MyBatis,这个数据持久化的魔法师,以其优雅的SQL映射和简洁的配置文件,为我们呈现出一场CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete)的奇妙之旅。在这篇博客中,我们将深入探讨MyBatis中的增、删、改、查操作,揭示其中的神秘面纱。
数据之美的前奏
在开始我们的CRUD之旅之前,让我们先欣赏一下数据之美的前奏,也就是如何配置和使用MyBatis。首先,我们需要一个简单的实体类User。
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
}
接下来,我们需要为User类编写一个Mapper映射文件UserMapper.xml,定义与User实体类相关的SQL语句。
<!-- UserMapper.xml -->
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="UserResultMap" type="com.example.model.User">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="username" column="username" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.example.model.User">
INSERT INTO user (username, password) VALUES (#{username}, #{password})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.example.model.User">
UPDATE user SET username = #{username}, password = #{password} WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
DELETE FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
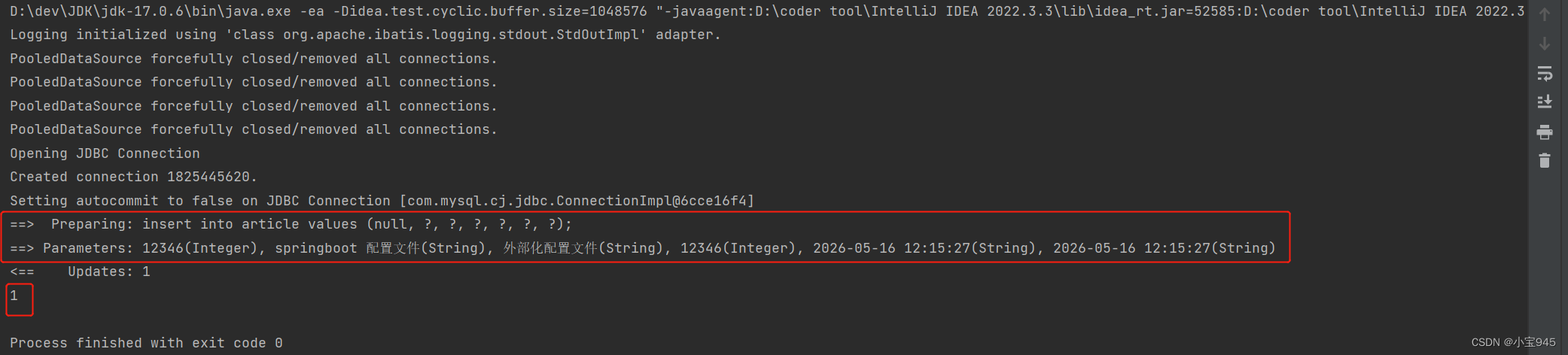
这个Mapper映射文件包含了四个SQL语句,分别对应CRUD的四个操作:查询、插入、更新、删除。接下来,让我们通过代码演示如何使用这些SQL语句进行CRUD操作。
查询之美:Read
查询是CRUD中最常见的操作,也是数据之美的起点。让我们通过MyBatis的select语句,查询用户信息。
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyBatisReadMagic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 读取MyBatis配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 执行查询操作
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.example.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById", 1);
// 打印查询结果
System.out.println("User ID: " + user.getId());
System.out.println("Username: " + user.getUsername());
System.out.println("Password: " + user.getPassword());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码首先读取MyBatis配置文件,创建SqlSessionFactory,然后通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession。接着,我们执行了一个查询操作,使用selectOne方法查询ID为1的用户信息。最后,打印查询结果。
插入之美:Create
插入操作是CRUD中的“C”(Create),用于向数据库中新增数据。MyBatis通过insert语句来实现插入操作。
public class MyBatisCreateMagic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个新用户对象
User newUser = new User();
newUser.setUsername("Alice");
newUser.setPassword("new_password");
// 读取MyBatis配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 执行插入操作
int affectedRows = sqlSession.insert("com.example.mapper.UserMapper.insertUser", newUser);
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// 打印插入结果
System.out.println("Inserted new user. Affected rows: " + affectedRows);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码中,我们首先创建了一个新的User对象,设置了用户名和密码。然后,通过MyBatis的insert语句将这个新用户插入到数据库中。最后,通过commit方法提交事务。
更新之美:Update
更新操作是CRUD中的“U”(Update),用于修改数据库中的数据。MyBatis通过update语句来实现更新操作。
public class MyBatisUpdateMagic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个待更新的用户对象
User updateUser = new User();
updateUser.setId(1); // 假设要更新ID为1的用户信息
updateUser.setUsername("UpdatedAlice");
updateUser.setPassword("updated_password");
// 读取MyBatis配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 执行更新操作
int affectedRows = sqlSession.update("com.example.mapper.UserMapper.updateUser", updateUser);
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// 打印更新结果
System.out.println("Updated user. Affected rows: " + affectedRows);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码中,我们创建了一个待更新的User对象,设置了新的用户名和密码。然后,通过MyBatis的update语句将这个用户对象的信息更新到数据库中。最后,通过commit方法提交事务。
删除之美:Delete
删除操作是CRUD中的“D”(Delete),用于从数据库中删除数据。MyBatis通过delete语句来实现删除操作。
public class MyBatisDeleteMagic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 待删除用户的ID
Long userIdToDelete = 1L; // 假设要删除ID为1的用户信息
// 读取MyBatis配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 执行删除操作
int affectedRows = sqlSession.delete("com.example.mapper.UserMapper.deleteUser", userIdToDelete);
// 提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
// 打印删除结果
System.out.println("Deleted user. Affected rows: " + affectedRows);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这段代码中,我们指定了要删除的用户的ID,然后通过MyBatis的delete语句将该用户从数据库中删除。最后,通过commit方法提交事务。
小结:CRUD的魔法之旅
通过MyBatis的增、删、改、查四个操作,我们深入探索了数据之美的奇妙之旅。MyBatis通过简洁的配置文件和直观的SQL映射,让CRUD操作变得如此优雅。无论是查询、插入、更新还是删除,MyBatis都以其独特的方式为我们展现了数据之美的不同层面。
在这场奇妙的CRUD之旅中,MyBatis是我们的向导,SQL语句是我们的咒语,数据库是我们的舞台。希望通过这篇博客,你能感受到MyBatis中CRUD操作的奇妙之处,为你的数据操作带来更多灵感和理解。让我们继续探索数据之美的未知领域,一起在编码的世界中畅游。
| 作者信息 作者 : 繁依Fanyi CSDN: https://techfanyi.blog.csdn.net 掘金:https://juejin.cn/user/4154386571867191 |