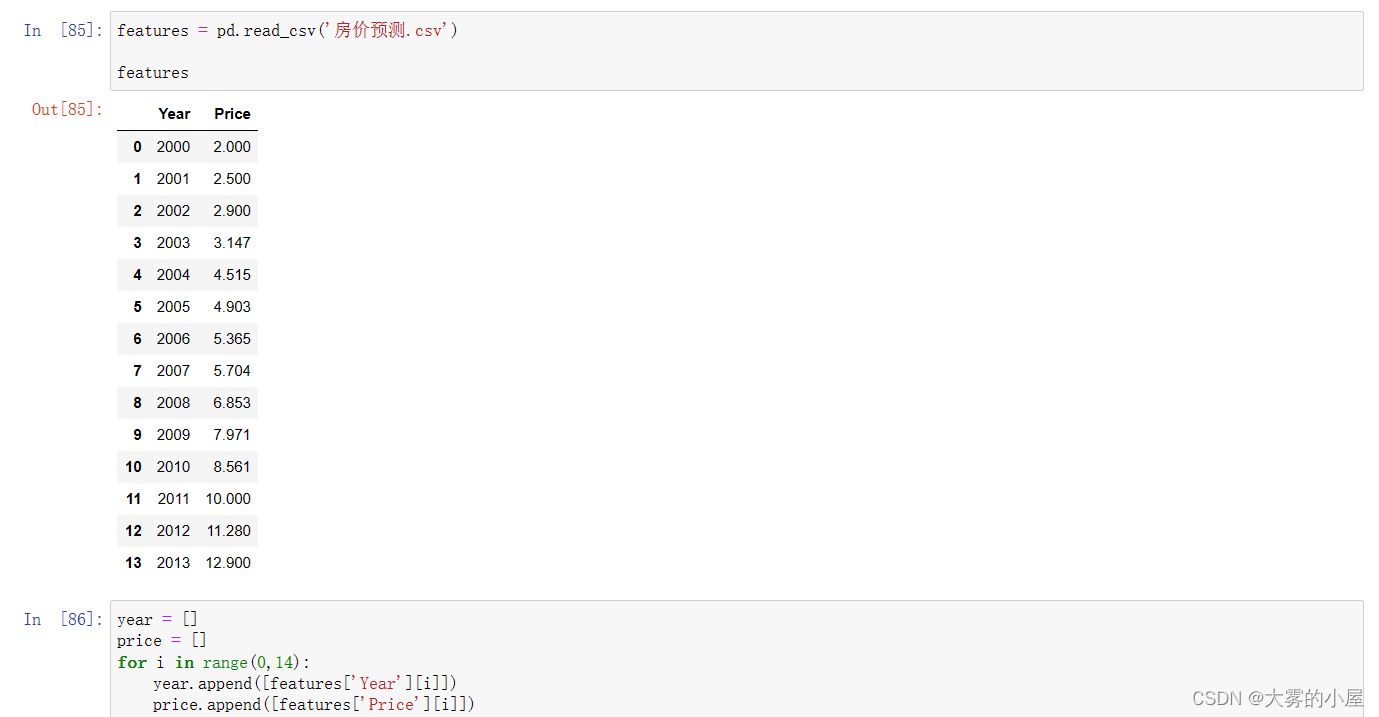
1、首先对数据进行读取和预处理 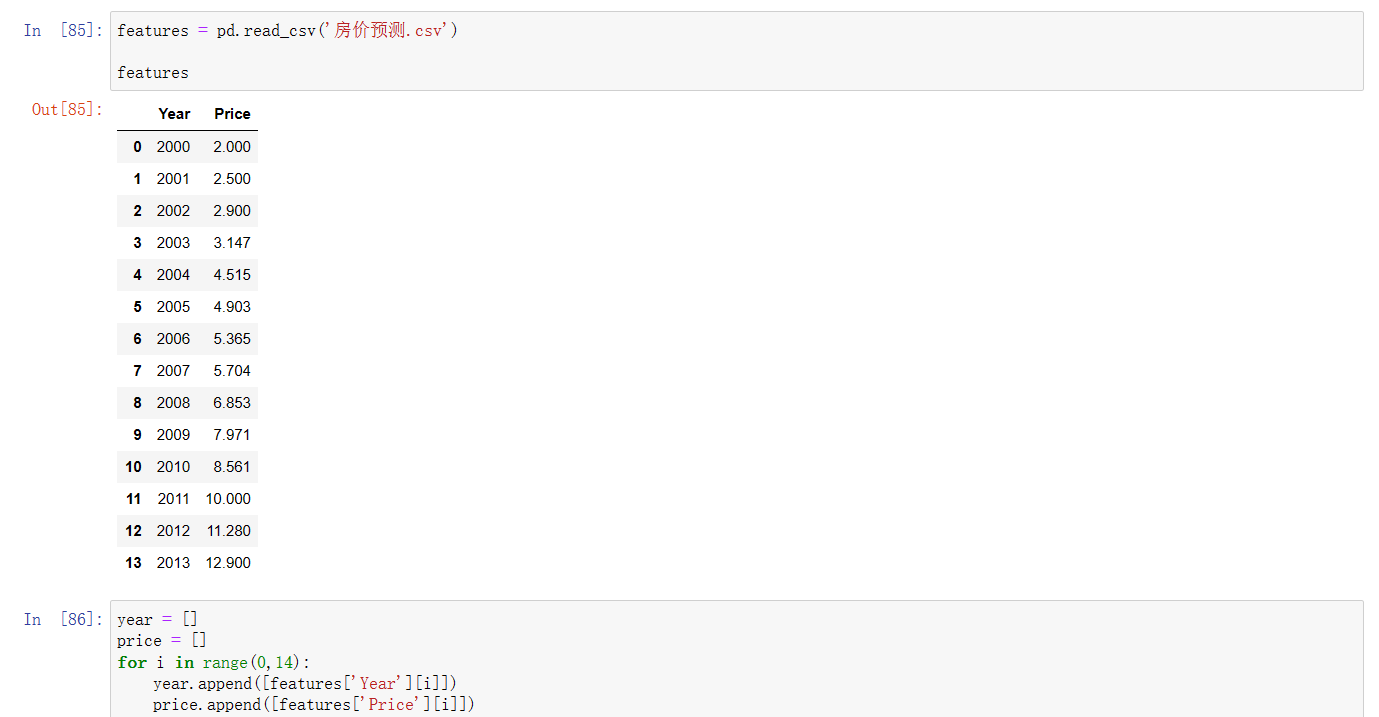
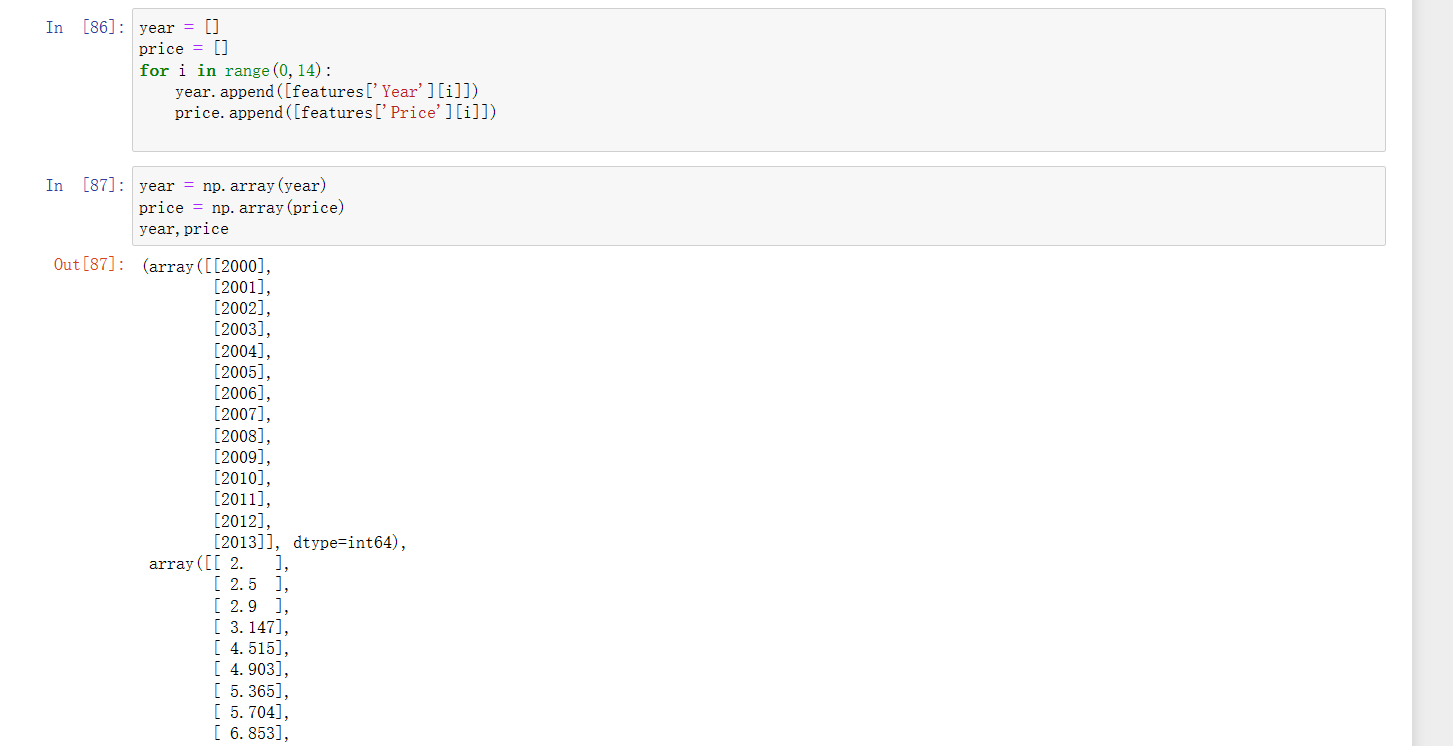 2、读取数据后,对x数据进行标准化处理,以便于后续训练的稳定性,并转换为tensor格式
2、读取数据后,对x数据进行标准化处理,以便于后续训练的稳定性,并转换为tensor格式 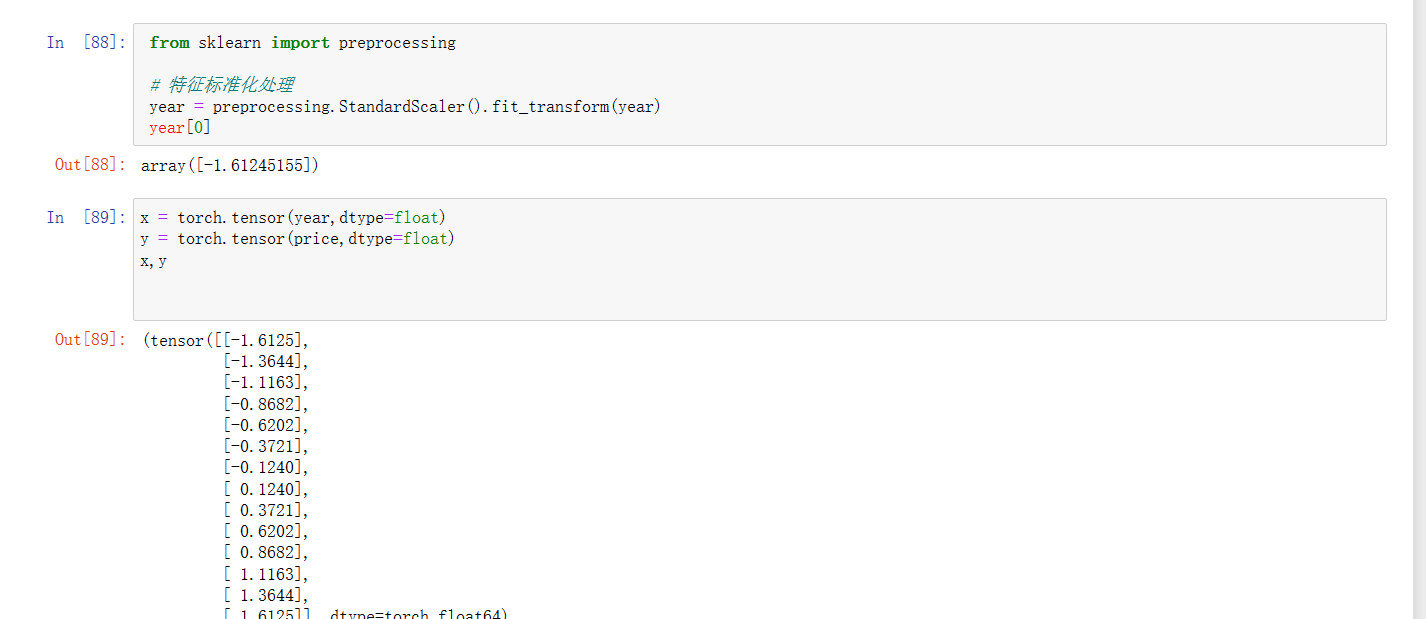 3、接下来设置训练参数和模型 这里采用回归模型,既y=x*weight1+bias1,设置的学习率为0.0006,损失函数采用了MSE(均方误差)
3、接下来设置训练参数和模型 这里采用回归模型,既y=x*weight1+bias1,设置的学习率为0.0006,损失函数采用了MSE(均方误差) 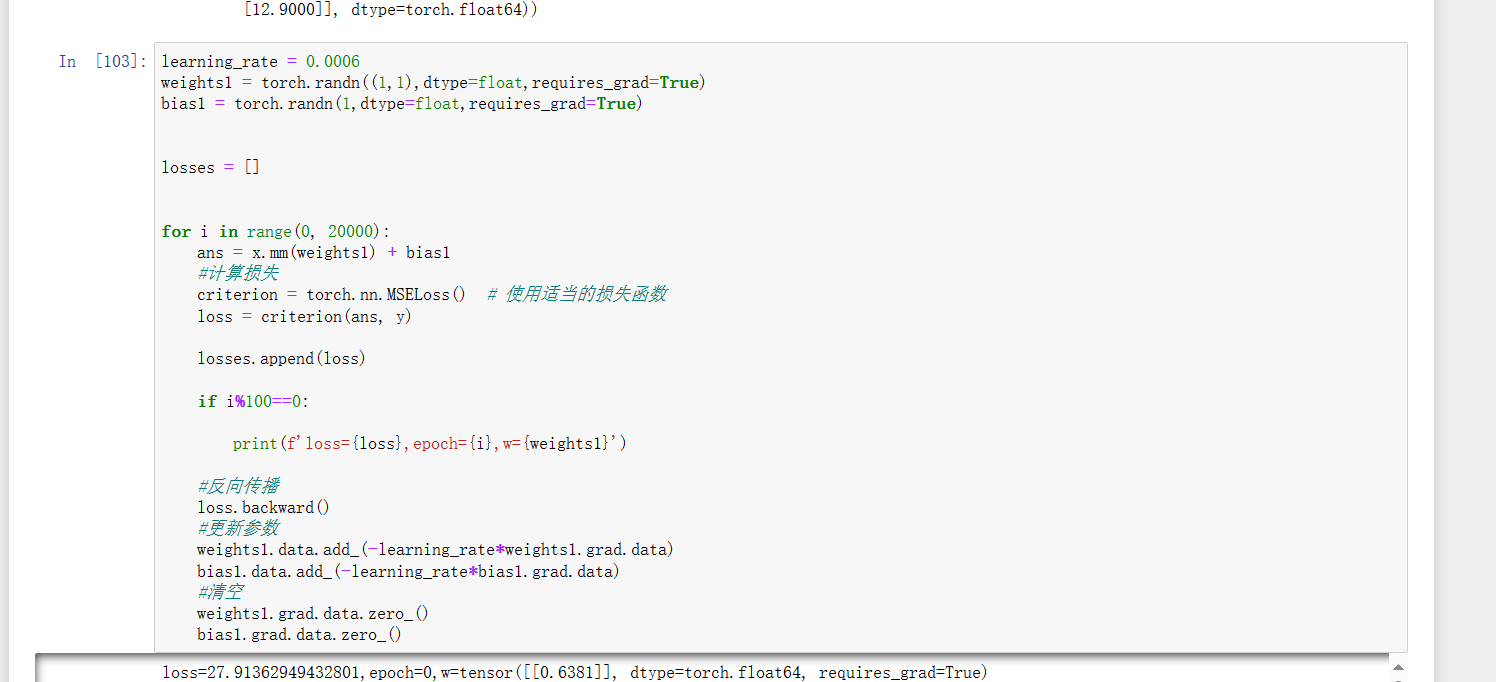 4、绘制图像 由于数据量较少,所以将整个训练集作为测试集,观察生成的图像
4、绘制图像 由于数据量较少,所以将整个训练集作为测试集,观察生成的图像
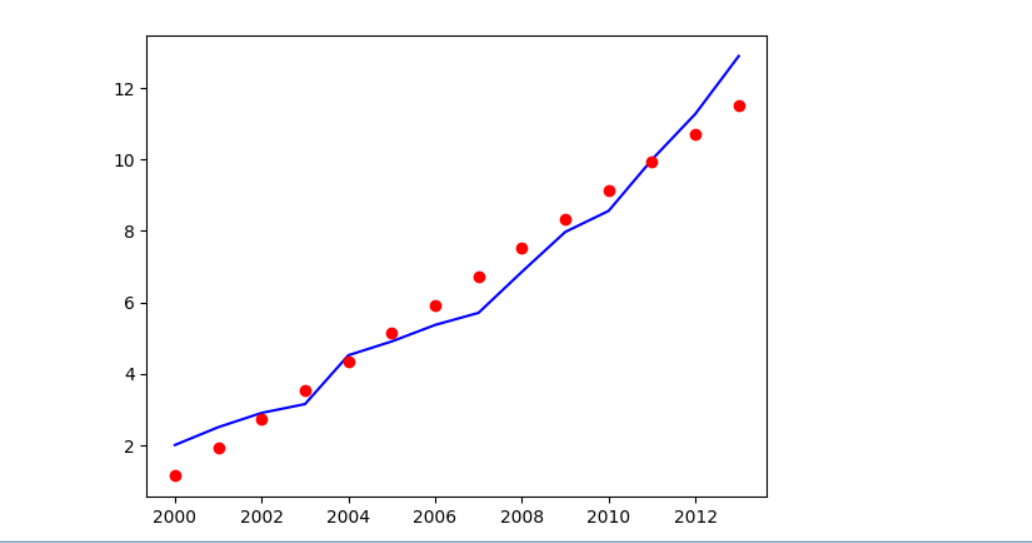
完整代码
import torch
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.optim as optim
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# In[4]:
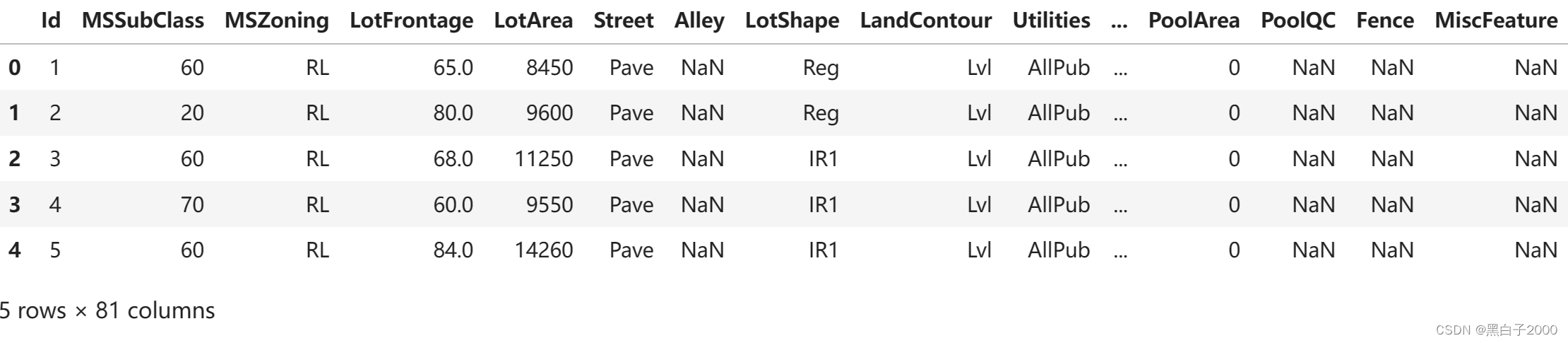
features = pd.read_csv('房价预测.csv')
features
# In[26]:
year = []
price = []
for i in range(0,12):
year.append([features['Year'][i]])
price.append([features['Price'][i]])
# In[27]:
year = np.array(year)
price = np.array(price)
year,price
# In[53]:
from sklearn import preprocessing
# 特征标准化处理
year = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(year)
year[0]
# In[54]:
x = torch.tensor(year,dtype=float)
y = torch.tensor(price,dtype=float)
x,y
# In[62]:
learning_rate = 0.0001
weights1 = torch.randn((1,1),dtype=float,requires_grad=True)
bias1 = torch.randn(1,dtype=float,requires_grad=True)
losses = []
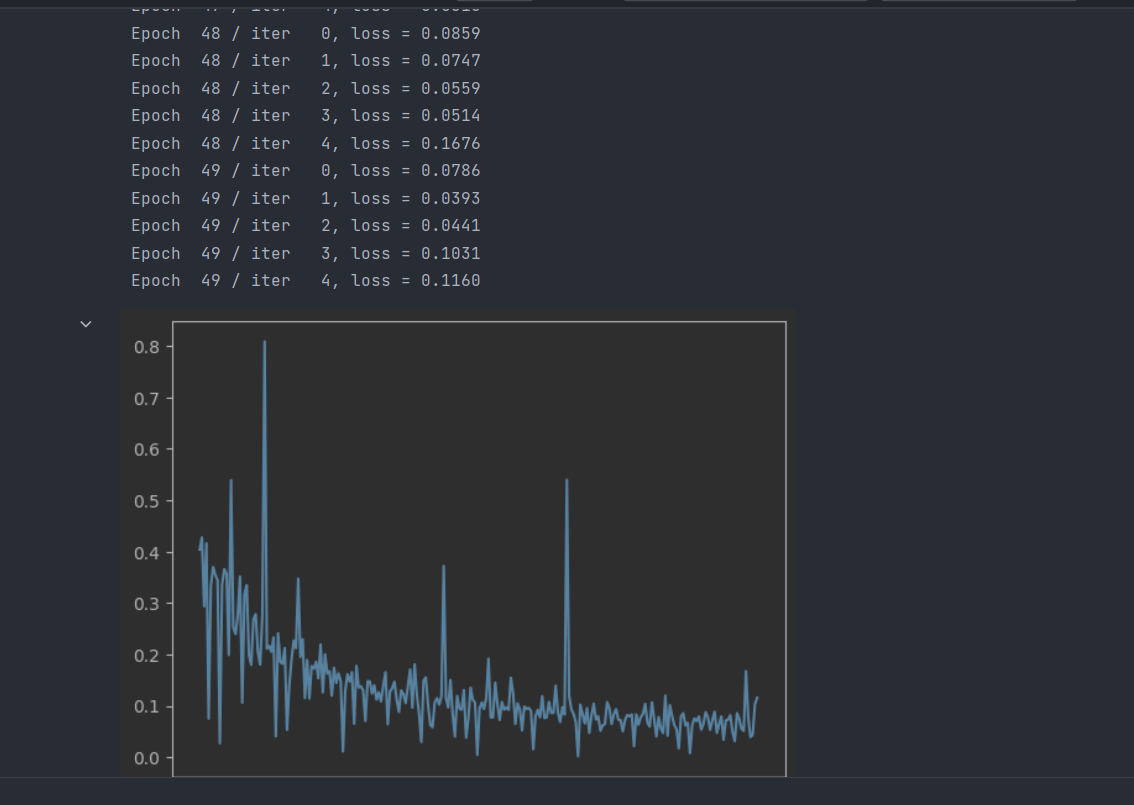
for i in range(0, 5000):
ans = x.mm(weights1) + bias1
#计算损失
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss() # 使用适当的损失函数
loss = criterion(ans, y)
losses.append(loss)
if i%100==0:
print(f'loss={loss},epoch={i},w={weights1}')
#反向传播
loss.backward()
#更新参数
weights1.data.add_(-learning_rate*weights1.grad.data)
bias1.data.add_(-learning_rate*bias1.grad.data)
#清空
weights1.grad.data.zero_()
bias1.grad.data.zero_()
# 使用 features['Year'] 和 features['Price'] 创建日期和价格的列表
year = features['Year']
price = features['Price']
# 将 ans 转换为 Python 列表
ans_list = ans.tolist()
# 提取列表中的每个元素(确保是单个的标量值)
predictions = [item[0] for item in ans_list]
# 创建一个表格来存日期和其对应的标签数值
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data={'date': year, 'actual': price})
predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data={'date': year, 'prediction': predictions})
# 真实值
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label='actual')
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label='prediction')
plt.xticks(rotation='60')
plt.legend()
# 图名
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price') # 注意修改为你的标签
plt.title('Actual and Predicted Values')
plt.show()本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!




















![第四章[结构化程序]:4.2:缩进规则](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9e5a63f14402033a8c219648f34e522e.jpeg)