一.加号运算符重载
1.成员函数重载加号
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person{
public:
int age_A;
int age_B;
Person operator+(Person p1){//成员函数重载了+号
Person temp;
temp.age_A=0;
temp.age_B=0;
temp.age_A=this->age_A+p1.age_A;
temp.age_B=this->age_B+p1.age_B;
return temp;
}
};
int main(){
Person p1;
p1.age_A=10;
p1.age_B=100;
Person p2;
p2.age_A=10;
p2.age_B=100;
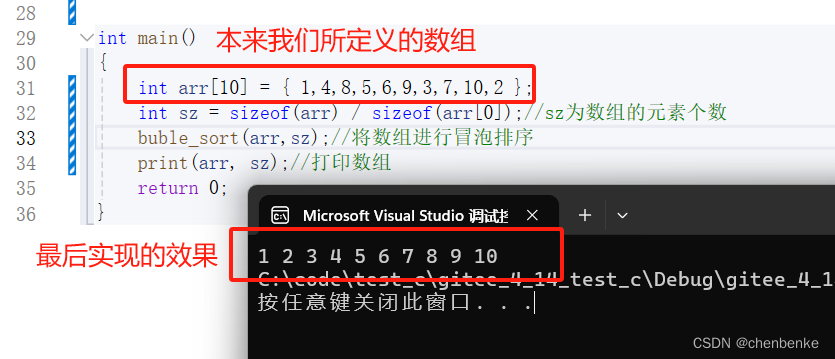
Person p3=p1+p2;//‘+’为重载之后的‘+’
cout<<p3.age_A<<endl;
cout<<p3.age_B<<endl;
}将函数名命名为operator+,就可以对‘+’进行重载
2.全局函数重载加号
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person{
public:
int age_A;
int age_B;
};
Person operator+(Person p1,Person p2){
Person temp;
temp.age_A=0;
temp.age_B=0;
temp.age_A=p1.age_A+p2.age_A;
temp.age_B=p1.age_B+p1.age_B;
return temp;
}
int main(){
Person p1;
p1.age_A=10;
p1.age_B=100;
Person p2;
p2.age_A=10;
p2.age_B=100;
Person p3=p1+p2;
cout<<p3.age_A<<endl;
cout<<p3.age_B<<endl;
}
原理和成员函数基本相同,返回值为类型,区别只是参数变成了两个类
二.左移运算符重载
左移运算符和加号运算符不同,如果在成员函数中进行重载,那么不能达到预期效果,这里通常只能在全局函数中重载
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person{
public:
int m_A;
int m_B;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& t,Person& p){
t<<"m_A="<<p.m_A<<" m_B="<<p.m_B<<endl;
return t;
}
int main(){
Person p1;
p1.m_A=10;
p1.m_B=10;
cout<<p1<<endl;
Person p2;
p2.m_A=20;
p2.m_B=20;
cout<<p2<<endl;
}1.注意看operator<<函数,将ostream类型进行改写,这里一定要是引用,否则后续在使用时会报错。
2.在最后返回了一个ostream的引用,是为了支持链式操作。(因为当我们使用 ostream 对象进行输出时,通常会进行链式操作,比如 cout << "Hello" << endl;。这是因为 << 运算符会返回其左操作数的引用,以便我们可以继续在其上执行输出操作。如果 ostream 对象作为值传递,那么每次 << 运算符调用都会生成一个新的 ostream 对象,导致链式操作失效。)
三.递增运算符重载
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyInt{
//设置为友元,访问私有成员变量
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout,const MyInt &i);
public:
MyInt(){
num=0;
}
//前置自增运算符
MyInt& operator++()
{
//先进行++运算
num++;
//再将自身返回
return *this;
}
// 后置自增运算符
// int代表占位参数,可以用于区分前置和后置自增
MyInt operator++(int)
{
MyInt temp = *this;
num++;
return temp;
}
private:
int num;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout,const MyInt &i){
cout << i.num;
return cout;
}
int main(){
MyInt myint;
cout << ++(++myint) <<endl;
cout << myint++ << endl;
cout << myint <<endl;
}注意看前置运算和后置运算的区别
前置递增时最后返回的是一个类的引用,这是因为前置递增一般可以进行链式操作。而后置运算符返回的是对象递增前的值的副本,因此不能进行链式操作。
链式操作详解:
在表达式 cout << a << b; 中,编译器会从左向右逐个解析表达式,并根据运算符的优先级和结合性确定表达式的含义。在这个例子中,<< 是左结合的,因此编译器会首先解析 cout << a 这个子表达式。
因此,编译器首先识别的是 cout << a 这一部分。它会查找一个与左操作数 cout 和右操作数 a 匹配的重载运算符 <<。由于标准库中已经定义了 cout 的 << 运算符,它将 a 的值输出到 cout 中,并返回一个 ostream& 对象,表示输出流本身。
然后,编译器将这个返回的 ostream& 对象视为整个表达式的左操作数,接着解析 << b 部分。同样地,编译器会查找与左操作数匹配的重载运算符 <<,并将 b 的值插入到输出流中。