目录
Netty的粘包问题
在网络通信中,粘包问题是一种常见的情况,特别是在使用TCP协议进行数据传输时。本文将探讨Netty中的粘包问题及其解决方案,帮助读者更好地理解和应对这一问题。
1. 粘包问题介绍
1.1 什么是粘包问题
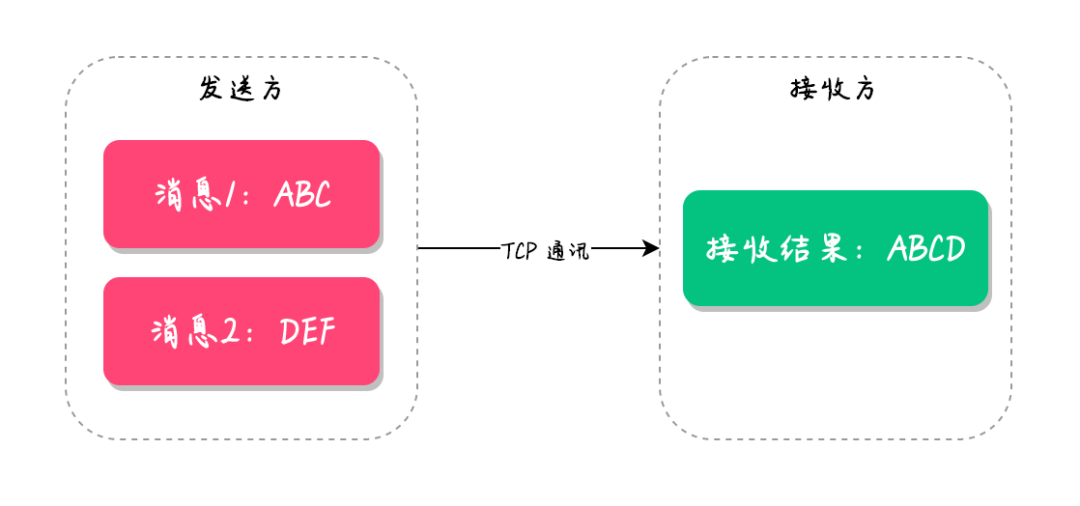
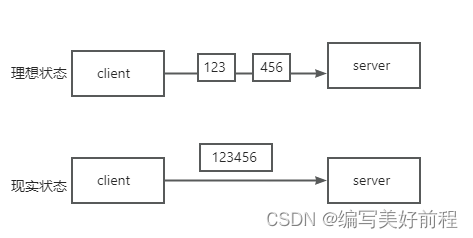
粘包问题是指发送端在将多个数据包连续发送到接收端时,接收端在接收数据时可能会将多个数据包粘合在一起,导致数据解析错误或丢失的情况。
1.2 粘包问题的影响
粘包问题可能导致接收端无法准确解析数据,从而影响系统的正常运行,甚至引发数据错误或丢失。
2. 粘包问题的原因
2.1 TCP协议的特点
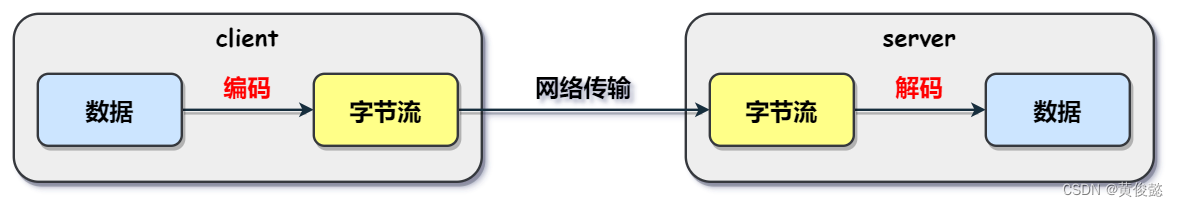
TCP协议是面向连接的、可靠的数据传输协议,其特性会导致粘包问题的产生。
2.2 发送端造成的粘包
发送端在短时间内连续发送多个数据包时,可能会导致多个数据包在传输过程中被合并成一个数据包。
2.3 接收端造成的粘包
接收端在接收数据时,可能会将多个数据包一次性读取到缓冲区,造成粘包现象。
3. 粘包问题的解决方案
3.1 固定长度消息
通过设置固定长度的消息格式,使得每个数据包的长度固定,从而解决粘包问题。
服务端代码示例
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16));
服务端完整代码
// 示例代码
/**
* @description: 固定长度方式解决粘包 问题服务端示例
* @author: xz
*/
@Slf4j
public class NettyFixLengthServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new NettyFixLengthServer().start();
}
void start() {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//调整 netty 的接受缓冲区(byteBuf)
.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR,new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator(16,16,16))
.group(boss, worker)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//设置定长解码器,位置必须再LoggingHandler之前,作用让所有数据包长度固定(假设长度为 16 字节)
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
//会在连接channel建立成功后,触发active事件
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("connected>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> {}", ctx.channel());
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("disconnect>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> {}", ctx.channel());
super.channelInactive(ctx);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080);
log.debug("{}>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> binding...", channelFuture.channel());
channelFuture.sync();
log.debug("{}>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> bound...", channelFuture.channel());
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
log.debug(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>stoped");
}
}
}
客户端代码
/**
* @description: 固定长度方式解决粘包 问题客户端示例
* @author: xz
*/
@Slf4j
public class NettyFixLengthClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
send();
}
//剩余位置用下划线填充
public static byte[] fill10Bytes(char c,int len){
byte[] bytes = new byte[16];
Arrays.fill(bytes, (byte) '_');
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
bytes[i] = (byte) c;
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
return bytes;
}
private static void send() {
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.debug("connetted...");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
log.debug("sending...");
//设置ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 发送内容随机的数据包
Random r = new Random();
char c = '0';
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//剩余位置用下划线填充方法
byte[] bytes =fill10Bytes(c,r.nextInt(16)+1);
c++;
//写入到ByteBuf
buffer.writeBytes(bytes);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
3.2 分隔符消息
在数据包之间添加特定的分隔符,通过分隔符来区分不同的数据包,从而解决粘包问题。
String recieveStr = ""$$$$这是一条粘包的消息&&&&$$$$这是一条粘包的消息&&&&"";
if (recieveStr.contains("&&&&$$$$")) {
log.debug("发生粘包");
//去掉首尾的分隔符
recieveStr = recieveStr.substring(4, recieveStr.length() - 4);
//将分离好的消息写入字符串数组
String[] totalBag = recieveStr.split("&&&&$$$$");
for (String thisTotalBag : totalBag) {
//每条消息的业务逻辑。。。
}
}
3.3 消息头+消息体
在消息中添加头部信息,包括消息长度等信息,接收端根据头部信息来解析数据包,从而解决粘包问题。
3.4 使用消息结束标志
在每个数据包的末尾添加特定的结束标志,接收端根据结束标志来识别数据包的边界,从而解决粘包问题。netty使用tcp/ip协议传输数据。而tcp/ip协议是类似水流一样的数据传输方式。多次访问的时候有可能出现数据粘包的问题。客户端和服务器,协商定义一个特殊的分隔符号,分隔符号长度自定义。如:‘#’、‘KaTeX parse error: Expected group after '_' at position 1: _̲’、‘AA@’。在通讯的时候,只要没有发送分隔符号,则代表一条数据没有结束。bootstrap.childHandler()方法,在该方法中,定义了一个ChannelHandler[] acceptorHandlers = new ChannelHandler[3];数组的三个元素分别对应:自定义结束符、自定义编码、自定义处理器。最后,将这个数组作为参数进行传递。
- 服务端代码
public class Server4Delimiter {
// 监听线程组,监听客户端请求
private EventLoopGroup acceptorGroup = null;
// 处理客户端相关操作线程组,负责处理与客户端的数据通讯
private EventLoopGroup clientGroup = null;
// 服务启动相关配置信息
private ServerBootstrap bootstrap = null;
public Server4Delimiter(){
init();
}
private void init(){
acceptorGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
clientGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// 绑定线程组
bootstrap.group(acceptorGroup, clientGroup);
// 设定通讯模式为NIO
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
// 设定缓冲区大小
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
// SO_SNDBUF发送缓冲区,SO_RCVBUF接收缓冲区,SO_KEEPALIVE开启心跳监测(保证连接有效)
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 16*1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 16*1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
}
public ChannelFuture doAccept(int port) throws InterruptedException{
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 数据分隔符, 定义的数据分隔符一定是一个ByteBuf类型的数据对象。
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$E$".getBytes());
ChannelHandler[] acceptorHandlers = new ChannelHandler[3];
// 处理固定结束标记符号的Handler。这个Handler没有@Sharable注解修饰,
// 必须每次初始化通道时创建一个新对象
// 使用特殊符号分隔处理数据粘包问题,也要定义每个数据包最大长度。netty建议数据有最大长度。
acceptorHandlers[0] = new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiter);
// 字符串解码器Handler,会自动处理channelRead方法的msg参数,将ByteBuf类型的数据转换为字符串对象
acceptorHandlers[1] = new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
acceptorHandlers[2] = new Server4DelimiterHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(acceptorHandlers);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
return future;
}
public void release(){
this.acceptorGroup.shutdownGracefully();
this.clientGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ChannelFuture future = null;
Server4Delimiter server = null;
try{
server = new Server4Delimiter();
future = server.doAccept(9999);
System.out.println("server started.");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != future){
try {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != server){
server.release();
}
}
}
}
public class Server4DelimiterHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
// 业务处理逻辑
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String message = msg.toString();
System.out.println("from client : " + message);
String line = "server message $E$ test delimiter handler!! $E$ second message $E$";
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8")));
}
// 异常处理逻辑
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server exceptionCaught method run...");
// cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
- 客户端代码
public class Client4Delimiter {
// 处理请求和处理服务端响应的线程组
private EventLoopGroup group = null;
// 服务启动相关配置信息
private Bootstrap bootstrap = null;
public Client4Delimiter(){
init();
}
private void init(){
group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
// 绑定线程组
bootstrap.group(group);
// 设定通讯模式为NIO
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
}
public ChannelFuture doRequest(String host, int port) throws InterruptedException{
this.bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 数据分隔符
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$E$".getBytes());
ChannelHandler[] handlers = new ChannelHandler[3];
handlers[0] = new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiter);
// 字符串解码器Handler,会自动处理channelRead方法的msg参数,将ByteBuf类型的数据转换为字符串对象
handlers[1] = new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
handlers[2] = new Client4DelimiterHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(handlers);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = this.bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
return future;
}
public void release(){
this.group.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client4Delimiter client = null;
ChannelFuture future = null;
try{
client = new Client4Delimiter();
future = client.doRequest("localhost", 9999);
Scanner s = null;
while(true){
s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter message send to server > ");
String line = s.nextLine();
future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8")));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != future){
try {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != client){
client.release();
}
}
}
}
public class Client4DelimiterHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try{
String message = msg.toString();
System.out.println("from server : " + message);
}finally{
// 用于释放缓存。避免内存溢出
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptionCaught method run...");
// cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
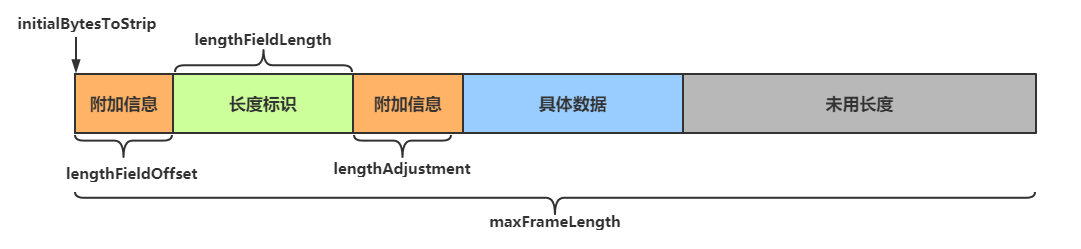
3.5 使用消息定长协议
利用Netty提供的LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder等解码器,处理定长消息,从而解决粘包问题。
public class Client4Delimiter {
// 处理请求和处理服务端响应的线程组
private EventLoopGroup group = null;
// 服务启动相关配置信息
private Bootstrap bootstrap = null;
public Client4Delimiter(){
init();
}
private void init(){
group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
// 绑定线程组
bootstrap.group(group);
// 设定通讯模式为NIO
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
}
public ChannelFuture doRequest(String host, int port) throws InterruptedException{
this.bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 数据分隔符
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$E$".getBytes());
ChannelHandler[] handlers = new ChannelHandler[3];
handlers[0] = new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiter);
// 字符串解码器Handler,会自动处理channelRead方法的msg参数,将ByteBuf类型的数据转换为字符串对象
handlers[1] = new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
handlers[2] = new Client4DelimiterHandler();
ch.pipeline().addLast(handlers);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = this.bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
return future;
}
public void release(){
this.group.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client4Delimiter client = null;
ChannelFuture future = null;
try{
client = new Client4Delimiter();
future = client.doRequest("localhost", 9999);
Scanner s = null;
while(true){
s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter message send to server > ");
String line = s.nextLine();
future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(line.getBytes("UTF-8")));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(null != future){
try {
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != client){
client.release();
}
}
}
}
public class Client4DelimiterHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try{
String message = msg.toString();
System.out.println("from server : " + message);
}finally{
// 用于释放缓存。避免内存溢出
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptionCaught method run...");
// cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
4. Netty中的粘包问题与解决方案
4.1 Netty中的粘包问题
分析Netty中可能出现的粘包问题。
4.2 Netty中的解决方案
介绍Netty提供的解决粘包问题的方案,如DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder、FixedLengthFrameDecoder等。
5. 注意事项与总结
5.1 注意事项
在处理粘包问题时需要注意的事项。
5.2 总结
总结解决粘包问题的方法及其优缺点,以及在实践中的应用。
通过本文的学习,读者可以更深入地了解Netty中的粘包问题及其解决方案,从而更好地应对实际开发中的网络通信挑战。