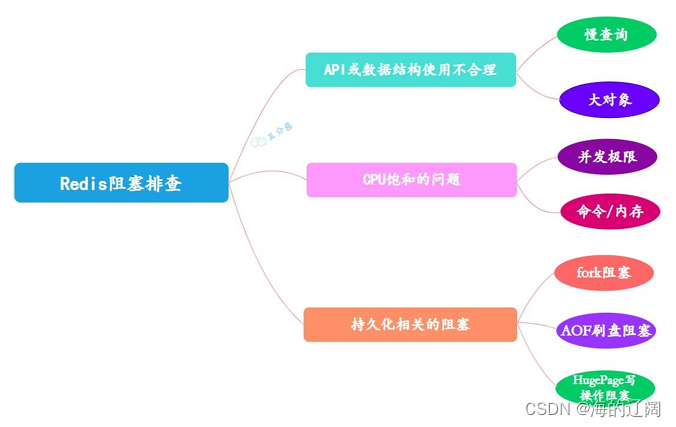
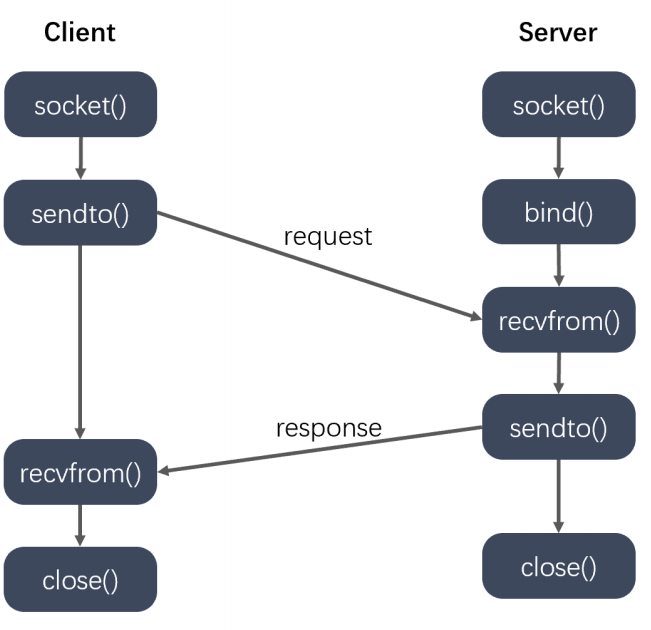
字符型数组
定义
char c[10];
初始化
char s[10] = "Hello";
字符型数组末尾会添加一个不可见的字符‘\0’,作为结束的标志;
“ABC1234\n” 这个字符串共9个字符;
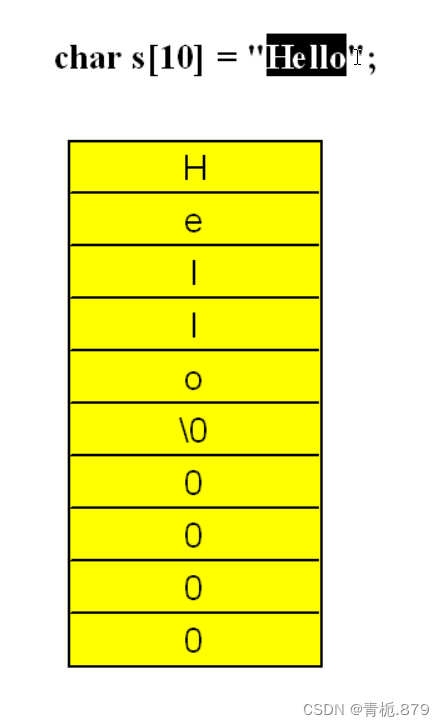
至少需要六个字节(六个格子,多余的格子可以是0或者‘\0’,都一样)
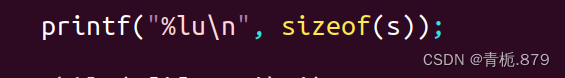
查看占用多少个字节
函数的调用
1.putchar()函数
打印单个字符
例题:打印”Hello“
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
char s[10] = "Hello";
while(s[i] != '\0')
{
putchar(s[i]);
++i;
}
return 0;
}2.puts()函数输出
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[10] = "Hello";
int i = 0;
puts(s);
}3.gets函数输入
调用gets函数、scanf函数(使用时注意越界访问)
scanf函数,输入字符串时不能有 回车和tab
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[10];
gets(s);
puts(s);
return 0;
}4.fgets函数输入
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[10];
fgets(s,sizeof(s),stdin);
puts(s);
return 0;
}5.strlen 求有效字符的个数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s[100] = "Hello";
unsigned long size;
size = strlen(s);
printf("%lu\n",size);
}6.strcpy
把 数组s1的字符串拷贝到s2中
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100];
strcpy(s2,s1);
puts(s2);
return 0;
}7.strcat
字符串的拼接操作 s1是目标,s2是源
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100] = "World";
strcat(s1,s2);
puts(s1);
return 0;
}8.strcmp 排序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100] = "He";
printf("%d\n",strcmp(s1,s2));
return 0;
}逆序
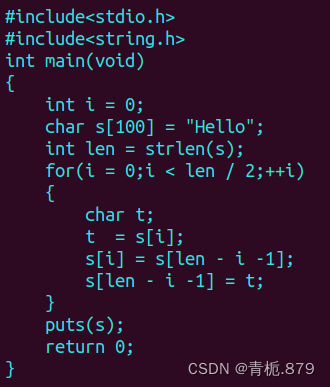
例题
1.小写字母转换成大写字母,大写字母不变

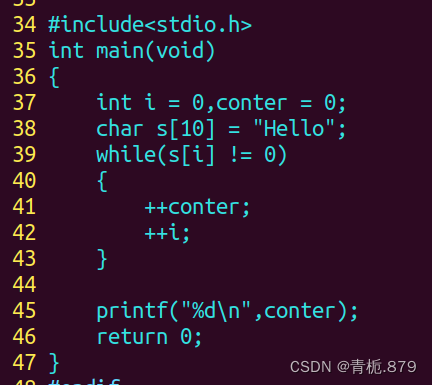
2.统计字符串中有效字符个数
3.将数组s1拷贝到s2中
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void)
{
char s1[100] = "Hello";
char s2[100];
int i = 0;
while(s1[i] != '\0')
{
s2[i] = s1[i];
++i;
}
s2[i] = '\0';
puts(s2);
return 0;
}4.字符串的拼接操作

5.排序

6.比较s1 s2

注意:

int 型 4个字节
字符型 一个字节 ascii码为 48
字符型 ascii码为 0
字符串 const char* 字符串常量 2个字节
二维数组的定义和引用
整型二维数组
定义
类型说明符 数组名[常量表达式][常量表达式]
[ ] 类型说明符
int [3] [4]; 是一个三行四列的数组,行/列号都是从0开始;
可以看成是三个一维数组,a[0] 、a[1]、a[2]
二维数组的本质:数组的数组
数组的特性
单一性、有序性、连续性
对数组的赋值

初始化
int a[3][4] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};二维数组省略
只能省略靠近变量名的一个
int a[][4] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};确定数组的行数和列数
int rows = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); //行数
int cols = sizeof(a[0]) / sizeof(a[0][0]); //列数