会向服务器发送 FIN段(第一次)此时服务器收到 FIN 后,会回应一个 ACK ,同时
read()会返回 0(第二次)read()返回之后,服务器就知道客户端关闭了连接,也调用close()关闭连接,这个时候服务器会向客户端发送一个 FIN (第三次)客户端收到 FIN,再返回一个 ACK 给服务器(第四次)
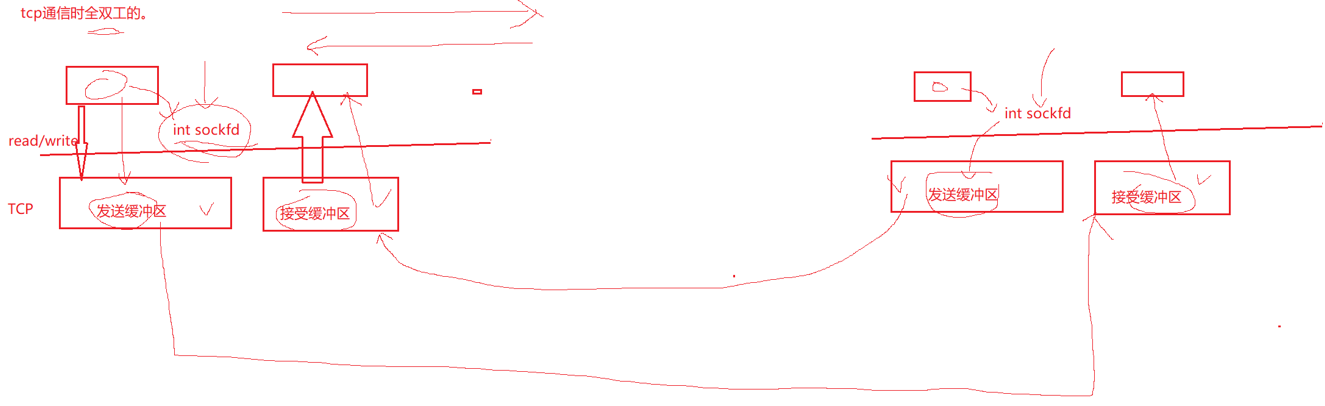

同一时刻可能会有多个客户端来连接服务器,所以在服务端一定会存在多个连接,服务端是需要把这多个连接管理起来的,管理一定是通过先描述再组织的方式。我们调用 write 接口本质上是将数据写入到 TCP 的发送缓冲区,至于写入的数据什么时候发送到对端的接收缓冲区,以及发送多少,出错了怎么办,完全是由 TCP 协议自主控制的, 所以 TCP 也叫做传输控制协议。我们使用的这些接口 write、read 、sendto、recvfrom 本质上都是在用户和内核之间进行数据拷贝。用户把数据交给操作系统,本质上就是把数据交给操作系统。
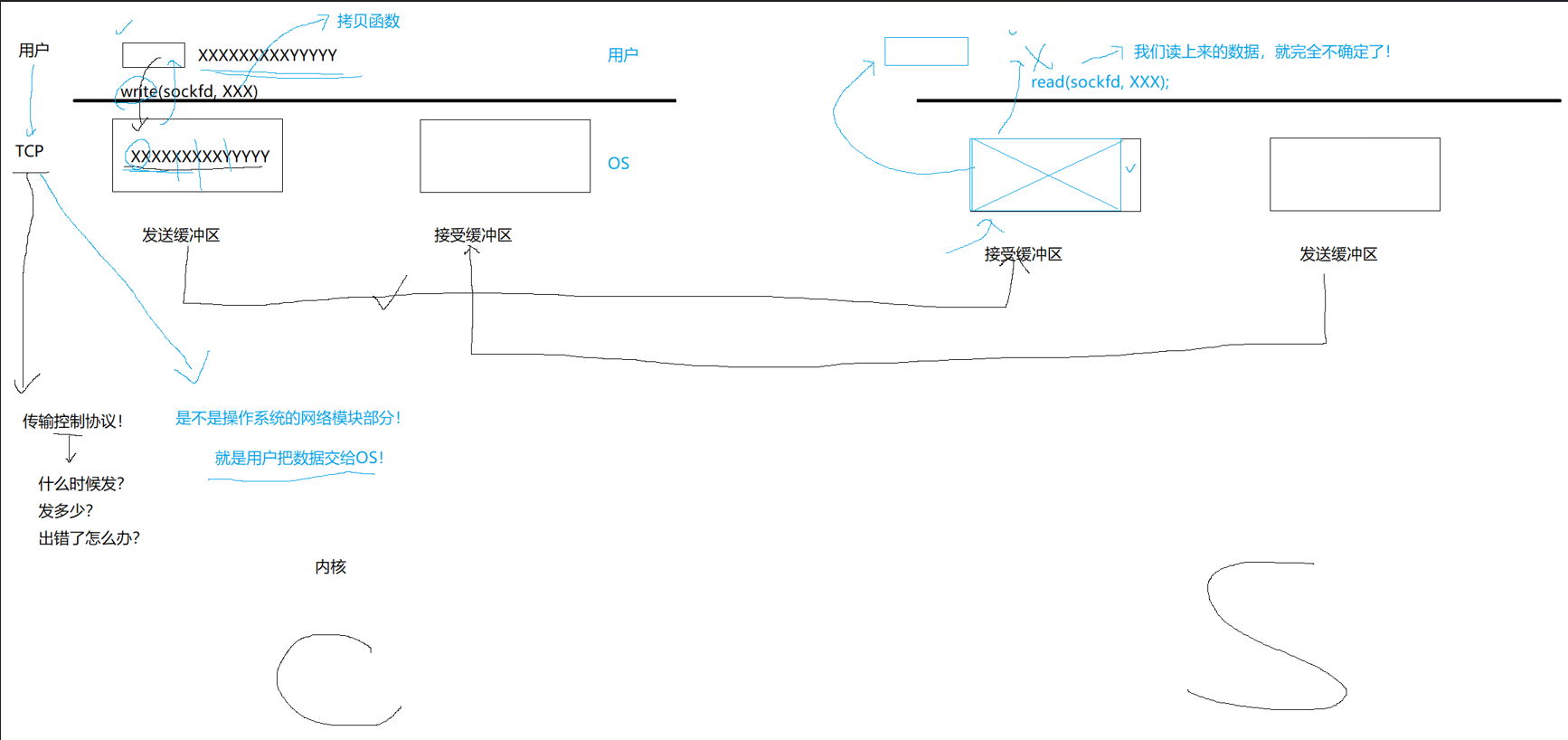
对于读方来说,可能 TCP 将发送方多次 write 的数据一次打包发了过来,接收方通过read 一次就多上来了多份数据,也可能 TCP 将发送方一次 write 的数据,分了好几次发送,read 每次读取到的都是部分数据。所以对接收方来说,它读上来的数据就存在很大的不确定性,它不清楚自己当前读到的数据是否是一个完整数据,也不清楚自己是否读到了多份数据。为了解决这个问题,就需要引入协议的概念,接收方可以根据协议来确定自己是否读取到了一份完整的数据。
十三、结语
今天的分享到这里就结束啦!如果觉得文章还不错的话,可以三连支持一下,春人的主页还有很多有趣的文章,欢迎小伙伴们前去点评,您的支持就是春人前进的动力!