目录
1. 顺序表的概念
用一段物理地址连续的内存依次存储数据元素的线性结构
本质就是数组,在数组基础上要求数据是连续存储的,不能有跳跃间隔。我们可以提前规划好顺序表的容量(静态顺序表),还可以根据添加数据动态增容(动态顺序表)
2. 实现的功能
1. void Seqlistpirnt(SL* ps);//顺序表打印
2. void SeqlistDestroy(SL* ps);//销毁接口
3. void SeqlistCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//扩容函数
4. void SeqlistInit(SL* ps);//顺序表初始化
5. void SeqlistPushBack(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);//尾插
6. void SeqlistPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
7. void SeqlistPushFront(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);//头插
8. void SeqlistPopFront(SL* ps);//头删
9. int SeqlistFind(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);//找到x位置返回下标,没找到返回-110. void SeqlistInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLdatatype x);//制定pos下标位置插入
11. void SeqlistErase(SL* ps, int pos);//删除pos位置的数据
3. 顺序表的定义
需要三个参数
1. a:指向动态内存开辟的空间
2. size:数组中的有效数据
3. capacity:存储的容量可动态增加
//#define N 100
//typedef int SLdatatype;
//
静态顺序表
//typedef struct Seqlist
//{
// SLdatatype a[N];
// int size;//表示数组中存储了多少个有效数据
//
//}Seqlist;
typedef int SLdatatype;
//动态顺序表
typedef struct Seqlist
{
SLdatatype* a;//指向存储数组的空间
int size;//表示数组中存储了多少个有效数据
int capacity;//容量
}SL;4.顺序表的实现
分为三个文件
4.1 seqlist.c
实现函数的功能
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#include"seqlist.h"
//动态增容
void SeqlistCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLdatatype* tmp = (SLdatatype*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SLdatatype));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
//打印输出顺序表
void Seqlistpirnt(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
printf("%d", ps->a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//销毁顺序表
void SeqlistDestroy(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
//顺序表初始化
void SeqlistInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
//尾部插入
void SeqlistPushBack(SL* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
//SeqlistCheckCapacity(ps);
//ps->a[ps->size] = x;
//ps->size++;
SeqlistInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
//尾部删除
void SeqlistPopBack(SL* ps)
{
ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0;
//if(ps->size>0)//温柔的处理方式
//ps->size--;
assert(ps->size>0);//暴力的处理方式
SeqlistErase(ps, ps->size);
}
//头部插入
void SeqlistPushFront(SL* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
//SeqlistCheckCapacity(ps);
//for (int i = ps->size-1; i >= 0; i--)
//{
// ps->a[i+1] = ps->a[i];
//}
//ps->a[0] = x;
//ps->size++;
SeqlistInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
//头部删除
void SeqlistPopFront(SL* ps)
{
//if(ps->size>0)
//{
// for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
// {
// ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
// }
// ps->size--;
//}
SeqlistErase(ps, 0);
}
//查找特定的数
int SeqlistFind(SL* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//插入数据到指定位置
void SeqlistInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLdatatype x)
{
SeqlistCheckCapacity(ps);
//assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
if (pos > ps->size || pos < 0)
{
printf("越界了\n");
return;
}
ps->size++;
for (int i = ps->size - 1; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
}
//删除指定位置的数
void SeqlistErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
if (pos == ps->size - 1)
{
ps->size--;
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}4.2 seqlist.h
方便调用函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLdatatype;
//动态顺序表
typedef struct Seqlist
{
SLdatatype* a;
int size;//表示数组中存储了多少个有效数据
int capacity;
}SL;
void Seqlistpirnt(SL* ps);
void SeqlistDestroy(SL* ps);//销毁接口
void SeqlistCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//扩容函数
void SeqlistInit(SL* ps);
void SeqlistPushBack(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);
void SeqlistPopBack(SL* ps);
void SeqlistPushFront(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);
void SeqlistPopFront(SL* ps);
int SeqlistFind(SL* ps, SLdatatype x);//找到x位置返回下标,没找到返回-1
void SeqlistInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLdatatype x);//制定pos下标位置插入
void SeqlistErase(SL* ps, int pos);//删除pos位置的数据
4.3 test.c
进行测试,使用
#define _CRT_voidSECURE_NO_WARNINGS h
#include"seqlist.h"
void TestSeqList1()
{
SL s1;
SeqlistInit(&s1);
SeqlistPushBack(&s1, 1);
SeqlistPushBack(&s1, 2);
SeqlistPushBack(&s1, 3);
SeqlistPushBack(&s1, 4);
SeqlistPushBack(&s1, 5);
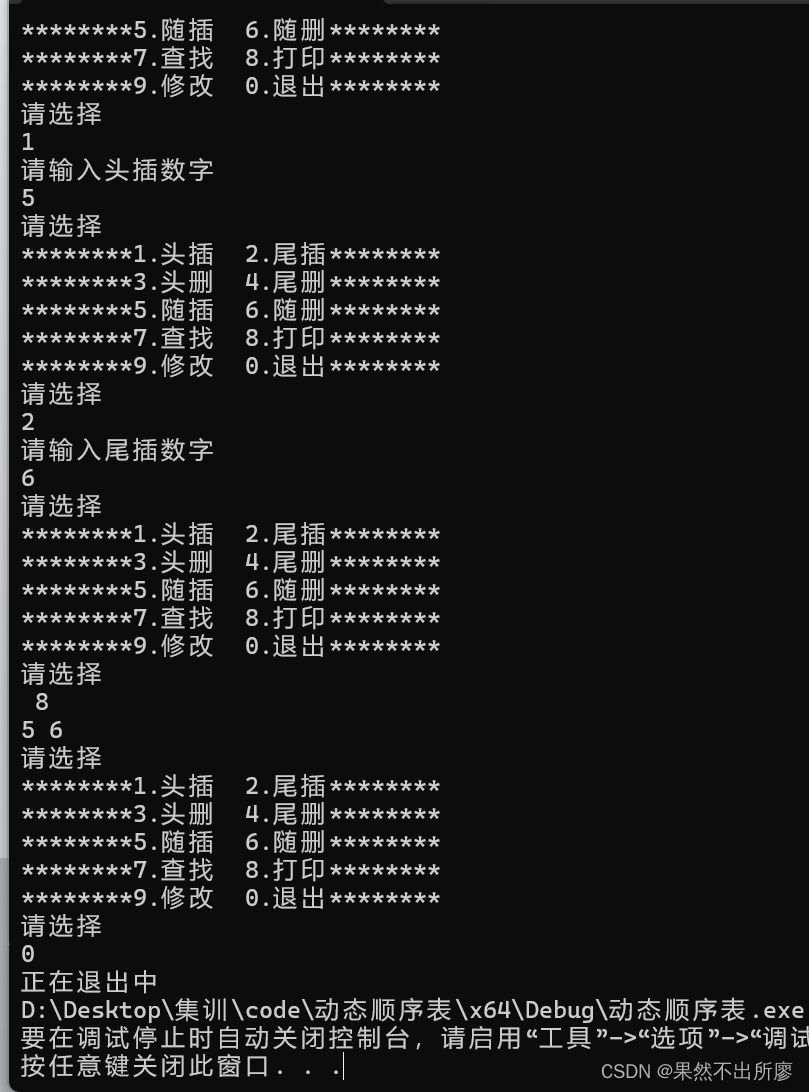
Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
SeqlistPopBack(&s1);
SeqlistPopBack(&s1);
Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
SeqlistDestroy(&s1);
}
void TestSeqList2()
{
SL s1;
SeqlistInit(&s1);
SeqlistPushFront(&s1, 1);
SeqlistPushFront(&s1, 2);
SeqlistPushFront(&s1, 3);
SeqlistPushFront(&s1, 4);
SeqlistPushFront(&s1, 5);
Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
SeqlistPopFront(&s1);
SeqlistPopFront(&s1);
Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
//int t = SeqlistFind(&s1, 2);
//printf("%d\n", t);
//int pos;
//scanf("%d", &pos);
//SeqlistInsert(&s1, pos, 6);
//Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
//scanf("%d", &pos);
//SeqlistErase(&s1, pos);
//Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
SeqlistPopFront(&s1);
//SeqlistPopFront(&s1);
//Seqlistpirnt(&s1);
SeqlistDestroy(&s1);
}
void TestSeqList3()//
{
SL s1;
int t = SeqlistFind(&s1, 2);
}
int main()
{
TestSeqList1();
TestSeqList2();
}5. 顺序表的优缺点
5.1优点
1.支持随机访问(用下标访问)需要随机访问结构,支持算法可以更好适用
2.cpu高速缓存命中率(连续存储)
5.2缺点
1.头部中部插入删除时间效率低O(N)
2.连续的物理空间,空间不够了以后需要增容
增容有一定程度的消耗
为了避免增容一般都按倍数去增容,用不完可能存在浪费
这篇到这里就结束了,希望可以帮到你
(づ ̄3 ̄)づ╭❤~