vector 的介绍:
1、vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器。
2、vector就像数组一样,也采用的连续空间来存储元素,这也意味着可以采用下标对vector的元素进行访问。
3、vector与普通数组不同的是,vector的大小是可以动态改变的。
4、当vector需要重新分配大小时,其做法是,分配一个新的数组,然后将全部元素移到这个数组当中,并释放原来的数组空间。
5、vector分配空间策略:vector会分配一些额外的空间以适应可能的增长,因此存储空间比实际需要的存储空间一般更大。不同的库采用不同的策略权衡空间的使用和重新分配,以至于在末尾插入一个元素的时候是在常数的时间复杂度完成的。
6、由于vector采用连续的空间来存储元素,与其他动态序列容器相比,vector在访问元素的时候更加高效,在其末尾添加和删除元素相对高效,而对于不在其末尾进行的删除和插入操作效率则相对较低。
vector 的使用
1.定义方式
法一:构造一个某类型的空容器。
vector<int> v1; //构造int类型的空容器
法二:构造一个含有n个val的某类型容器。
vector<int> v2(10, 2); //构造含有10个2的int类型容器
法三:拷贝构造某类型容器的复制品
vector<int> v3(v2); //拷贝构造int类型的v2容器的复制品
法四:使用迭代器拷贝构造某一段内容。
vector<int> v4(v2.begin(), v2.end()); //使用迭代器拷贝构造v2容器的某一段内容
注意:该方式也可用于拷贝其他容器的某一段内容。
string s("hello world");
vector<char> v5(s.begin(), s.end()); //拷贝构造string对象的某一段内容
vector的空间增长问题
size和capacity
通过size函数获取当前容器中的有效元素个数,通过capacity函数获取当前容器的最大容量。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
cout << v.size() << endl; //获取当前容器中的有效元素个数
cout << v.capacity() << endl; //获取当前容器的最大容量
return 0;
}
reserve和resize
通过reserse函数改变容器的最大容量,resize函数改变容器中的有效元素个数。
reserve规则:
1、当所给值大于容器当前的capacity时,将capacity扩大到该值。
2、当所给值小于容器当前的capacity时,什么也不做。
resize规则:
1、当所给值大于容器当前的size时,将size扩大到该值,扩大的元素为第二个所给值,若未给出,则默认为0。
2、当所给值小于容器当前的size时,将size缩小到该值。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
cout << v.size() << endl; //10
cout << v.capacity() << endl; //10
v.reserve(20); //改变容器的capacity为20,size不变
cout << v.size() << endl; //10
cout << v.capacity() << endl; //20
v.resize(15); //改变容器的size为15
cout << v.size() << endl; //15
cout << v.capacity() << endl; //20
return 0;
}
empty
通过empty函数判断当前容器是否为空。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
cout << v.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}
vector的迭代器使用
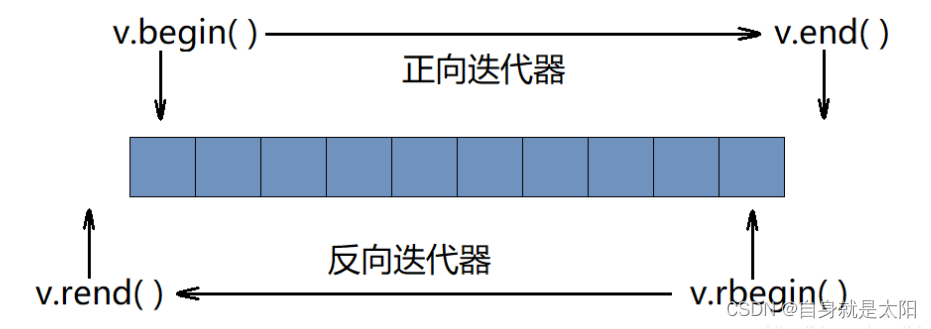
begin和end
通过begin函数可以得到容器中第一个元素的正向迭代器,通过end函数可以得到容器中最后一个元素的后一个位置的正向迭代器。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
//正向迭代器遍历容器
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
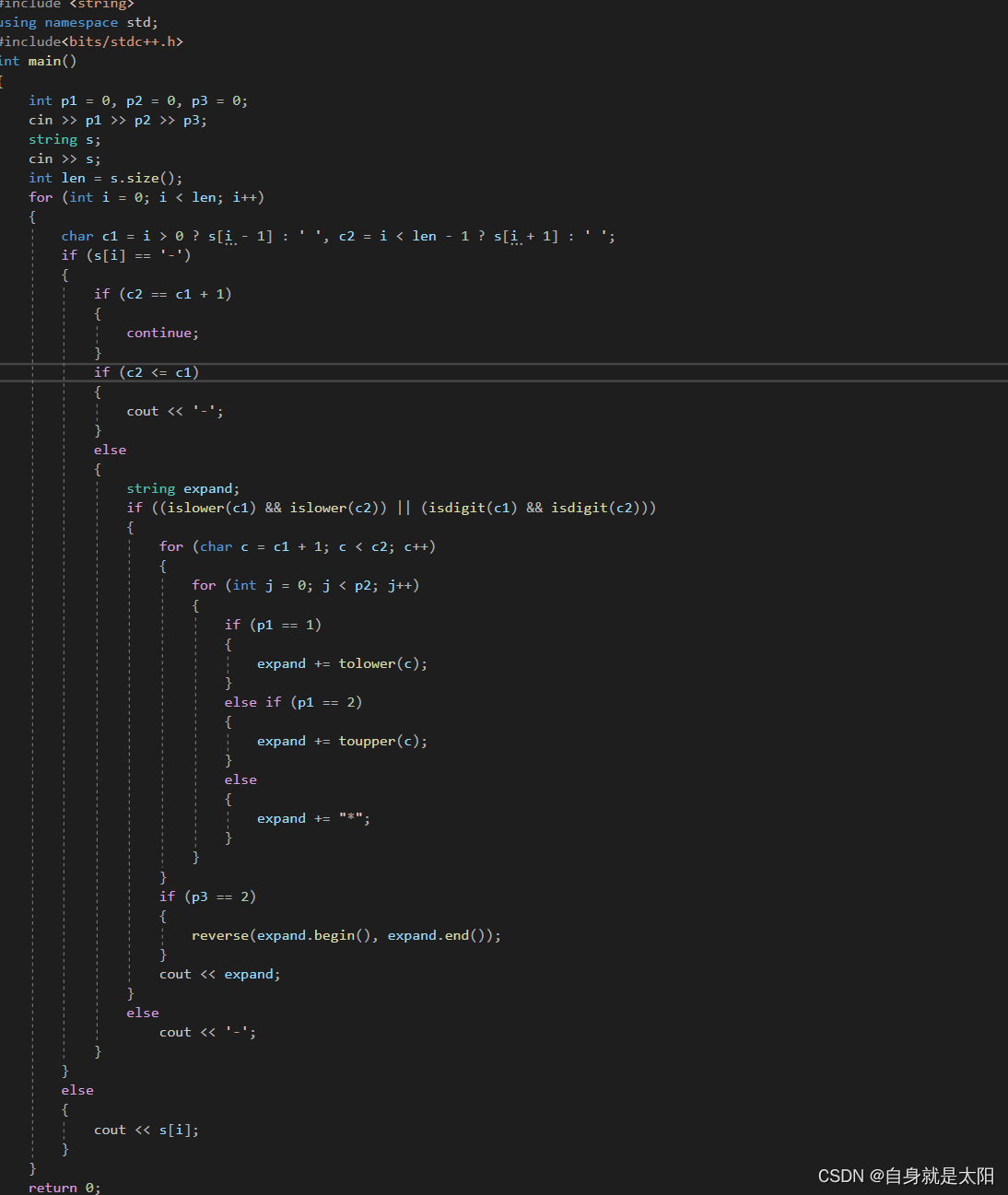
比方说这道题中,在一行中需要,排序,我们这里使用了迭代器

rbegin和rend
通过rbegin函数可以得到容器中最后一个元素的反向迭代器,通过rend函数可以得到容器中第一个元素的前一个位置的反向迭代器。
反向迭代器遍历容器:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
//反向迭代器遍历容器
vector<int>::reverse_iterator rit = v.rbegin();
while (rit != v.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
vector的增删查改
push_back和pop_back
通过push_back函数对容器进行尾插,pop_back函数对容器进行尾删。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1); //尾插元素1
v.push_back(2); //尾插元素2
v.push_back(3); //尾插元素3
v.push_back(4); //尾插元素4
v.pop_back(); //尾删元素
v.pop_back(); //尾删元素
v.pop_back(); //尾删元素
v.pop_back(); //尾删元素
return 0;
}
这里的应用非常广,尤其在字符串那一块,这里给大家整一道相关的编程题
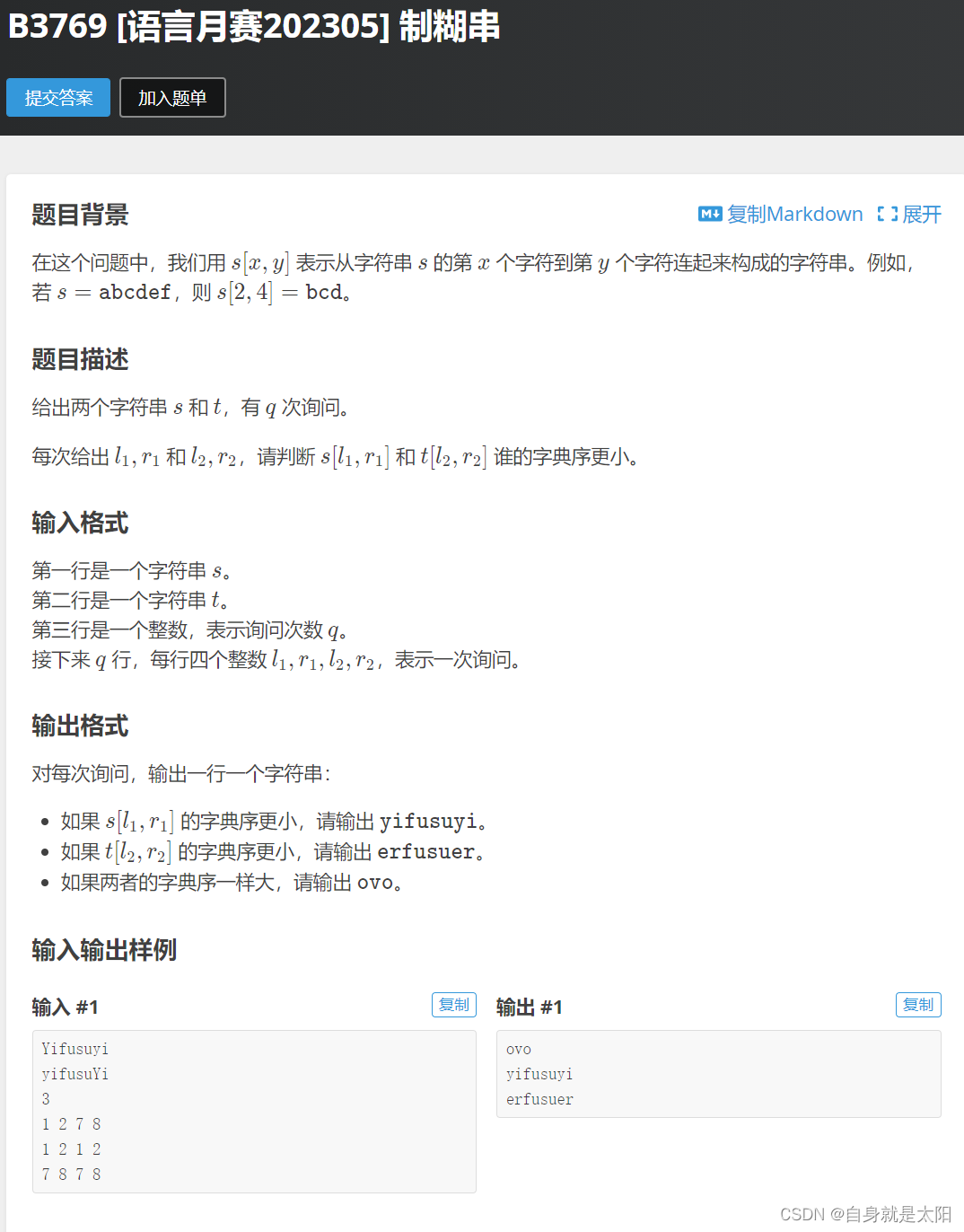
如果用上述我说的来解决的话
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--)
{
string s1, t1;
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;
for (int i = l1-1; i <= r1-1; i++)
{
s1.push_back(s[i]);
}
for (int i = l2 - 1; i <= r2-1; i++)
{
t1.push_back(t[i]);
}
if (s1 > t1)
cout << "erfusuer"<<endl;
else if (s1 < t1)
{
cout << "yifusuyi" << endl;
}
else
cout << "ove"<<endl;
s1 = "";
t1 = "";
}
return 0;
}即可依葫芦画瓢解决,详解在我之前发的字符串的编程题有解释,若代码看不懂可以往前看。
insert和erase
通过insert函数可以在所给迭代器位置插入一个或多个元素,通过erase函数可以删除所给迭代器位置的元素,或删除所给迭代器区间内的所有元素(左闭右开)。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.insert(v.begin(), 0); //在容器开头插入0
v.insert(v.begin(), 5, -1); //在容器开头插入5个-1
v.erase(v.begin()); //删除容器中的第一个元素
v.erase(v.begin(), v.begin() + 5); //删除在该迭代器区间内的元素(左闭右开)
return 0;
}
find函数:
find函数共三个参数,前两个参数确定一个迭代器区间(左闭右开),第三个参数确定所要寻找的值。
find函数在所给迭代器区间寻找第一个匹配的元素,并返回它的迭代器,若未找到,则返回所给的第二个参数。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 2); //获取值为2的元素的迭代器
v.insert(pos, 10); //在2的位置插入10
pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3); //获取值为3的元素的迭代器
v.erase(pos); //删除3
return 0;
}
注意: find函数是在算法模块(algorithm)当中实现的,不是vector的成员函数。
在这里再给大家介绍一个典型题
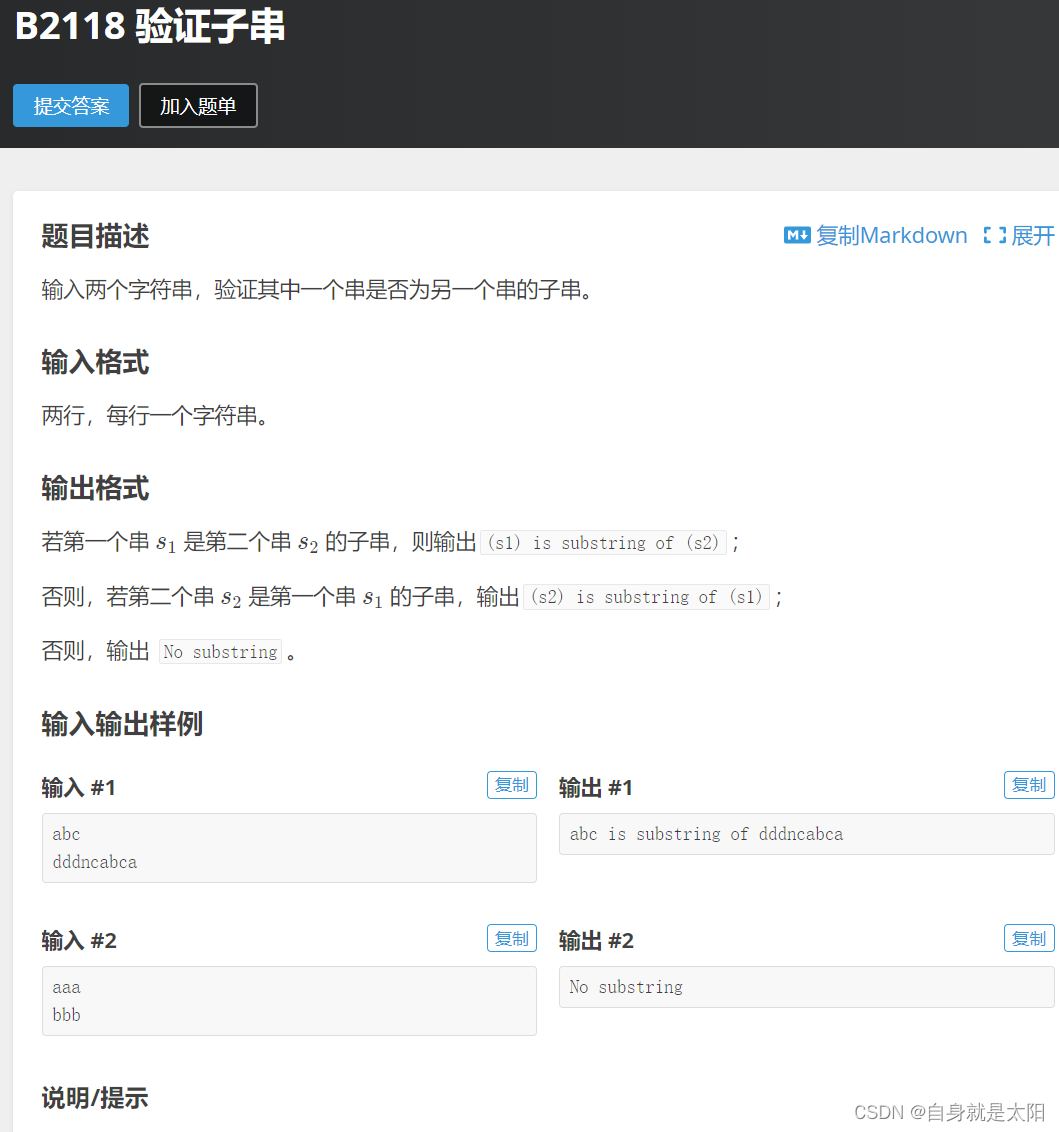
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
if (s2.find(s1) != -1)//如果找到返回首位置,未找到返回-1
{
cout << s1 << " is substring of " << s2 << endl;
}
else if (s1.find(s2) != -1)
{
cout << s2 << " is substring of " << s1 << endl;
}
else
cout << "No substring" << endl;
return 0;
}通过swap函数可以交换两个容器的数据空间,实现两个容器的交换。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1(10, 1);
vector<int> v2(10, 2);
v1.swap(v2); //交换v1,v2的数据空间
return 0;
}
在c语言中交换两个数我们需要设立中间变量,而在c++中可以直接通过swap函数来解决
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1(10, 1);
vector<int> v2(10, 2);
v1.swap(v2); //交换v1,v2的数据空间
return 0;
}
clear
清除字符串内容
#include"vector.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//dabai::test1();
vector<int> arr;
vector<int> s;
arr.push_back(11);
arr.push_back(11);
arr.push_back(11);
arr.push_back(11);
arr.pop_back();
arr.insert(arr.begin()+2, 30);
arr.erase(arr.begin() + 2);
//arr.resize(2);
//arr.reserve(100);
s.swap(arr);
cout << arr.size()<< endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
其实也相当于 s="";
元素访问
vector当中实现了 [ ] 操作符的重载,因此我们也可以通过“下标+[ ]”的方式对容器当中的元素进行访问。
即你可以把他当作数组一样使用
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 1);
//使用“下标+[]”的方式遍历容器
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
我们上面说到vector是支持迭代器的,所以我们还可以用范围for对vector容器进行遍历。(支持迭代器就支持范围for,因为在编译时编译器会自动将范围for替换为迭代器的形式)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 1);
//范围for
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}