写出二叉树的非递归遍历很难么?这次让你不再害怕非递归!|二叉树的非递归遍历 | 二叉树的遍历迭代法 | 前序与中序_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
递归是可以用栈来模拟出来的
迭代法
前序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
}
return result;
}
};中序:
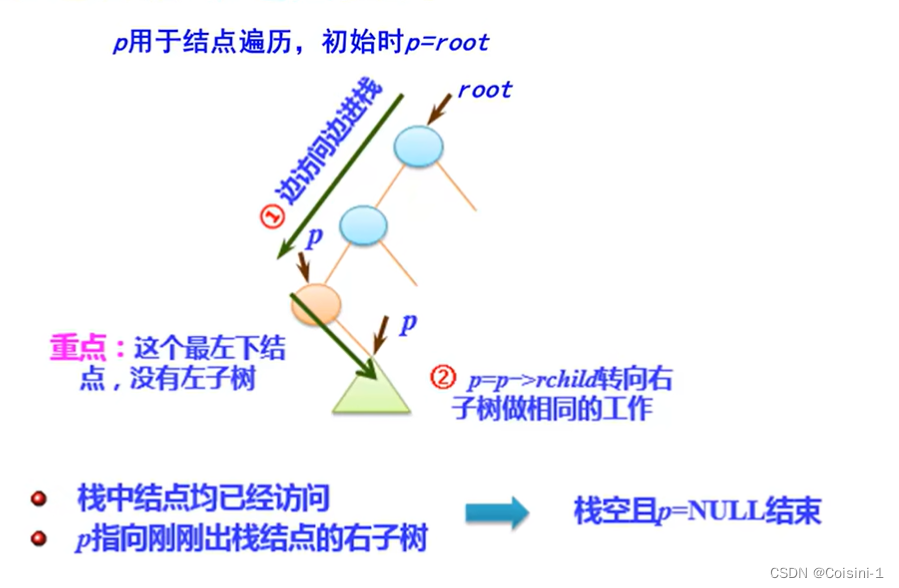
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top(); // 从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据)
st.pop();
result.push_back(cur->val); // 中
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
};后序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 相对于前序遍历,这更改一下入栈顺序 (空节点不入栈)
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 空节点不入栈
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 将结果反转之后就是左右中的顺序了
return result;
}
};
从思路到代码实现
前序和后序稍微改一下就能求得
访问和处理不同
写出二叉树的非递归遍历很难么?这次再带你写出中序遍历的迭代法!|二叉树的非递归遍历 | 二叉树的遍历迭代法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
思路看一下视频,我想也是好理解的。
二叉树的统一迭代法
前序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return result;
}
};中序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop(); // 将该节点弹出,避免重复操作,下面再将右中左节点添加到栈中
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 添加右节点(空节点不入栈)
st.push(node); // 添加中节点
st.push(NULL); // 中节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点做为标记。
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 添加左节点(空节点不入栈)
} else { // 只有遇到空节点的时候,才将下一个节点放进结果集
st.pop(); // 将空节点弹出
node = st.top(); // 重新取出栈中元素
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val); // 加入到结果集
}
}
return result;
}
};后序:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
}
}
return result;
}
};风格统一可能好记一点,但最重要的还是理解它实现的思路。
不过这个代码思路不是很好理解,还是之前的好理解一点。






















![[数据结构]堆](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/47805bcf9919453ab49088b86c448246.png)