Network management in an Acropolis cluster consists of the following tasks:
- Configuring L2 switching (configuring bridges, bonds, and VLANs.)
- Optionally changing the IP address, netmask, and default gateway that AHV specified for the hosts during the imaging process.
This video walks through AHV networking concepts, including both CLI and Prism examples.
Recommended Network Configuration
You need to change the default network configuration to the recommended configuration below.
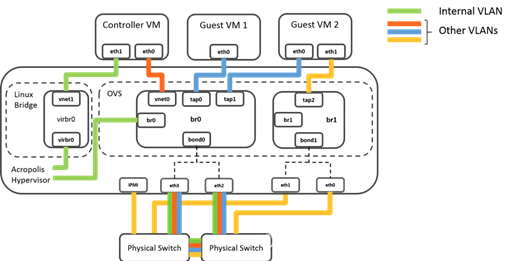
AHV Networking Best Practices
Click each element to learn more.
Virtual Switch
Do not modify the OpenFlow tables of any bridges configured in any VS configurations in the AHV hosts. Do not rename default virtual switch vs0. You cannot delete the default virtual switch vs0. Do not delete or rename OVS bridge br0. Do not modify the native Linux bridge virbr0.
Switch Hops
Nutanix nodes send storage replication traffic to each other in a distributed fashion over the top-of-rack network. One Nutanix node can, therefore, send replication traffic to any other Nutanix node in the cluster. The network should provide low and predictable latency for this traffic. Ensure that there are no more than three switches between any two Nutanix nodes in the same cluster.
switch fabric
A switch fabric is a single leaf-spine topology or all switches connected to the same switch aggregation layer. The Nutanix VLAN shares a common broadcast domain within the fabric. Connect all Nutanix nodes that form a cluster to the same switch fabric. Do not stretch a single Nutanix cluster across multiple, disconnected switch fabrics. Every Nutanix node in a cluster should therefore be in the same L2 broadcast domain and share the same IP subnet.
WAN Links
A WAN (wide area network) or metro link connects different physical sites over a distance. As an extension of the switch fabric requirement, do not place Nutanix nodes in the same cluster if they are separated by a WAN.
VLANs
Add the Controller VM and the AHV host to the same VLAN. Place all CVMs and AHV hosts in a cluster in the same VLAN. By default the CVM and AHV host are untagged, shown as VLAN 0, which effectively places them on the native VLAN configured on the upstream physical switch. Do not add any other device (including guest VMs) to the VLAN to which the CVM and hypervisor host are assigned. Isolate guest VMs on one or more separate VLANs.
Nutanix recommends configuring the CVM and hypervisor host VLAN as the native, or untagged, VLAN on the connected switch ports. This native VLAN configuration allows for easy node addition and cluster expansion. By default, new Nutanix nodes send and receive untagged traffic. If you use a tagged VLAN for the CVM and hypervisor hosts instead, you must configure that VLAN while provisioning the new node, before adding that node to the Nutanix cluster.
Default VS bonded port(br0-up)
Use tagged VLANs for all guest VM traffic and add the required guest VM VLANs to all connected switch ports for hosts in the Nutanix cluster. Limit guest VLANs for guest VM traffic to the smallest number of physical switches and switch ports possible to reduce broadcast network traffic load. If a VLAN is no longer needed, remove it.
Aggregate the fastest links of the same speed on the physical host to a VS bond on the default vs0 and provision VLAN trunking for these interfaces on the physical switch.
By default, interfaces in the bond in the virtual switch operate in the recommended active-backup mode. The mixing of bond modes across AHV hosts in the same cluster is not recommended and not supported.
1GbE and 10 GbE interfaces(physical host)
If 10 GbE or faster uplinks are available, Nutanix recommends that you use them instead of 1 GbE uplinks.
If you plan to use 1 GbE uplinks, do not include them in the same bond as the 10 GbE interfaces. Nutanix recommends that you do not use uplinks of different speeds in the same bond.
If you choose to configure only 1 GbE uplinks, when migration of memory-intensive VMs becomes necessary, power off and power on in a new host instead of using live migration. In this context, memory-intensive VMs are VMs whose memory changes at a rate that exceeds the bandwidth offered by the 1 GbE uplinks.
Nutanix recommends the manual procedure for memory-intensive VMs because live migration, which you initiate either manually or by placing the host in maintenance mode, might appear prolonged or unresponsive and might eventually fail.
If you must use only 1GbE uplinks, add them into a bond to increase bandwidth and use the balance-TCP (LACP) or balance-SLB bond mode.
IPMI port on the hypervisor host
Do not use VLAN trunking on switch ports that connect to the IPMI interface. Configure the switch ports as access ports for management simplicity.
Upstream physical switch
Nutanix does not recommend the use of Fabric Extenders (FEX) or similar technologies for production use cases. While initial, low-load implementations might run smoothly with such technologies, poor performance, VM lockups, and other issues might occur as implementations scale upward (see Knowledge Base article KB1612). Nutanix recommends the use of 10Gbps, line-rate, non-blocking switches with larger buffers for production workloads.
Cut-through versus store-and-forward selection depends on network design. In designs with no oversubscription and no speed mismatches you can use low-latency cut-through switches. If you have any oversubscription or any speed mismatch in the network design, then use a switch with larger buffers. Port-to-port latency should be no higher than 2 microseconds.
Use fast-convergence technologies (such as Cisco PortFast) on switch ports that are connected to the hypervisor host.
Physical Network Layout
Use redundant top-of-rack switches in a traditional leaf-spine architecture. This simple, flat network design is well suited for a highly distributed, shared-nothing compute and storage architecture.
Add all the nodes that belong to a given cluster to the same Layer-2 network segment.
Other network layouts are supported as long as all other Nutanix recommendations are followed.
Jumbo Frames
The Nutanix CVM uses the standard Ethernet MTU (maximum transmission unit) of 1,500 bytes for all the network interfaces by default. The standard 1,500 byte MTU delivers excellent performance and stability. Nutanix does not support configuring the MTU on network interfaces of a CVM to higher values.
You can enable jumbo frames (MTU of 9,000 bytes) on the physical network interfaces of AHV hosts and guest VMs if the applications on your guest VMs require them. If you choose to use jumbo frames on hypervisor hosts, be sure to enable them end to end in the desired network and consider both the physical and virtual network infrastructure impacted by the change.
Controller VM
Do not remove the Controller VM from either the OVS bridge br0 or the native Linux bridge virbr0.
Block awareness and rack awareness
Block awareness and rack awareness provide smart placement of Nutanix cluster services, metadata, and VM data to help maintain data availability, even when you lose an entire block or rack. The same network requirements for low latency and high throughput between servers in the same cluster still apply when using block and rack awareness.
Do not use features like block or rack awareness to stretch a Nutanix cluster between different physical sites.
Oversubscription
Oversubscription occurs when an intermediate network device or link does not have enough capacity to allow line rate communication between the systems connected to it. For example, if a 10 Gbps link connects two switches and four hosts connect to each switch at 10 Gbps, the connecting link is oversubscribed. Oversubscription is often expressed as a ratio—in this case 4:1, as the environment could potentially attempt to transmit 40 Gbps between the switches with only 10 Gbps available. Achieving a ratio of 1:1 is not always feasible. However, you should keep the ratio as small as possible based on budget and available capacity. If there is any oversubscription, choose a switch with larger buffers.
In a typical deployment where Nutanix nodes connect to redundant top-of-rack switches, storage replication traffic between CVMs traverses multiple devices. To avoid packet loss due to link oversubscription, ensure that the switch uplinks consist of multiple interfaces operating at a faster speed than the Nutanix host interfaces. For example, for nodes connected at 10 Gbps, the inter-switch connection should consist of multiple 10 Gbps or 40 Gbps links.