给定一个由 n 个均匀分布值 arr[] 组成的排序数组,编写一个函数来搜索数组中的特定元素 x。
线性搜索需要 O(n) 时间找到元素,跳转搜索需要 O(? n) 时间,二分搜索需要 O(log n) 时间。 插值搜索是对实例二分搜索的改进,其中排序数组中的值是均匀分布的。
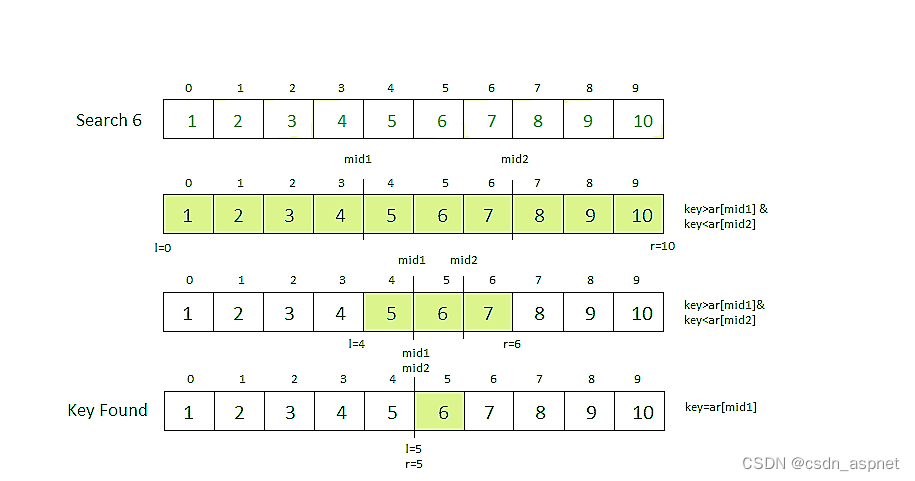
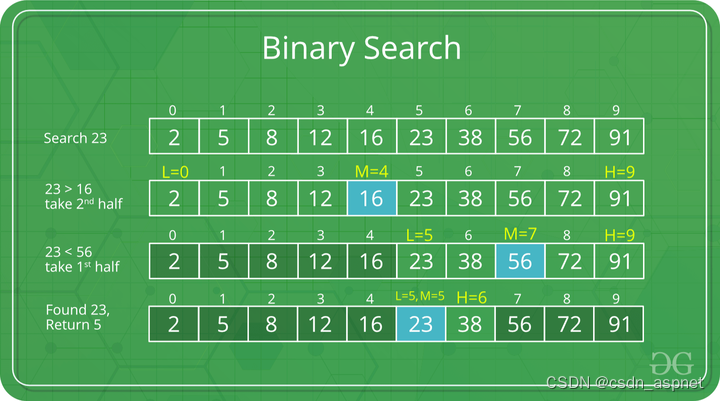
插值在一组离散的已知数据点的范围内构造新的数据点。二分查找总是到中间元素去检查。
另一方面,插值搜索可以根据正在搜索的键的值去不同的位置。例如,如果键的值更接近最后一个元素,则插值搜索很可能从末尾侧开始搜索。为了找到要搜索的位置,它使用以下公式。
// 公式的思想是
当要搜索的元素更接近arr[hi]时,返回较高的pos值。
// 当接近 arr[lo] 时值更小
arr[] ==> 需要查找元素的数组
x ==> 要搜索的元素
lo ==> arr[] 中的起始索引
hi ==> arr[] 中的结束索引
![]()
有许多不同的插值方法,其中一种称为线性插值。线性插值采用两个数据点,我们假设为 (x1,y1) 和 (x2,y2),公式为:在点 (x,y) 处。
该算法的工作原理类似于我们在字典中搜索单词。插值搜索算法改进了二分搜索算法。查找值的公式为:K = 数据-低/高-低。
K是一个常数,用于缩小搜索空间。在二分查找的情况下,该常数的值为:K=(low+high)/2。
pos 的公式可以推导如下:
我们假设数组的元素是线性分布的,直线的一般方程:y = m*x + c,y 是数组中的值,x 是其索引。
现在将 lo、hi 和 x 的值代入方程:
arr[hi] = m*hi+c ----(1)
arr[lo] = m*lo+c ----(2)
x = m* pos + c ----(3)
m = (arr[hi] - arr[lo] )/ (hi - lo)
从 (3) x - arr[lo] = m * (pos - lo) 减去 eqxn (2) lo)
lo + (x - arr[lo])/m = pos
pos = lo + (x - arr[lo]) *(hi - lo)/(arr[hi] - arr[lo])
算法
除了上面的划分逻辑之外,插值算法的其余部分是相同的。
步骤1:在循环中,使用探针位置公式计算“pos”的值。
步骤2:如果匹配,则返回该项的索引,并退出。
步骤3:如果该项小于arr[pos],则计算左子数组的探针位置。否则,在右侧子数组中计算相同的值。
步骤4:重复直到找到匹配项或子数组减少到零。
下面是算法的实现:
# Python3 program to implement
# interpolation search
# with recursion
# If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then
# returns index of it, else returns -1.
def interpolationSearch(arr, lo, hi, x):
# Since array is sorted, an element present
# in array must be in range defined by corner
if (lo <= hi and x >= arr[lo] and x <= arr[hi]):
# Probing the position with keeping
# uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + ((hi - lo) // (arr[hi] - arr[lo]) *
(x - arr[lo]))
# Condition of target found
if arr[pos] == x:
return pos
# If x is larger, x is in right subarray
if arr[pos] < x:
return interpolationSearch(arr, pos + 1,
hi, x)
# If x is smaller, x is in left subarray
if arr[pos] > x:
return interpolationSearch(arr, lo,
pos - 1, x)
return -1
# Driver code
# Array of items in which
# search will be conducted
arr = [10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20,
21, 22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47]
n = len(arr)
# Element to be searched
x = 18
index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x)
if index != -1:
print("Element found at index", index)
else:
print("Element not found")
# This code is contributed by Hardik Jain
输出
在索引 4 处找到的元素
时间复杂度:平均情况为O(log 2 (log 2 n)),最坏情况为 O(n)
辅助空间复杂度: O(1)
另一种方法:
这是插值搜索的迭代方法。
步骤1:在循环中,使用探针位置公式计算“pos”的值。
步骤2:如果匹配,则返回该项的索引,并退出。
步骤3:如果该项小于arr[pos],则计算左子数组的探针位置。否则,在右侧子数组中计算相同的值。
步骤4:重复直到找到匹配项或子数组减少到零。
下面是算法的实现:
# Python equivalent of above C++ code
# Python program to implement interpolation search by using iteration approach
def interpolationSearch(arr, n, x):
# Find indexes of two corners
low = 0
high = (n - 1)
# Since array is sorted, an element present
# in array must be in range defined by corner
while low <= high and x >= arr[low] and x <= arr[high]:
if low == high:
if arr[low] == x:
return low;
return -1;
# Probing the position with keeping
# uniform distribution in mind.
pos = int(low + (((float(high - low)/( arr[high] - arr[low])) * (x - arr[low]))))
# Condition of target found
if arr[pos] == x:
return pos
# If x is larger, x is in upper part
if arr[pos] < x:
low = pos + 1;
# If x is smaller, x is in lower part
else:
high = pos - 1;
return -1
# Main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Array of items on whighch search will
# be conducted.
arr = [10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21,
22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47]
n = len(arr)
x = 18 # Element to be searched
index = interpolationSearch(arr, n, x)
# If element was found
if index != -1:
print ("Element found at index",index)
else:
print ("Element not found")
输出
在索引 4 处找到的元素
时间复杂度:平均情况为 O(log2(log2 n)),最坏情况为 O(n)
辅助空间复杂度: O(1)