Nginx线程池源码刨析
相关的API
int thread_mutex_create (pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_destroy (pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_lock (pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_unlock (pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_cond_create (pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_destroy (pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_signal (pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_wait (pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
thread_task_t *thread_task_alloc(size_t size);//分配任务
int_t thread_task_post(thread_pool_t *tp, thread_task_t *task);
thread_pool_t* thread_pool_init();
void thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *tp);
//一些static函数
static void thread_pool_exit_handler(void *data);
static void *thread_pool_cycle(void *data);
static int_t thread_pool_init_default(thread_pool_t *tpp, char *name);
thread_mutex_destroy()
int thread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_destroy(mtx);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_mutex_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}
thread_mutex_create()
//创建锁且使用互斥量属性
int thread_mutex_create(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
//pthread_mutexattr_t 是用于线程互斥量属性的数据类型
//使用 pthread_mutexattr_t 可以更精确地控制互斥量的行为和特性。
//例如,你可以通过设置互斥量属性来指定互斥量的类型(如普通互斥量、递归互斥量等)以及是否可跨进程共享。
pthread_mutexattr_t attr;//设置锁的属性
err = pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutexattr_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
//PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK是一个宏,用于设置线程互斥锁的类型为错误检查锁。
//线程互斥锁是一种用于保护共享资源的数据结构,可以防止多个线程同时访问同一个资源。
//错误检查锁是一种特殊的互斥锁,它在尝试获取锁时,如果锁已经被其他线程持有,
//那么它会立即返回错误,而不是等待。
/*THREAD_MUTEX_TIME_UP 错误通常表示在等待互斥量时超时了。
/这可能是因为互斥量一直处于被其他线程持有的状态,导致当前线程无法获取到互斥量的所有权。
/超时发生后,系统会返回这个错误代码,以提示调用者当前无法获取互斥量,并需要适当处理该情况,
/例如等待一段时间后重试,或者采取其他的处理方式。*/
err = pthread_mutexattr_settype(&attr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK);//设置属性
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutexattr_settype(PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK) failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
//初始化互斥量
err = pthread_mutex_init(mtx, &attr);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_mutex_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
//销毁互斥量属性
err = pthread_mutexattr_destroy(&attr);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_mutexattr_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
}
return OK;
}
thread_mutex_unlock()
int thread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);//解锁
#if 0
ngx_time_update();
#endif
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_mutex_unlock() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_mutex_lock()
int thread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr,"pthread_mutex_lock() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_cond_wait()
int thread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
//条件变量
err = pthread_cond_wait(cond, mtx);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_wait() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_cond_destroy()
int thread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_destroy(cond);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_cond_signa()
int thread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_signal(cond);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_signal() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_cond_create()
int thread_cond_create(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_init(cond, NULL);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
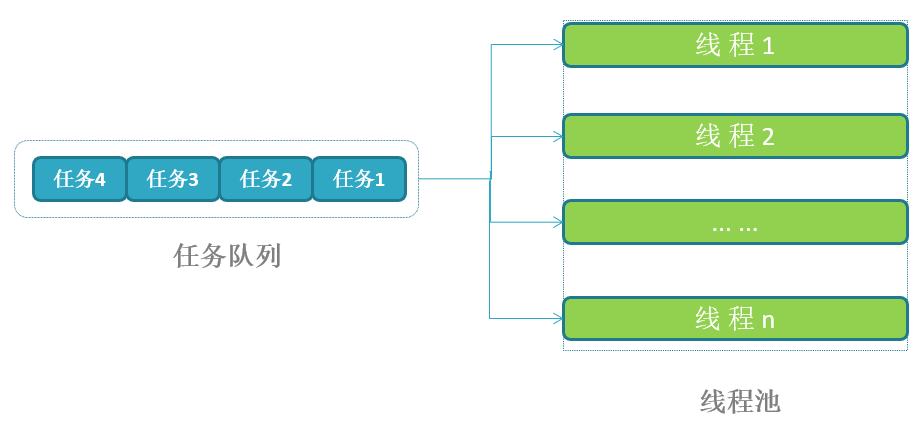
thread_pool_cycle()
函数参数 data 是一个 void 指针,指向一个 thread_pool_t 结构体,该结构体包含了线程池的相关信息。
在函数中,将 data 强制类型转换为 thread_pool_t 结构体指针,并将其赋值给 tp 变量,以便后续操作可以使用线程池的信息。
函数进入一个无限循环 for (;😉 {},这表示线程会持续运行,直到被外部强制终止。
在每次循环迭代中,线程会首先尝试获取线程池的互斥锁 tp->mtx,以确保线程安全地访问线程池的资源。
然后,线程将 tp->waiting 减少,表示线程池中等待执行任务的线程数量减少一个。
接着,线程会进入一个循环,等待任务队列中有任务可执行。如果任务队列为空,线程会等待条件变量 tp->cond,直到有任务被添加到队列中。
一旦有任务可执行,线程会从任务队列中取出第一个任务,并将其移出队列。
然后,线程会释放线程池的互斥锁,允许其他线程访问线程池的资源。
线程会执行任务的处理函数 task->handler(task->ctx),该函数处理任务,并在完成后释放任务所占用的内存空间。
最后,线程会回到循环的开头,继续等待新的任务。
static void *thread_pool_cycle(void *data)
{
thread_pool_t *tp = data;
int err;
thread_task_t *task;//线程任务
if(debug)fprintf(stderr,"thread in pool \"%s\" started\n", tp->name);
for ( ;; ) {
//上锁
if (thread_mutex_lock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
tp->waiting--;
while (tp->queue.first == NULL) {
if (thread_cond_wait(&tp->cond, &tp->mtx)
!= OK)
{
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
return NULL;
}
}
task = tp->queue.first;
tp->queue.first = task->next;
if (tp->queue.first == NULL) {
tp->queue.last = &tp->queue.first;
}
if (thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
if(debug) fprintf(stderr,"run task #%lu in thread pool \"%s\"\n",
task->id, tp->name);
task->handler(task->ctx);
if(debug) fprintf(stderr,"complete task #%lu in thread pool \"%s\"\n",task->id, tp->name);
task->next = NULL;
free(task);
}
}
thread_pool_destroy()
void thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *tp)
{
uint_t n;
thread_task_t task;
volatile uint_t lock;//volatile关键字用于修饰变量,表示该变量在多个线程之间是可见的
memset(&task,'\0', sizeof(thread_task_t));
task.handler = thread_pool_exit_handler;
task.ctx = (void *) &lock;
for (n = 0; n < tp->threads; n++) {
lock = 1;
if (thread_task_post(tp, &task) != OK) {
return;
}
while (lock) {
//使用sched_yield函数让出CPU,以便其他线程可以执行。
sched_yield();
}
//task.event.active = 0;
}
(void) thread_cond_destroy(&tp->cond);
(void) thread_mutex_destroy(&tp->mtx);
free(tp);
}
thread_pool_init()
相关的解释全部在注释里了,这个函数的作用是初始化一个线程池,该函数返回一个thread_pool_t类型的指针
thread_pool_t* thread_pool_init()
{
int err;//错误代号
pthread_t tid;//线程ID
/*
使用pthread_attr_t可以更精确地控制线程的行为和特性。
例如,你可以通过设置线程属性来指定线程的调度策略、优先级,以及分配给线程的栈大小等。
*/
pthread_attr_t attr; //线程属性
thread_pool_t *tp = NULL;//线程结构体
//分配内存 且 初始化为0
//sizeof(thread_pool_t) 表示 thread_pool_t 类型的大小,而 1 表示分配的内存块数量。
tp = calloc(1,sizeof(thread_pool_t));
//检查分配是否成功
if(tp == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "thread_pool_init: calloc failed!\n");
}
thread_pool_init_default(tp, NULL);
//初始化队列
thread_pool_queue_init(&tp->queue);
//初始化锁及其互斥量属性
if (thread_mutex_create(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
//初始化条件变量
if (thread_cond_create(&tp->cond) != OK) {
(void) thread_mutex_destroy(&tp->mtx);
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
//初始化线程属性
err = pthread_attr_init(&attr);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_attr_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
// 设置线程属性为分离状态
//PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED 在线程创建是其属性设置为分离状态(detached),主线程使用pthread_join 无法等待道结束的子线程
err = pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_attr_setdetachstate() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
for (uint_t n = 0; n < tp->threads; n++) {
//创建线程后执行函数thread_pool_cycle tp为该函数的参数
err = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, thread_pool_cycle, tp);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
}
(void) pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return tp;
}
thread_pool_queue_init()
//初始化为空队列
#define thread_pool_queue_init(q) \
(q)->first = NULL; \
(q)->last = &(q)->first
thread_pool_init_default()
static int_t thread_pool_init_default(thread_pool_t *tpp, char *name)
{
if(tpp)
{
tpp->threads = DEFAULT_THREADS_NUM;//线程数设为default
tpp->max_queue = DEFAULT_QUEUE_NUM;//队列数设为default -65535(猜猜why 65535
//strdup() 函数会在堆上为新字符串分配内存,并将原始字符串的内容复制到这块内存中。
//这样做的好处是,你可以在不担心内存越界或释放问题的情况下,安全地操作新字符串。需要注意的是,使用完 strdup() 函数分配的 内存后,你需要在不再需要时手动释放这块内存,以免造成内存泄漏。
tpp->name = strdup(name?name:"default");
if(debug)fprintf(stderr,"thread_pool_init, name: %s ,threads: %lu max_queue: %ld\n",pp->name, tpp->threads, tpp->max_queue);
return OK;
}
return ERROR;
}
thread_task_alloc()
一段很香的代码
thread_task_t * thread_task_alloc(size_t size)
{
thread_task_t *task;
task = calloc(1,sizeof(thread_task_t) + size);
if (task == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
task->ctx = task + 1;
//使用柔性数组 在结构体的尾部分批size大小的内存给ctx上下文作为
return task;
}
thread_task_post()
/**
* @brief 将任务添加到线程池的任务队列中
*
* @param tp 线程池指针
* @param task 待添加的任务指针
* @return int_t 成功返回 OK,失败返回 ERROR
*/
int_t thread_task_post(thread_pool_t *tp, thread_task_t *task)
{
// 获取线程池的互斥锁
if (thread_mutex_lock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return ERROR;
}
// 检查任务队列是否已满
if (tp->waiting >= tp->max_queue) {
// 如果队列已满,释放互斥锁并返回错误
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
fprintf(stderr,"thread pool \"%s\" queue overflow: %ld tasks waiting\n",
tp->name, tp->waiting);
return ERROR;
}
// 为任务分配唯一的ID
task->id = thread_pool_task_id++;
task->next = NULL;
// 发送信号唤醒等待任务的线程
if (thread_cond_signal(&tp->cond) != OK) {
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
return ERROR;
}
// 将任务添加到队列尾部
*tp->queue.last = task;
tp->queue.last = &task->next;
// 增加等待执行任务的数量
tp->waiting++;
// 释放线程池的互斥锁
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
// 打印调试信息
if(debug) fprintf(stderr,"task #%lu added to thread pool \"%s\"\n",
task->id, tp->name);
// 返回操作成功
return OK;
}
相关的结构体
typedef unsigned long atomic_uint_t;
typedef intptr_t int_t;
typedef uintptr_t uint_t;
//线程池结构体
typedef struct thread_pool_s_ {
pthread_mutex_t mtx;//锁
thread_pool_queue_t queue;//队列
int_t waiting;//正在等待的任务数量
pthread_cond_t cond;//condition 信号
char *name;//线程池的名字
uint_t threads;//线程数量
int_t max_queue;//最大的队列数量
}thread_pool_t,thread_pool_s_ ;
//任务结构体
typedef struct thread_task_s_ {
thread_task_t *next;//下一个任务的指针
uint_t id;//任务ID
void *ctx;//任务上下文 也就是线程执行函数的参数。使用动态分配内存(柔性数组)
void (*handler)(void *data);//线程执行的函数
}thread_task_s,thread_task_t;
//队列结构体
typedef struct thread_pool_queue_t_{
thread_task_t *first;
thread_task_t **last;
} thread_pool_queue_t;
相关宏
#define DEFAULT_THREADS_NUM 4 //默认线程数量
#define DEFAULT_QUEUE_NUM 65535//默认队列数量
#define OK 0
#define ERROR -1