文章目录
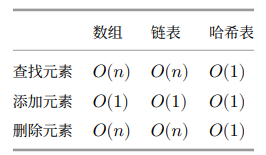
1.哈希表
public class HashTable {
// 节点类
static class Entry {
int hash; // 哈希码 未考虑 hash 码的生成
Object key; // 键
Object value; // 值
Entry next;
public Entry(int hash, Object key, Object value) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
Entry[] table = new Entry[16];
int size = 0; // 元素个数
float loadFactor = 0.75f; // 12 阈值
int threshold = (int) (loadFactor * table.length);
/* 求模运算替换为位运算
- 前提:数组长度是 2 的 n 次方
- hash % 数组长度 等价于 hash & (数组长度-1)
*/
// 根据 hash 码获取 value
Object get(int hash, Object key) {
int idx = hash & (table.length - 1);
if (table[idx] == null) {
return null;
}
Entry p = table[idx];
while (p != null) {
if (p.key.equals(key)) {
return p.value;
}
p = p.next;
}
return null;
}
// 向 hash 表存入新 key value,如果 key 重复,则更新 value
void put(int hash, Object key, Object value) {
int idx = hash & (table.length - 1);
if (table[idx] == null) {
// 1. idx 处有空位, 直接新增
table[idx] = new Entry(hash, key, value);
} else {
// 2. idx 处无空位, 沿链表查找 有重复key更新,否则新增
Entry p = table[idx];
while (true) {
if (p.key.equals(key)) {
p.value = value; // 更新
return;
}
if (p.next == null) {
break;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new Entry(hash, key, value); // 新增
}
size++;
if (size > threshold) {
resize();
}
}
private void resize() {
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[table.length << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
Entry p = table[i]; // 拿到每个链表头
if (p != null) {
/*
拆分链表,移动到新数组,拆分规律
* 一个链表最多拆成两个
* hash & table.length == 0 的一组
* hash & table.length != 0 的一组
p
0->8->16->24->32->40->48->null
a
0->16->32->48->null
b
8->24->40->null
*/
Entry a = null;
Entry b = null;
Entry aHead = null;
Entry bHead = null;
while (p != null) {
if ((p.hash & table.length) == 0) {
if (a != null) {
a.next = p;
} else {
aHead = p;
}
a = p; // 分配到a
} else {
if (b != null) {
b.next = p;
} else {
bHead = p;
}
b = p; // 分配到b
}
p = p.next;
}
// 规律: a 链表保持索引位置不变,b 链表索引位置+table.length
if (a != null) {
a.next = null;
newTable[i] = aHead;
}
if (b != null) {
b.next = null;
newTable[i + table.length] = bHead;
}
}
}
table = newTable;
threshold = (int) (loadFactor * table.length);
}
// 根据 hash 码删除,返回删除的 value
Object remove(int hash, Object key) {
int idx = hash & (table.length - 1);
if (table[idx] == null) {
return null;
}
Entry p = table[idx];
Entry prev = null;
while (p != null) {
if (p.key.equals(key)) {
// 找到了, 删除
if (prev == null) { // 链表头
table[idx] = p.next;
} else { // 非链表头
prev.next = p.next;
}
size--;
return p.value;
}
prev = p;
p = p.next;
}
return null;
}
}
2.生成 hashCode
Hash算法,是一种从任意长度的数据输入到固定长度输出的映射函数。输出通常称为哈希值或哈希码。哈希算法的主要特点是高效计算、输出长度固定、输入敏感、抗碰撞性强、不可逆性。
常见的哈希算法包括:
- MD5:输出128位哈希值,主要用于文件校验,但由于安全性较低,不推荐用于密码存储。
- SHA-1:输出160位哈希值,比MD5更安全,用于TLS和SSL的证书签名,但现在也逐渐被认为不够安全。
- SHA-256:属于SHA-2家族,输出256位哈希值,广泛用于区块链技术和数据完整性验证。
- SHA-3:最新的安全哈希算法标准,提供多种输出长度选项。
- BLAKE2:比SHA-3更快,安全性相当,广泛用于软件安全和数据验证。
Hash 算法是将任意对象,分配一个编号的过程,其中编号是一个有限范围内的数字(如 int 范围内)
Object.hashCode
- Object 的 hashCode 方法默认是生成随机数作为 hash 值(会缓存在对象头当中)
- 缺点是包含相同值的不同对象,他们的 hashCode 不一样,不能够用 hash 值来反映对象的值特征,因此诸多子类都会重写 hashCode 方法
String.hashCode
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "bac";
String s2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
// 原则:值相同的字符串生成相同的 hash 码, 尽量让值不同的字符串生成不同的 hash 码
/*
对于 abc a * 100 + b * 10 + c
对于 bac b * 100 + a * 10 + c
*/
int hash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
char c = s1.charAt(i);
System.out.println((int) c);
// (a*10 + b)*10 + c ==> a*100 + b*10 + c 2^5
hash = (hash << 5) - hash + c;
}
System.out.println(hash);
}
- 经验表明如果每次乘的是较大质数,可以有更好地降低 hash 冲突,因此改【乘 10】为【乘 31】
- 【乘 31】可以等价为【乘 32 - hash】,进一步可以转为更高效地【左移5位 - hash】
检查 hash 表的分散性
public void print() {
int[] sum = new int[table.length];
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
Entry p = table[i];
while (p != null) {
sum[i]++;
p = p.next;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sum));
Map<Integer, Long> result = Arrays.stream(sum).boxed()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s, Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(result);
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 测试 Object.hashCode
HashTable table = new HashTable();
for (int i = 0; i < 200000; i++) {
Object obj = new Object();
table.put(obj, obj);
}
table.print();
// 测试 String.hashCode
table = new HashTable();
List<String> strings = Files.readAllLines(Path.of("words"));
for (String string : strings) {
table.put(string, string);
}
table.print();
}
习题
E01. 两数之和-Leetcode 1
public class E01Leetcode1 {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int k = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(k)) {
return new int[]{i, map.get(k)};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return null; // 不会执行
}
}
E02. 无重复字符的最长字串-Leetcode 3
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int begin = 0;
int maxLength = 0;
for (int end = 0; end < s.length(); end++) {
char ch = s.charAt(end);
if (map.containsKey(ch)) { // 重复时调整 begin
begin = Math.max(begin, map.get(ch) + 1);
map.put(ch, end);
} else { // 不重复
map.put(ch, end);
}
System.out.println(s.substring(begin, end + 1));
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, end - begin + 1);
}
return maxLength;
}
begin 调整时的解释,遇到重复的 begin 应该向右调整,例如
abca
- 遇到重复的 a,这时 begin 应该调整到上个重复字符 a 索引加 1 处,即 map.get(‘a’) + 1 = 1,
但还有一种情况需要考虑,就是连续遇到两次重复,例如
abba
- 遇到重复的 b,这时 begin 应该调整到上个重复字符 b 索引加 1 处,即 map.get(‘b’) + 1 = 2
- 不过接下来,又遇到了重复的 a,此时若还执行 map.get(‘a’) + 1 = 1,则 begin 相当于向左退了,不对
- 应该是 Math.max(2, map.get(‘a’) + 1),即 begin 应该是两个重复字符索引中更靠右者
题目中说明 s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成,因此它的范围是有限的(在 0 ~127 之内),可以用数组来替代 HashMap 优化
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int[] map = new int[128];
Arrays.fill(map, -1);
int begin = 0;
int maxLength = 0;
for (int end = 0; end < s.length(); end++) {
char ch = s.charAt(end);
if (map[ch] != -1) { // 重复时调整 begin
begin = Math.max(begin, map[ch] + 1);
map[ch] = end;
} else { // 不重复
map[ch] = end;
}
System.out.println(s.substring(begin, end + 1));
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, end - begin + 1);
}
return maxLength;
}
E03. 字母异位词分组-Leetcode 49
解法1
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
HashMap<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
String key = new String(chars);
List<String> strings = map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>());
strings.add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
解法2
static class ArrayKey {
int[] key = new int[26];
public ArrayKey(String str) {
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
key[ch - 'a']++;
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
ArrayKey arrayKey = (ArrayKey) o;
return Arrays.equals(key, arrayKey.key);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Arrays.hashCode(key);
}
}
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
HashMap<ArrayKey, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
List<String> strings = map.computeIfAbsent(new ArrayKey(str), k -> new ArrayList<>());
strings.add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
E04. 判断有没有重复元素-Leetcode 217
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) { // 5ms
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int key : nums) {
if (!set.add(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
E05. 找出出现一次的数字-Leetcode 136
解法1:用 HashSet
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (!set.add(num)) {
set.remove(num);
}
}
return set.toArray(new Integer[0])[0];
}
解法2:用 xor
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int num = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
num = num ^ nums[i];
}
return num;
}
E06. 判断字母异位词-Leetcode 242
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) { // 1ms
return Arrays.equals(getKey(s), getKey(t));
}
private static int[] getKey(String s) {
int[] array = new int[26];
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chars) {
array[ch - 97]++;
}
return array;
}
E07. 第一个不重复字符-Leetcode 387
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
int[] array = new int[26];
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chars) {
array[ch-97]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char ch = chars[i];
if (array[ch - 97] == 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
E08. 出现次数最多的单词-Leetcode 819
解法1
public String mostCommonWord(String paragraph, String[] banned) {
Set<String> banSet = Set.of(banned);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
String[] split = paragraph.toLowerCase().split("[^A-Za-z]+");
for (String key : split) {
if(banSet.contains(key)) {
continue;
}
map.compute(key, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);
}
Optional<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> optional = map.entrySet().stream().max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue());
return optional.map(Map.Entry::getKey).orElse(null);
}
解法2
public String mostCommonWord(String paragraph, String[] banned) {
Set<String> banSet = Set.of(banned);
String[] split = paragraph.toLowerCase().split("[^A-Za-z]+");
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String key : split) {
if(banSet.contains(key)) {
continue;
}
map.compute(key, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);
}
Integer max = 0;
String maxKey = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet()) {
Integer value = e.getValue();
if (value > max) {
max = value;
maxKey = e.getKey();
}
}
return maxKey;
}
解法3
public String mostCommonWord(String paragraph, String[] banned) {
Set<String> banSet = Set.of(banned);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
char[] chars = paragraph.toLowerCase().toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char ch : chars) {
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
sb.append(ch);
} else {
put(banSet, map, sb);
sb = new StringBuilder();
}
}
put(banSet, map, sb);
Integer max = 0;
String maxKey = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : map.entrySet()) {
Integer value = e.getValue();
if (value > max) {
max = value;
maxKey = e.getKey();
}
}
return maxKey;
}
private static void put(Set<String> banSet, HashMap<String, Integer> map, StringBuilder sb) {
if (sb.length() > 0) {
String key = sb.toString();
if(!banSet.contains(key)) {
map.compute(key, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);
}
}
}
sb 避免每次新建
sb.setLength(0);
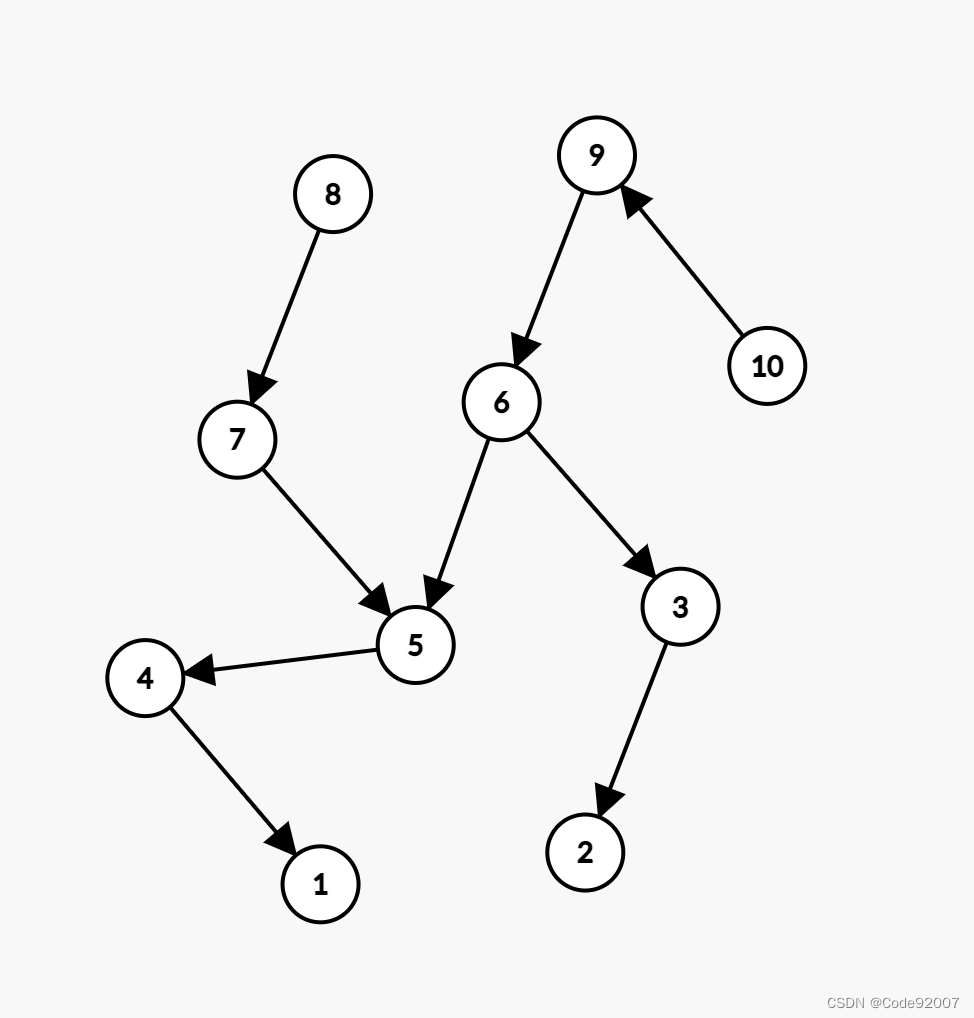
E09. 根据前序与中序遍历结果构造二叉树-Leetcode105 Improved
public class E09Leetcode105Improved {
// 用 hashmap 改善查找性能,其中 key 是 inOrder 值, value 是 inOrder 索引
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preOrder, int[] inOrder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inOrder.length; i++) {
map.put(inOrder[i], i);
}
return helper(preOrder, 0, 0, inOrder.length - 1);
}
// preBegin 决定了每次在 preOrder 中找到根元素
// inBegin 和 inEnd 可以用来获取区间内元素个数,结束递归等
private TreeNode helper(int[] preOrder, int preBegin, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
if (inBegin > inEnd) {
return null;
}
int rootValue = preOrder[preBegin];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
int i = map.get(rootValue);
int leftSize = i - inBegin;
System.out.println("元素:" + rootValue + " left[" + (preBegin + 1) + "] inOrder 索引范围[" + inBegin + "~" + (i - 1) + "]");
System.out.println("元素:" + rootValue + " right[" + (preBegin + 1 + leftSize) + "] inOrder 索引范围[" + (i + 1) + "~" + inEnd + "]");
root.left = helper(preOrder, preBegin + 1, inBegin, i - 1);
root.right = helper(preOrder, preBegin + 1 + leftSize, i + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] preOrder = {1, 2, 4, 3, 6, 7};
int[] inOrder = {4, 2, 1, 6, 3, 7};
/*
例如:
根据根节点[1] 到中序遍历数组中一分为2,首次递归
[1] 2 4 3 6 7 前
0 1 2 3 4 5 前索引
4 2 [1] 6 3 7 中
0 1 2 3 4 5 中索引
确定 preOrder 中 left 和 right 的递归起始索引,当然也要确定 inOrder 对应的两个索引位置
left right
1 [2] 4 [3] 6 7 前
0 1 2 3 4 5 前索引
left inOrder 索引范围: 0~1
right inOrder 索引范围: 3~5
*/
TreeNode root = new E09Leetcode105Improved().buildTree(preOrder, inOrder);
System.out.println(root);
}
}
E10. 根据中序与后序遍历结果构造二叉树-Leetcode106 Improved
public class E10Leetcode106Improved {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inOrder, int[] postOrder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inOrder.length; i++) {
map.put(inOrder[i], i);
}
return helper(postOrder, postOrder.length - 1, 0, inOrder.length - 1);
}
/*
inOrder = {4,2,1,6,3,7}
postOrder = {4,2,6,7,3,1}
*/
private TreeNode helper(int[] postOrder, int postEnd, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
if (inBegin > inEnd) {
return null;
}
int rootValue = postOrder[postEnd];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
Integer i = map.get(rootValue);
// int leftSize = i - inBegin;
int rightSize = inEnd - i;
System.out.println("元素:" + rootValue + " left[" + (postEnd - 1 - rightSize) + "] inOrder 索引范围[" + inBegin + "~" + (i - 1) + "]");
System.out.println("元素:" + rootValue + " right[" + (postEnd - 1) + "] inOrder 索引范围[" + (i + 1) + "~" + inEnd + "]");
root.left = helper(postOrder, postEnd - 1 - rightSize, inBegin, i - 1);
root.right = helper(postOrder, postEnd - 1, i + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] postOrder = {4, 2, 6, 7, 3, 1};
int[] inOrder = {4, 2, 1, 6, 3, 7};
TreeNode root = new E10Leetcode106Improved().buildTree(inOrder, postOrder);
System.out.println(root);
}
}



![[<span style='color:red;'>数据</span><span style='color:red;'>结构</span><span style='color:red;'>与</span><span style='color:red;'>算法</span>]<span style='color:red;'>哈</span><span style='color:red;'>希</span><span style='color:red;'>算法</span>](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/532ea498252842a2b2fa977fc3ddcee2.png)