目录
前言:
本篇我们来讲解数据结构中的顺序表和顺序表,因为Java有集合框架,所以可以直接使用类创建对象来完成。
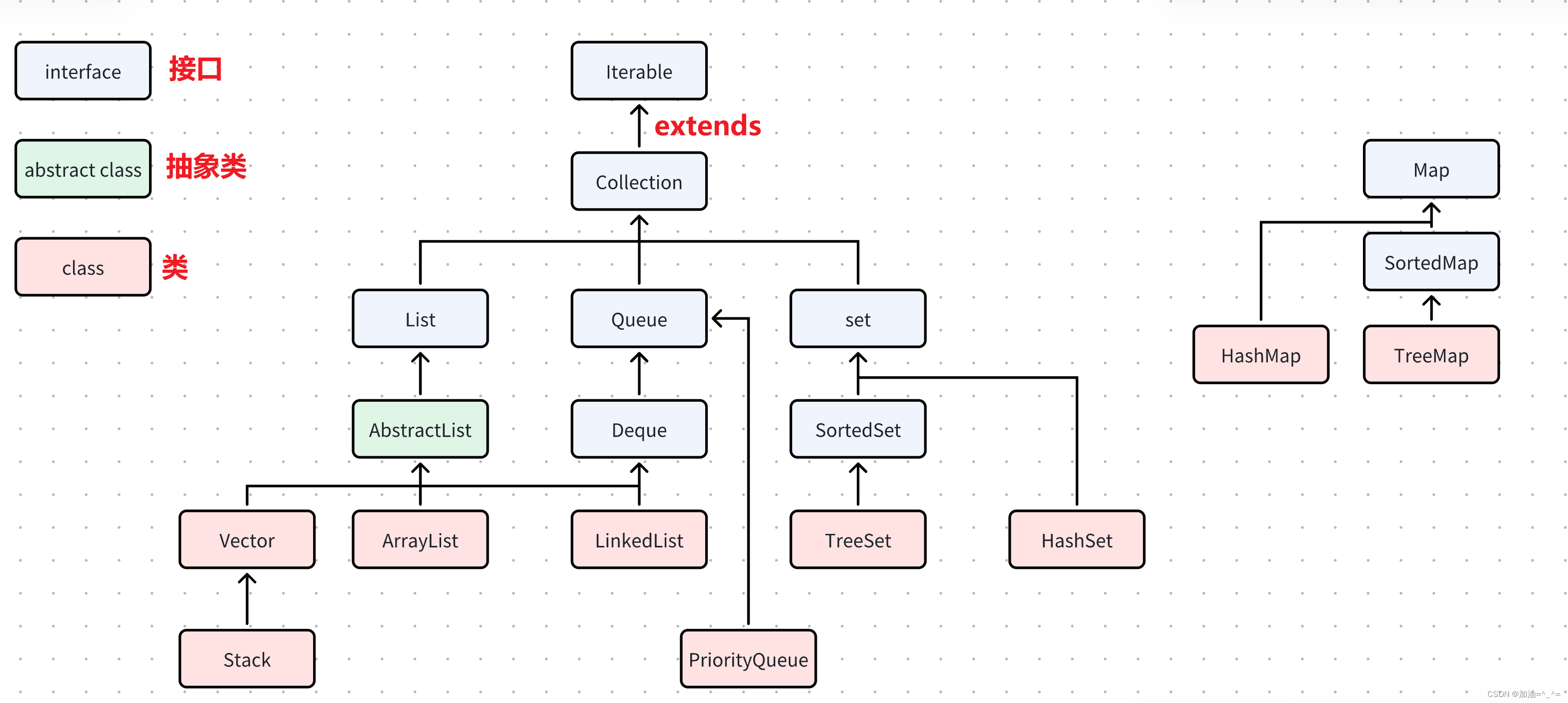
顺序表(ArrayList):
顺序表的原理:
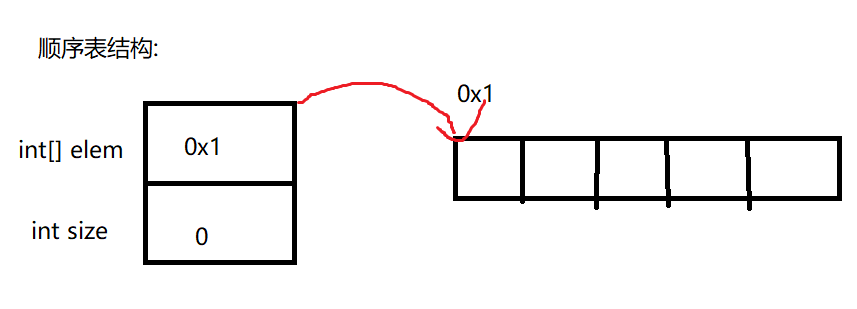
顾名思义,就是有顺序的表,类是ArrayList,底层原理是一个数组,当到达最大容量时,会进行扩容。
当一个数组(顺序表)中存放的基本类型数据时,我们想要全部清除可以直接将有效下标置为0,这样再添加就是覆盖的效果。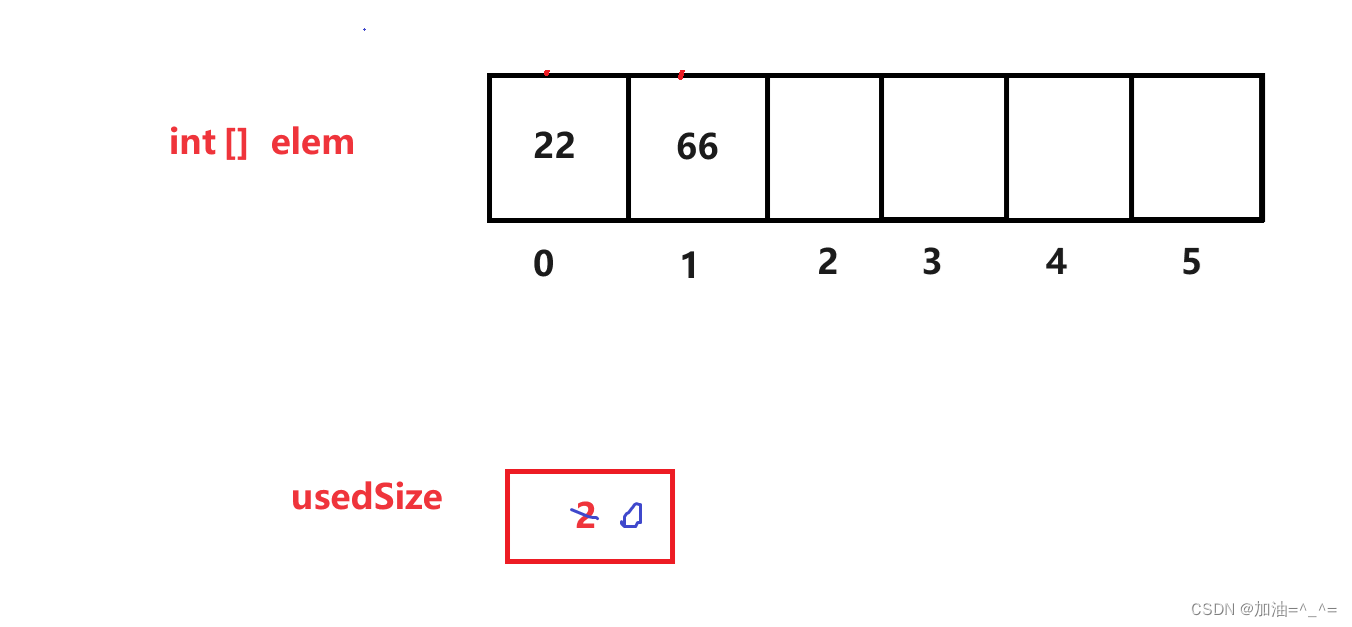
但是如果数组中存放的是引用类型,则不能这样。因为基本类型都会默认初始化,比如整形会默认初始化为0。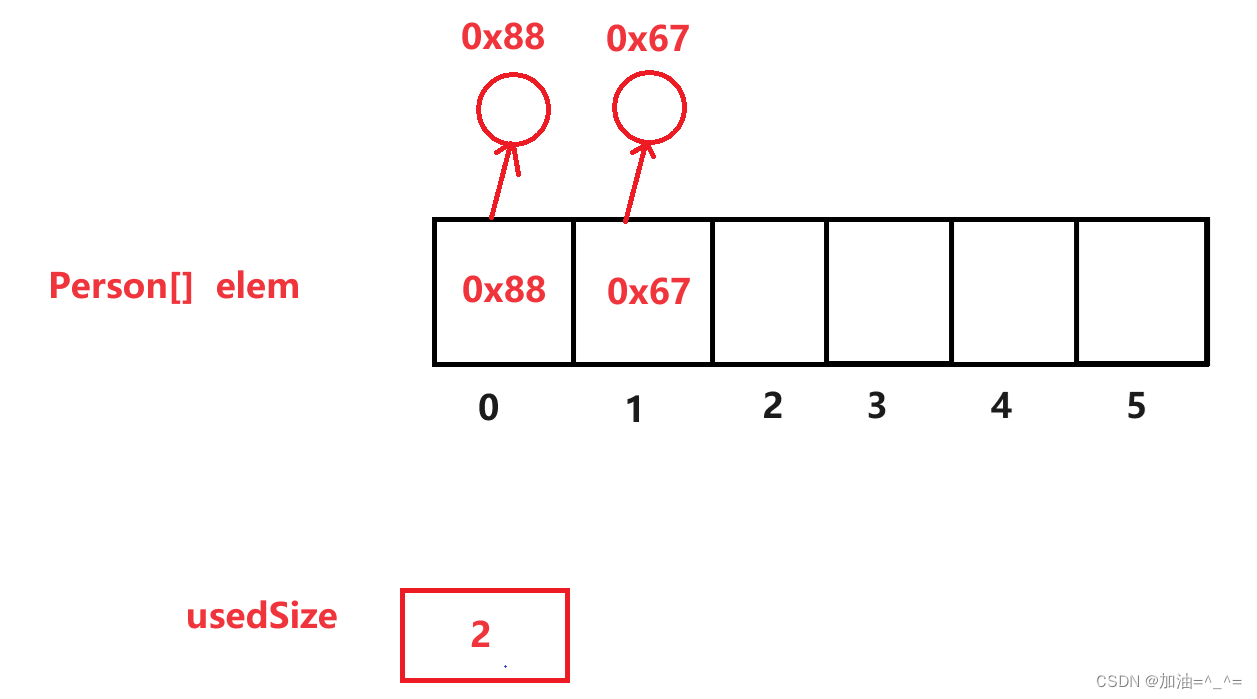
此时引用类型不能直接将有效下标置为0,否则会发生内存泄漏。 因为引用类型开辟的空间没有回收,JVM中,回收算法有很多。最好通过for循环来置空。
for() {
elem[i] = null;
}ArrayList源码:
接下来我们就来细致观察ArrayList源码: ArrayList底层就是顺序表,继承了AbstractList类,里面重写了toString方法。
ArrayList底层就是顺序表,继承了AbstractList类,里面重写了toString方法。
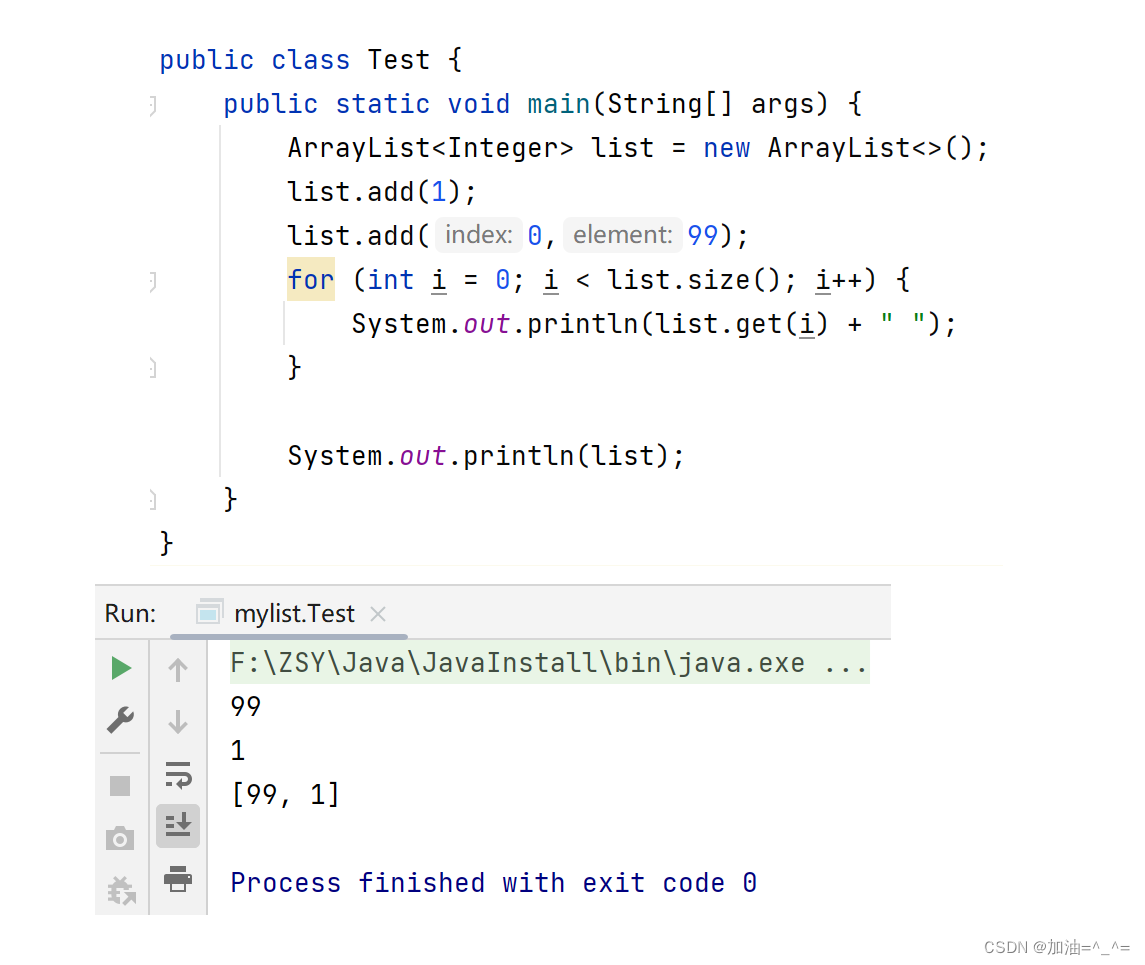
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(0,99);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println(list);
}
ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表。
我们再来看源码: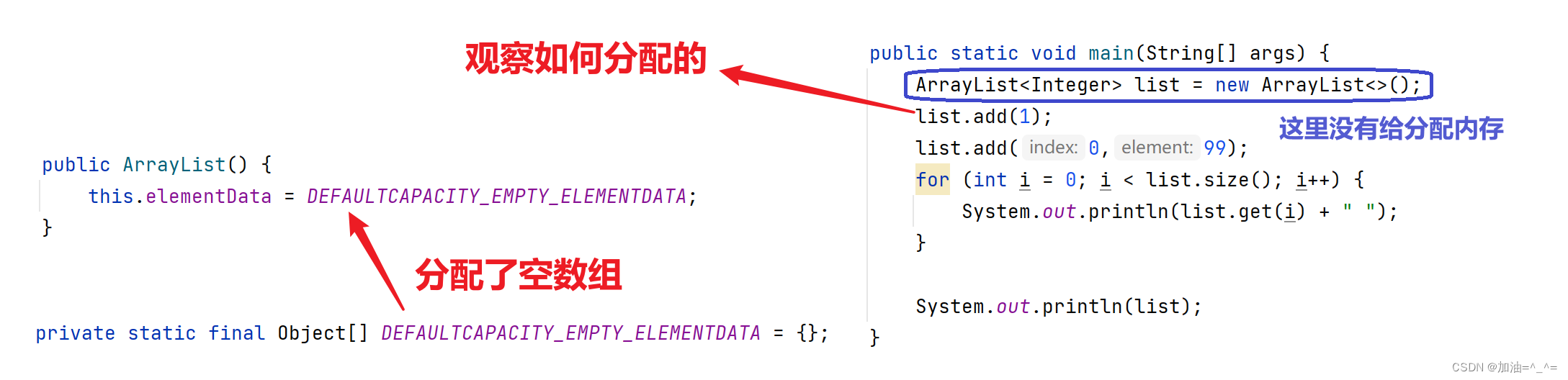

此时就分配了10个空间。 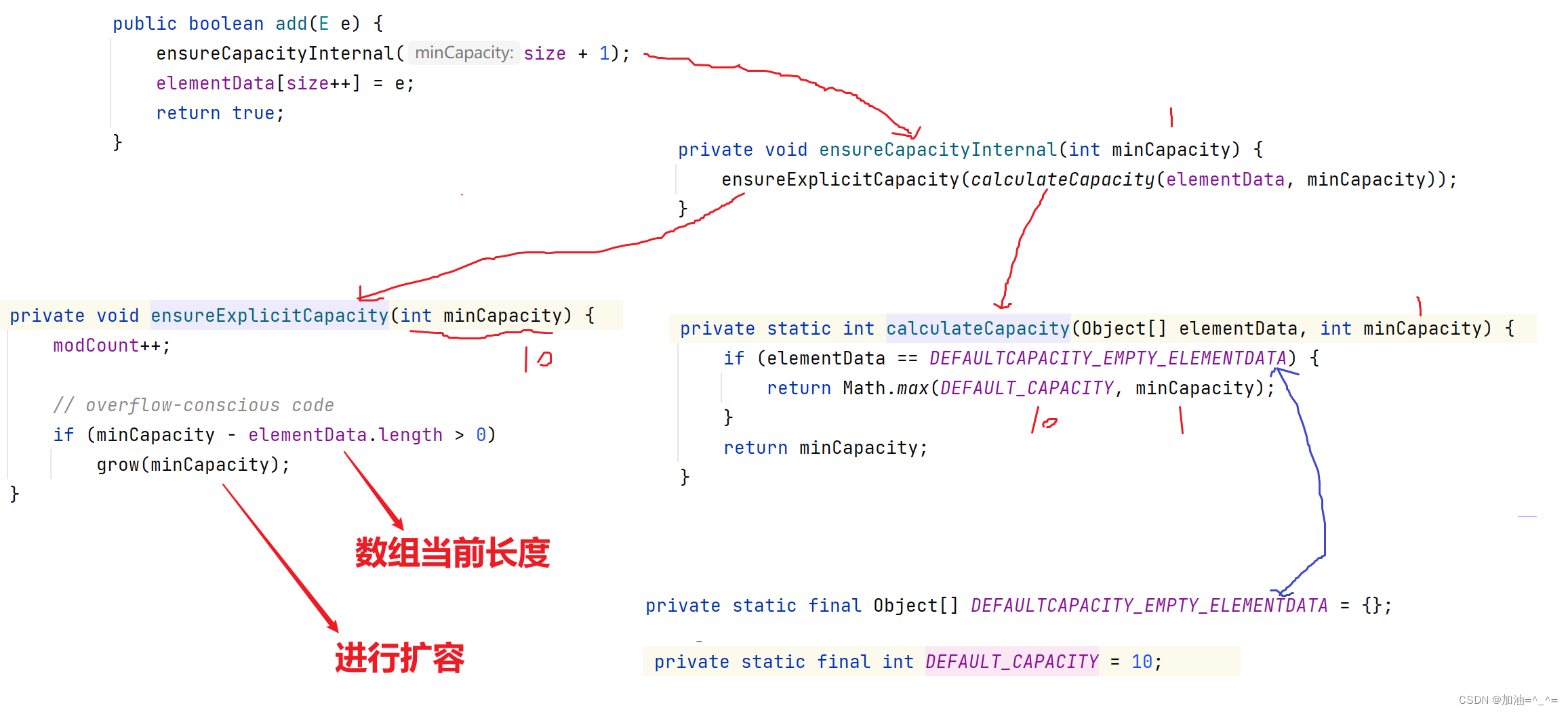
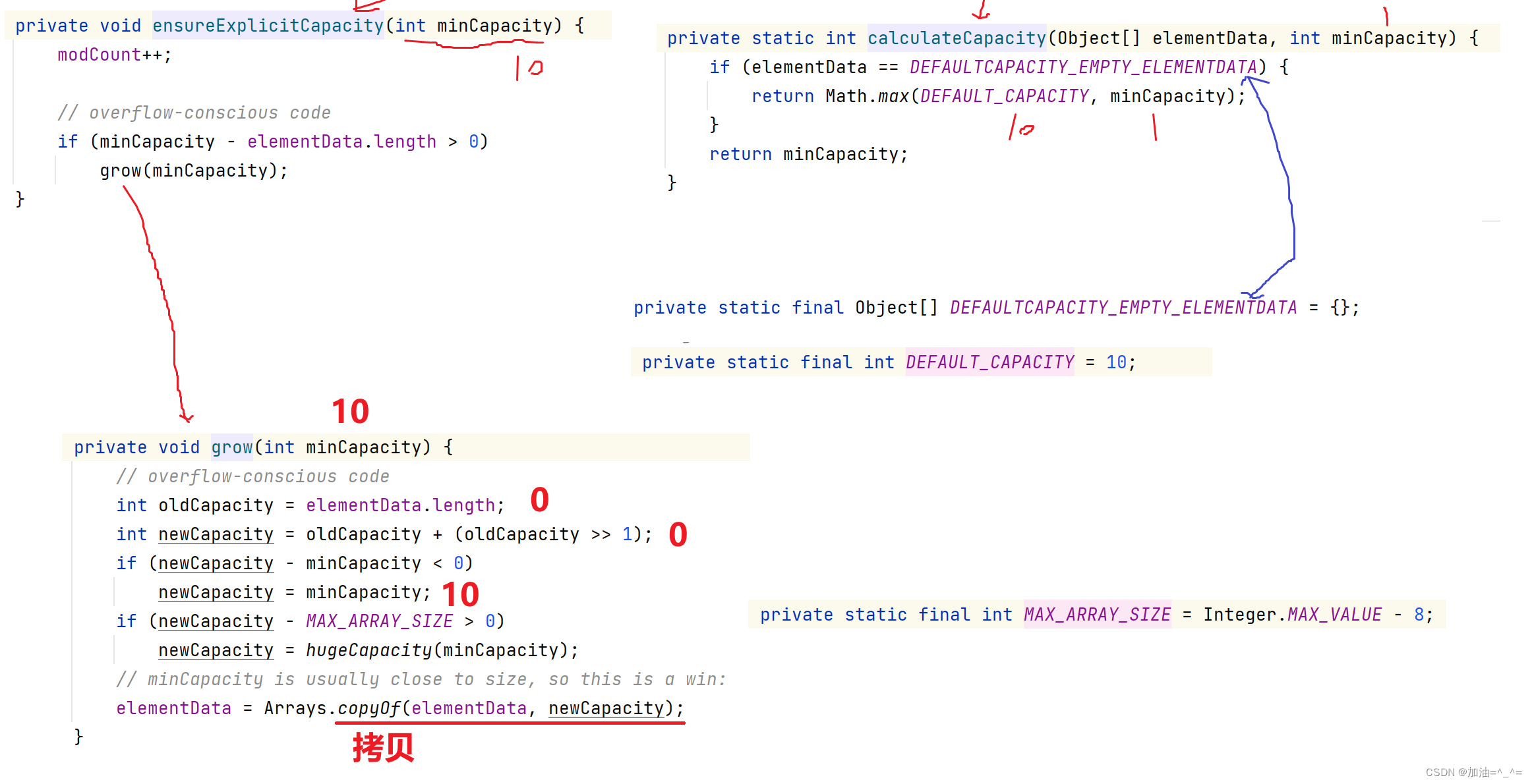 所以当使用无参构造器时,第一次添加元素是申请10个空间,之后每次到达上限以后就扩容1.5倍。
所以当使用无参构造器时,第一次添加元素是申请10个空间,之后每次到达上限以后就扩容1.5倍。
<? extends E>的含义:
因为ArrayList实现了Collection接口。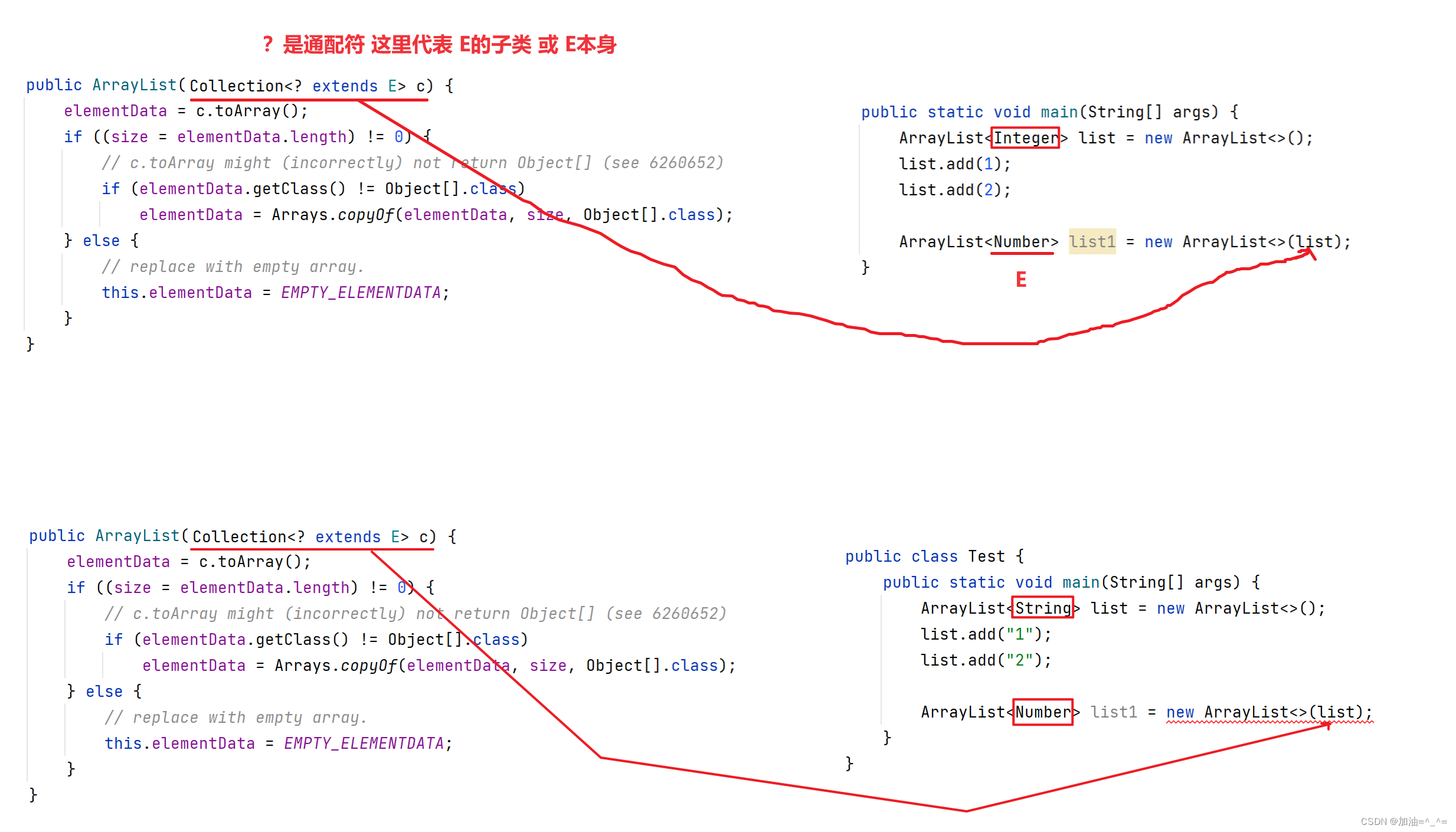

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
ArrayList<Number> list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);
list1.add(99);
list1.add(88);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}ArrayList的相关方法:

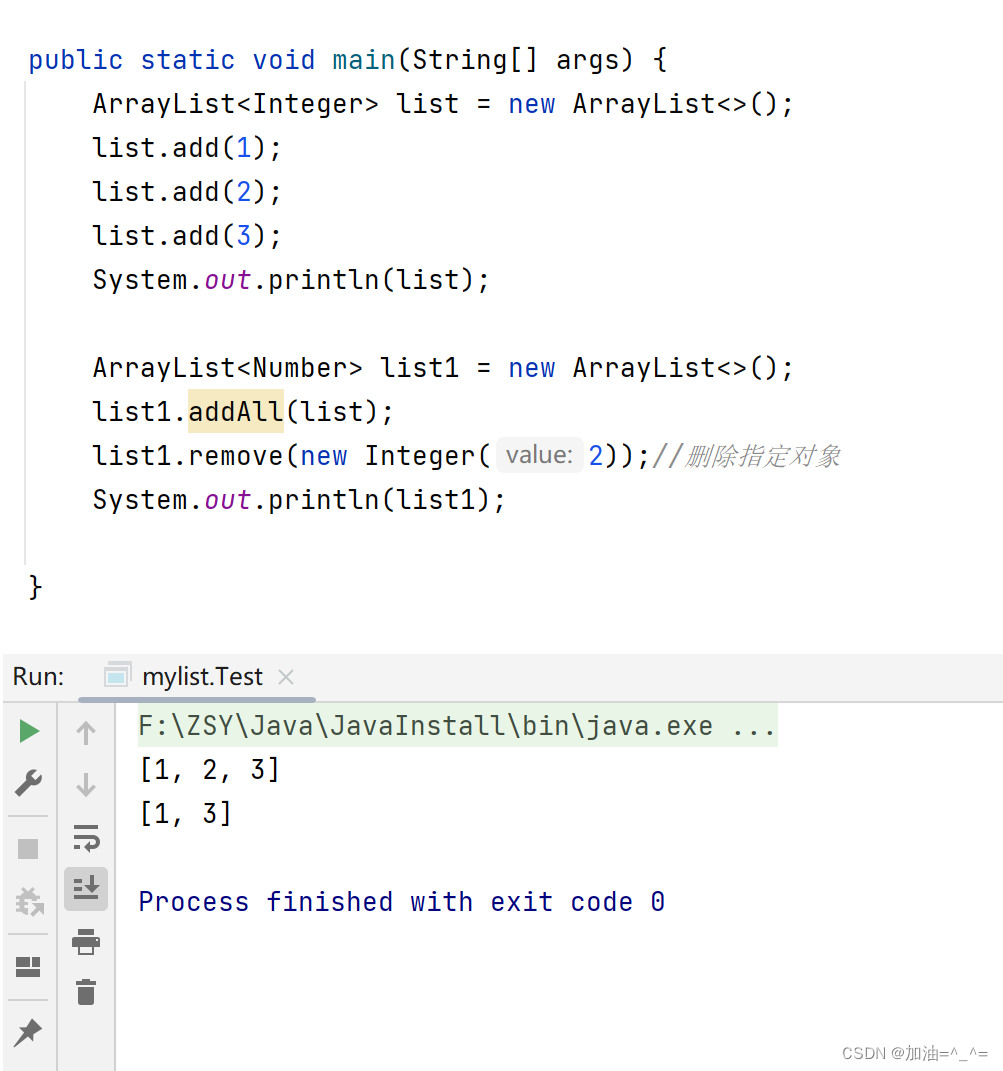
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
System.out.println(list);
ArrayList<Number> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.addAll(list);
list1.remove(new Integer(2));//删除指定对象
System.out.println(list1);
}
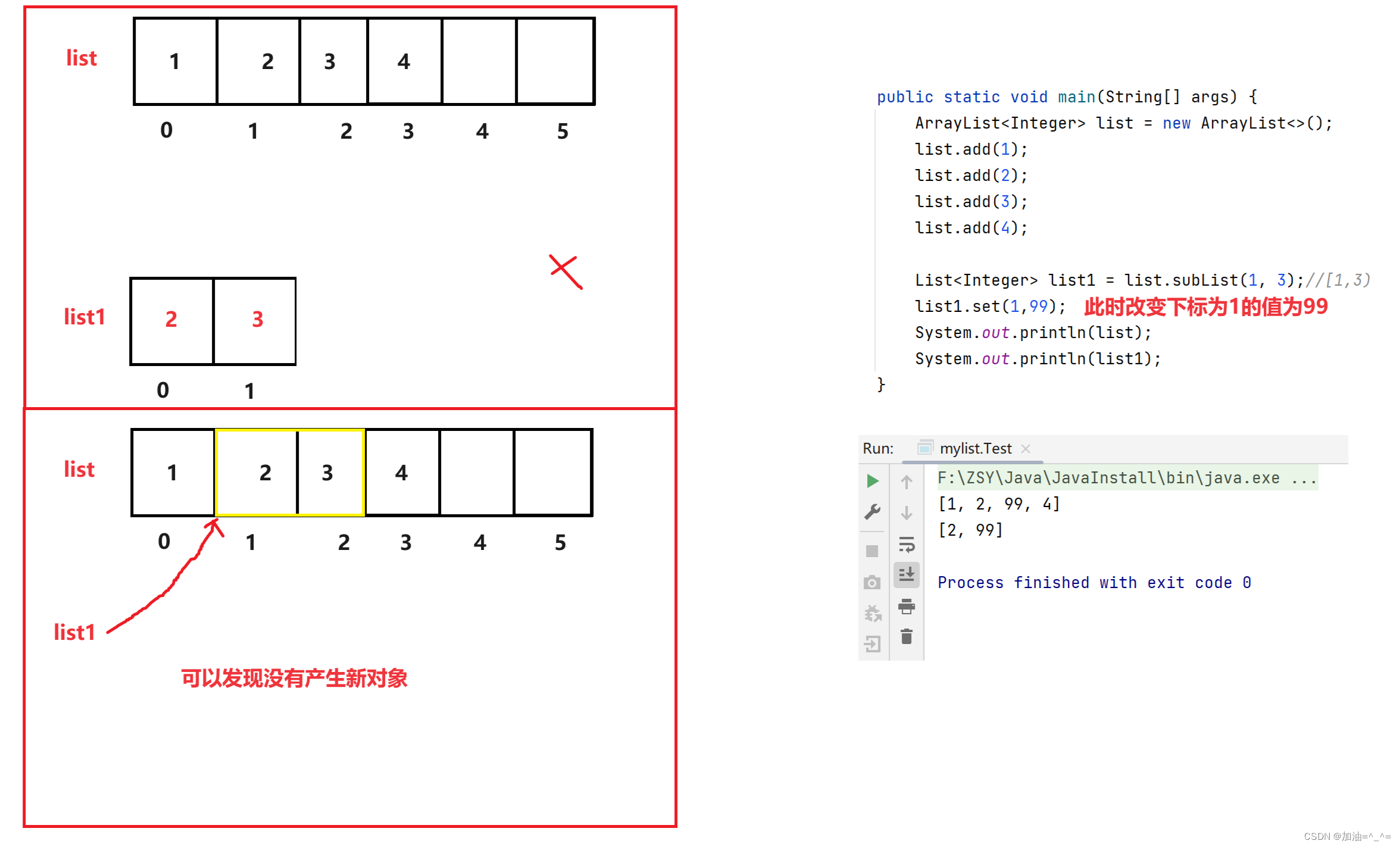
我们来观察一下代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
List<Integer> list1 = list.subList(1, 3);//[1,3)
list1.set(1,99);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list1);
}
向上转型List:
List<List<Integer>> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(new ArrayList<>());
list1.add(new ArrayList<>()); 观察这个代码,意思其实是有一个ArrayList类,每一个元素里面是一个ArrayList存放整形的引用类型(List是一个接口)。其实可以理解为二维数组。
练习题(杨辉三角):
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
ret.add(list);
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
cur.add(1);
//获取上一行
List<Integer> prev = ret.get(i - 1);
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
int val = prev.get(j) + prev.get(j - 1);
cur.add(val);
}
//将此行最后一个元素置为1
cur.add(1);
ret.add(cur);
}
return ret;
}
}扑克牌游戏:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CardDome cardDome = new CardDome();
List<Card> cardList = cardDome.buyCard();
System.out.println("买的牌如下:");
System.out.println(cardList);
System.out.println("洗牌");
cardDome.shuffle(cardList);
System.out.println(cardList);
System.out.println("揭牌:");
cardDome.getCards(cardList);
}
}public class CardDome {
//定义四种花色
private static final String[] suits = {"♥","♣","♦","♠"};
//52张
//J - 11 Q - 12 K - 13
//买一副牌
public List<Card> buyCard() {
List<Card> cardList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
Card card = new Card(suits[i], j);
cardList.add(card);
}
}
return cardList;
}
//洗牌
public void shuffle(List<Card> cardList) {
//生成随机数
Random random = new Random();
//从后向前打乱
for (int i = cardList.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
//有52张牌
//第一次生成的就是 0 - 50 的随机数
int index = random.nextInt(i);
//index i 交换
swap(cardList, i, index);
}
}
private void swap(List<Card> cardList, int e1,int e2) {
Card tmp = cardList.get(e1);
cardList.set(e1,cardList.get(e2));
cardList.set(e2,tmp);
}
//揭牌
public void getCards (List<Card> cardList) {
//3个人
List<Card> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> hand = new ArrayList<>();
hand.add(hand1);
hand.add(hand2);
hand.add(hand3);
//3个人轮流抓牌5张牌
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//j 代表人
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cardList.remove(0);
hand.get(j).add(card);
}
}
System.out.println("第一个人揭牌如下:");
System.out.println(hand1);
System.out.println("第二个人揭牌如下:");
System.out.println(hand2);
System.out.println("第三个人揭牌如下:");
System.out.println(hand3);
System.out.println("剩下的牌:");
System.out.println(cardList);
}
}public class Card {
private String suit;//花色
private int rank;//数字
public Card(String suit, int rank) {
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
public String getSuit() {
return suit;
}
public void setSuit(String suit) {
this.suit = suit;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return suit + ":" + rank + " ";
}
}链表(LinkedList):
链表的原理:
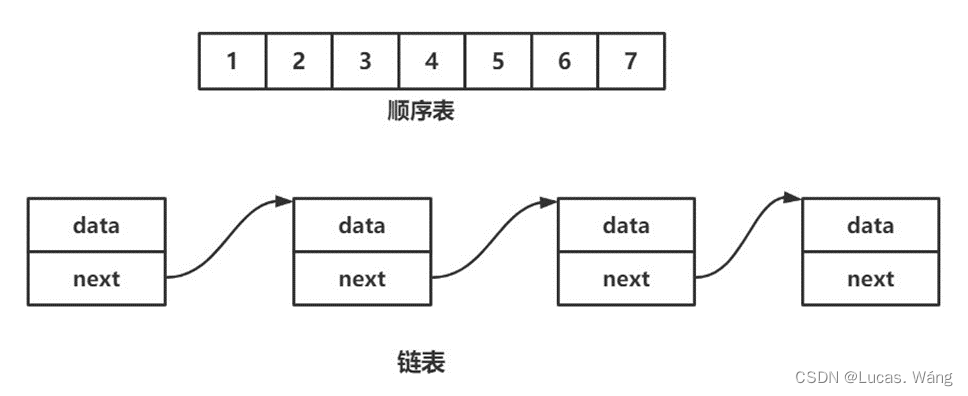
顺序表还是有缺点的,因为每次都是1.5倍扩容,所以有时量大时就会浪费内存,所以就衍生出了链表,不是连续内存,如果了解C语言中的链表,那么将是易如反掌。
自定义链表的实现:
我们定义head成员,是为了保存头结点。
public class MySingleList {
//节点使用内部类来写
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
//定义一个链表的成员的头结点
public ListNode head;
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(33);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(99);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(67);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(88);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}
}LinkedList源码:

LinkedList的底层代码,可以发现这就是一个双向循环链表。 LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素师效率比较高,时间复杂度为O(1),比较适合任意位置插入的场景。
还有很多方法无法注意介绍,大家可以看Structure里面的所有相关方法、属性和内部类。因为效率高,所以底层只使用了双向链表,没有使用单向链表。
LinkedList使用注意事项:
当我们使用的是自定义链表时(就是没用Java框架),清空链表,可以直接将头尾置空,也可以逐个将其置空。因为Java有回收算法。
这里我们使用迭代器进行遍历,我们也可以反向遍历:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
System.out.println(linkedList);
//通过迭代器遍历链表
ListIterator<Integer> it1 = linkedList.listIterator();
while (it1.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it1.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===反向===");
ListIterator<Integer> it2 = linkedList.listIterator(linkedList.size());
while (it2.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(it2.previous() + " ");
}
}
}
练习题(判断是否是会问链表):
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
// write code here
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//翻转slow以后的链表
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode nextPos = cur.next;
//翻转(利用指针翻转)
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = nextPos;
}
//从前向后 从后向前
while(head != slow) {
if (slow.val != head.val) {
return false;
}
if (head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}迭代器(Iterator):
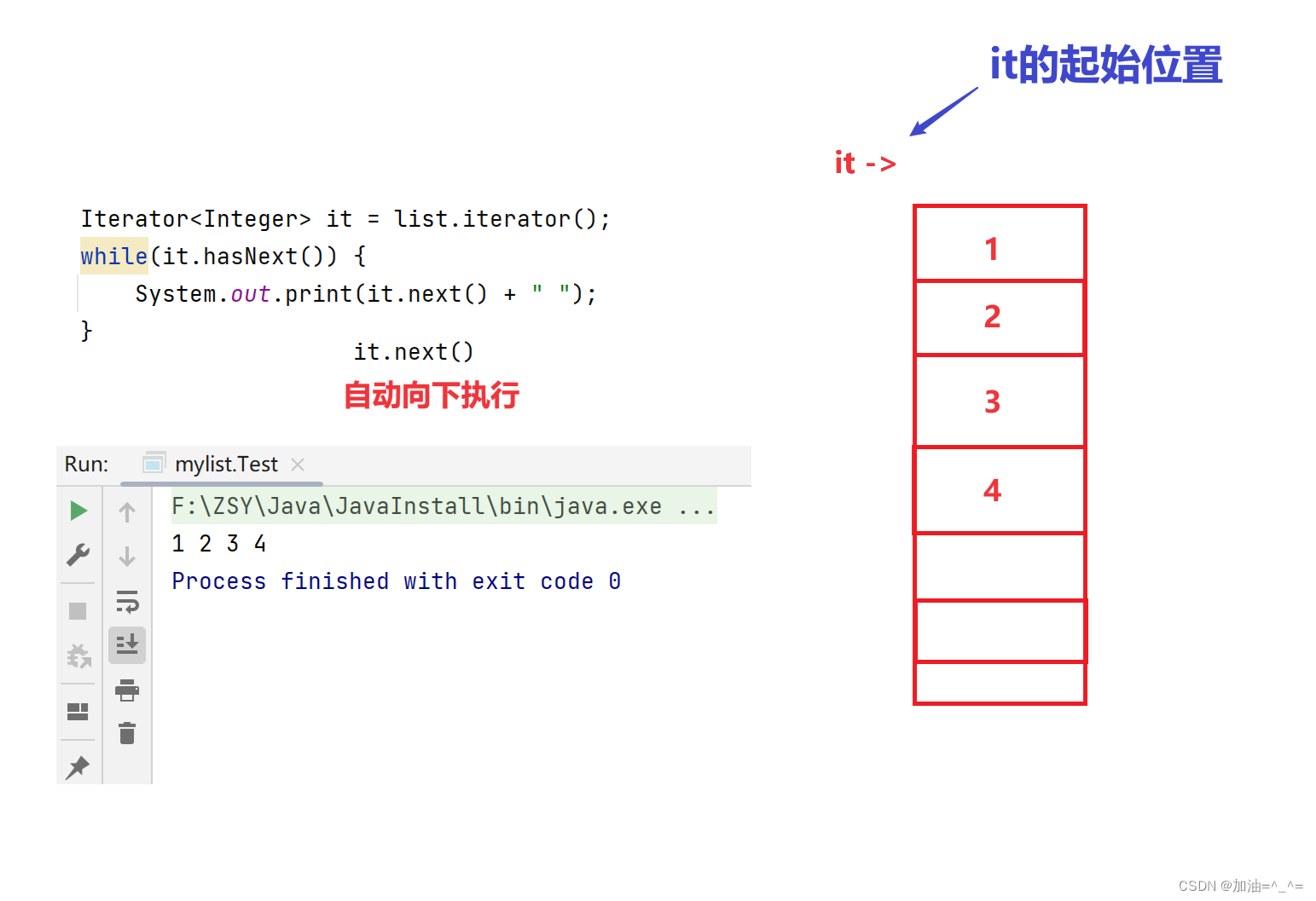
我们可以利用迭代器进行遍历:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
}
总结:
这里我还是默认各位都有基础,希望可以对有基础的人有些帮助(更多的是记笔记),感谢各位支持。






























![[职场] 面试被问优点的回答参考 #知识分享#其他#学习方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/835c9793d3a4fe95191548cd5e642b02.jpeg)