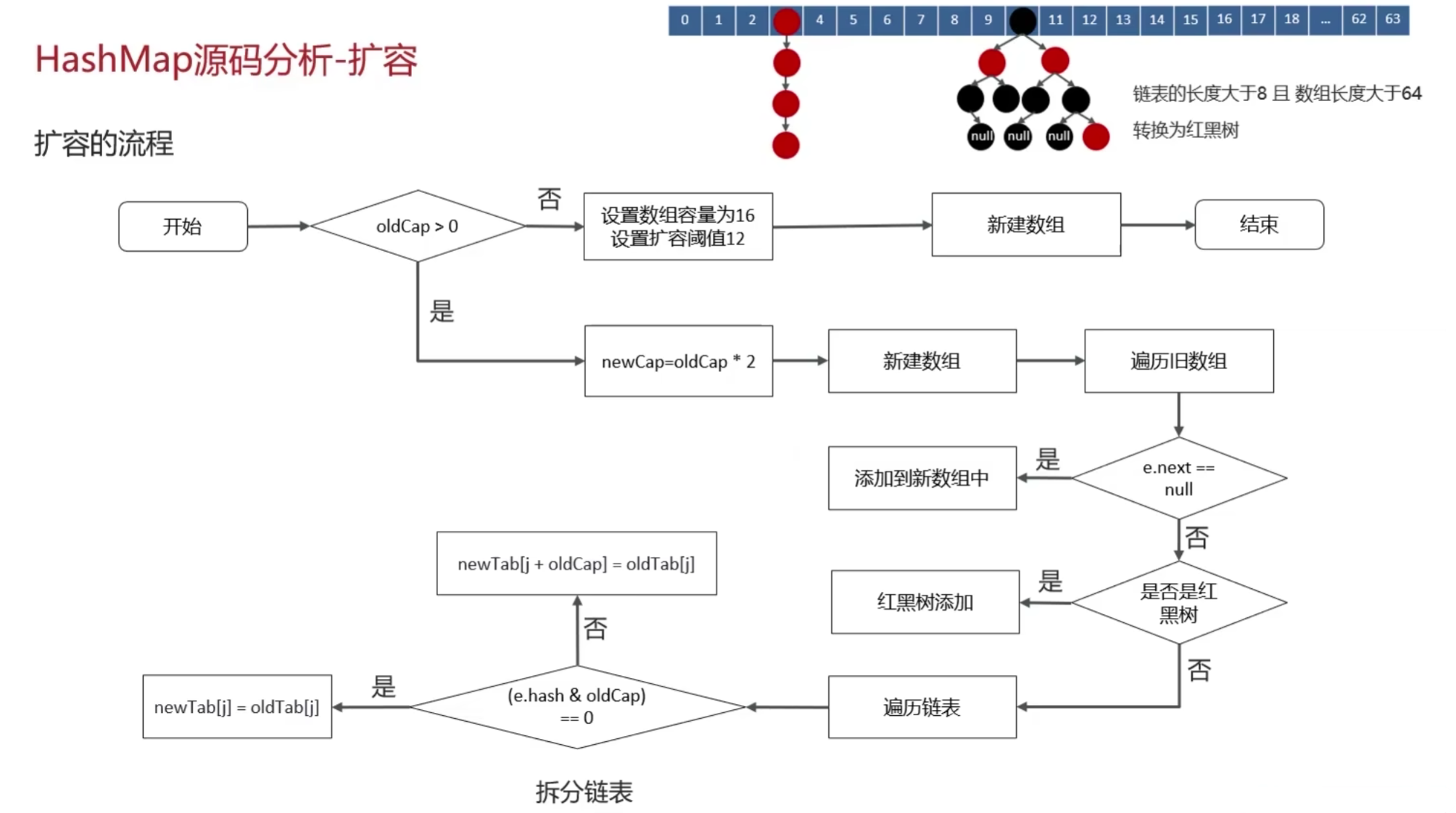
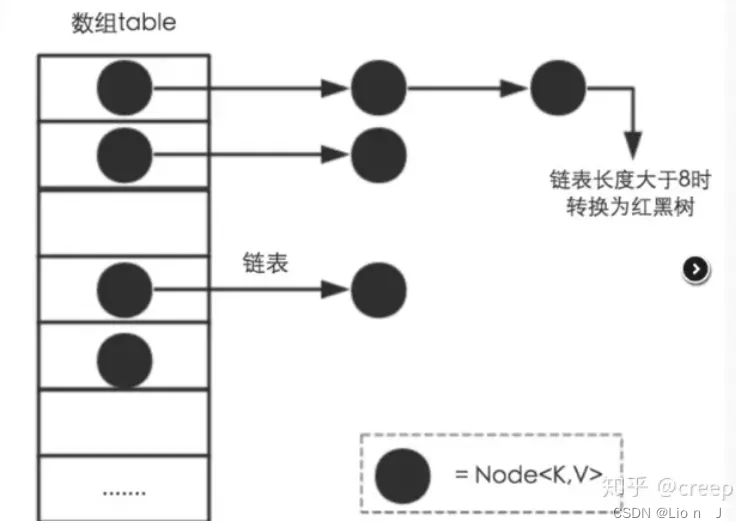
1、今天学了什么
(1)HashMap resize()方法
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//获取了原容量,如果哈希表为null则返回0,否则返回原长度
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//获取原来的扩容阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
//定义两个变量保存新的容量和阈值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//如果原容量长度大于0
if (oldCap > 0) {
//如果原容量大于最大容量,直接返回原哈希表,不在扩容
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//扩容阈值设置为Integer的最大值
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//将原容量扩大两倍
//如果新容量小于最大容量,并且原容量大于等于默认容量
//将扩容的阈值扩大两倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
//使用HashMap无参构造创建对象后,第一次扩容,会执行到此处
//容量赋值为初始容量
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
//计算扩容阈值
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
//调用HashMap有参构造指定了容量和负载因子后第一次扩容时会执行到次数
if (newThr == 0) {
//指定了容量和负载因子后,计算扩容原值
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
//如果原hash表不为null
if (oldTab != null) {
//遍历hash表
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
//如果某个位置上有元素
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
//如果这个位置上只是一个Node,没有链表
if (e.next == null)
//计算在新哈希表中的位置
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//如果该位置处是树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
//如果不是树,则复制该出的链表
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
/**
源码分析 */ public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student,String> map = new HashMap<>(); Student s1 = new Student(); Student s2 = new Student(); Student s3 = new Student(); Student s4 = new Student(); Student s5 = new Student(); Student s6 = new Student(); Student s7 = new Student(); Student s8 = new Student(); Student s9 = new Student(); Student s10 = new Student(); Student s11 = new Student(); map.put(s1,"胡卫东"); map.put(s2,"巩晓彬"); map.put(s3,"张卫平"); map.put(s4,"宋小波"); map.put(s5,"宋军"); map.put(s6,"姚明"); map.put(s7,"王治郅");//key为s7时 bincount为6 size为7 map.put(s8,"易建联");//key为s8时 数组长度为16 map.put(s9,"朱芳雨");//key为s9时 进入方法binTree 第一次扩容 16->32 map.put(s10,"杜锋");//key为s10时 第二次扩容 32-64 map.put(s11,"李楠");//该节点添加成功后,转换为红黑树 System.out.println(map.get(s10));
} }
(2)HashMap get(Object key)方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//判断哈希表不为null,并且长度大于0,并且计算出索引处不为null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//如果传入的key和计算出位置处的节点hash相等,并且key相等
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//代码执行到这里,说明传入的key和该位置上的节点key,hash相等,但是key不相等
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//判断该节点后面是否有元素
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
//如果该位置处是红黑树,则从树种查找
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//如果代码执行到此处,说明该位置处是链表
do {
//如果链表中某个节点的hash和传入的key的相等,并且key也相等,则返回该节点的值
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
(3)HashMap remove(Object key)方法
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
//如果hash表不为null,且长度大于0,并且该位置上有元素,如果没有元素则返回null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//如果hash相等, 并且key相等,则获取该节点
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
//代码执行到这里,说明key的hash相等,但是key不相等
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
//判断该结点是否有后置节点(其实就是判断这个位置上是树链表)
//如果是树
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//从树中获取该节点
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
//遍历链表
do {
//如果链表中某个节点和传入的key hash相等且key也相等,则从链表中移除
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//如果上述的节点不为null
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
(4)HashMap和Hashtable的区别:
Hashtable 是一个线程安全的 Map接口实现,但 HashMap 是线程不安全的实现,所以 HashMap 比 Hashtable 的性能高一点;但如果有多个线程访问同一个 Map 对象时,使用 Hashtable 实现类会更好。 Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value,如果试图把 null 值放进 Hashtable 中,将会引发 NullPointerException 异常; 但 HashMap 可以使用 null 作为 key 或 value。 HashMap数组初始长度为16,扩容后长度是原长度的2倍,Hashtable初始长度为11,扩容后的长度是原长度的2n+1
public class MapDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(null,null);
map.put(null,"111");
map.put("1",null);
map.put("2",null);
System.out.println(map.get("2"));
// hashTable不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value // Map<String,String> hashTable = new Hashtable<>(); // hashTable.put("111",null);
}
}
(5)LinkedHashMap
HashMap也有一个LinkedHashMap子类; LinkedHashMap 也使用双向链表来维护 key-value 对的次序(其实只需要考虑 key 的次序),该链表负责维护 Map 的迭代顺序,迭代顺序与 key-value 对的插入顺序保持一致。
(6)使用Properties读写文件
Properties 类是 Hashtable 类的子类,该对象在处理属性文件时特别方便(Windows 操作平台上的 ini 文件就是一种属性文件)。 Properties 类可以把 Map 对象和属性文件关联起来,从而可以把Map 对象中的 key-value 对写入属性文件中,也可以把属性文件中的"属性名=属性值"加载到 Map 对象中。 由于属性文件里的属性名、属性值只能是字符串类型,所以 Properties 里的 key、 value 都是字符串类型。该类提供了如下三个方法来修改 Properties 里的 key、value 值。