目录
1) 入门例子
/**
* 回溯
*
* 程序在运行过程中分成了多个阶段
* 通过某些手段,将数据恢复到之前某一阶段,这就称之为回溯
* 手段包括
* 方法栈
* 自定义栈
*/
public class Backtracking {
public static void main(String[] args) {
rec(1);
}
private static void rec(int n) {
if(n==3){
return ;
}
System.out.println(n);
rec(n+1);
System.out.println(n);
}
}
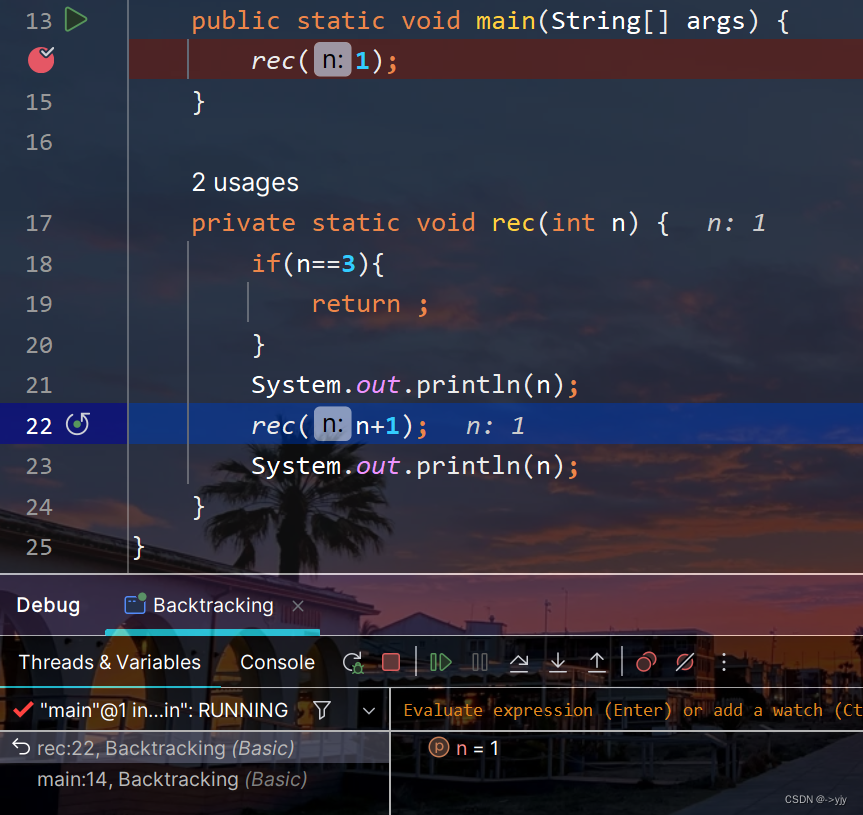
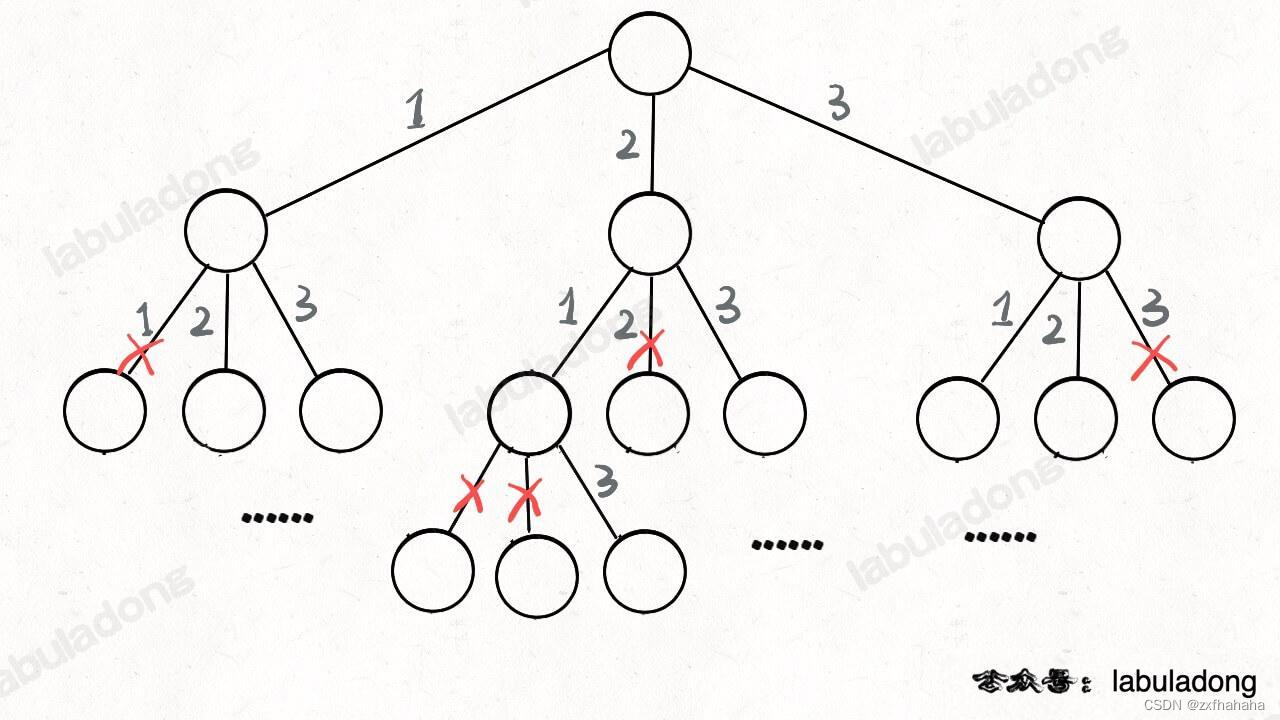
 方法栈
方法栈
如果是集合又有什么样的效果呢?
如果用的是可变的集合或者数组必须手动的恢复集合状态
public class Backtracking {
public static void main(String[] args) {
rec(1, new LinkedList<>());
}
static void rec(int n, LinkedList<String> list) {
if (n == 3) {
return;
}
System.out.println("before:" + list);
list.push("a");
rec(n + 1, list);
list.pop();
System.out.println("after:" + list);
}
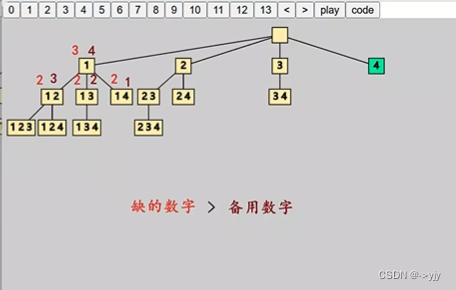
}2) 全排列-Leetcode 46

public class PermuteLeetcode46 {
static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> r = new ArrayList<>();
rec(nums, visited, stack, r);
return r;
}
static void rec(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> r) {
if (stack.size() == nums.length) {
r.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(visited[i]){
continue;
}
stack.push(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
rec(nums, visited, stack, r);
stack.pop();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> permute = permute(new int[]{1, 2, 3});
for (List<Integer> s : permute) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}3) 全排列II-Leetcode 47

public class PermuteLeetcode47 {
static List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nums, new boolean[nums.length], new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (stack.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !visited[i-1]) { // 找出重复数字
continue;
}
if (!visited[i]) {
stack.push(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
dfs(nums, visited, stack, result);
visited[i] = false;
stack.pop();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 1, 3};
List<List<Integer>> permute = permuteUnique(nums);
for (List<Integer> list : permute) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
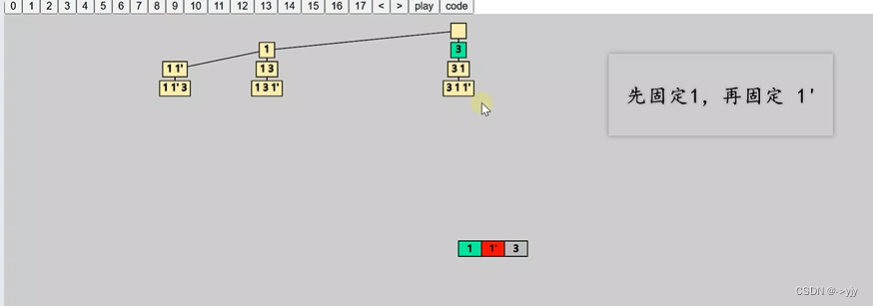
}排好序,这样重复的数字会相邻
定好规则:必须 1 固定之后才能固定 1',即 1 的 visited = true 才能继续处理 1'
在遍历时,遇到了
nums[i] == nums[i - 1](即 1 和 1‘ 这种情况),进一步检查 i-1 位置的数字有没有 visited,没有,则不处理(剪枝)
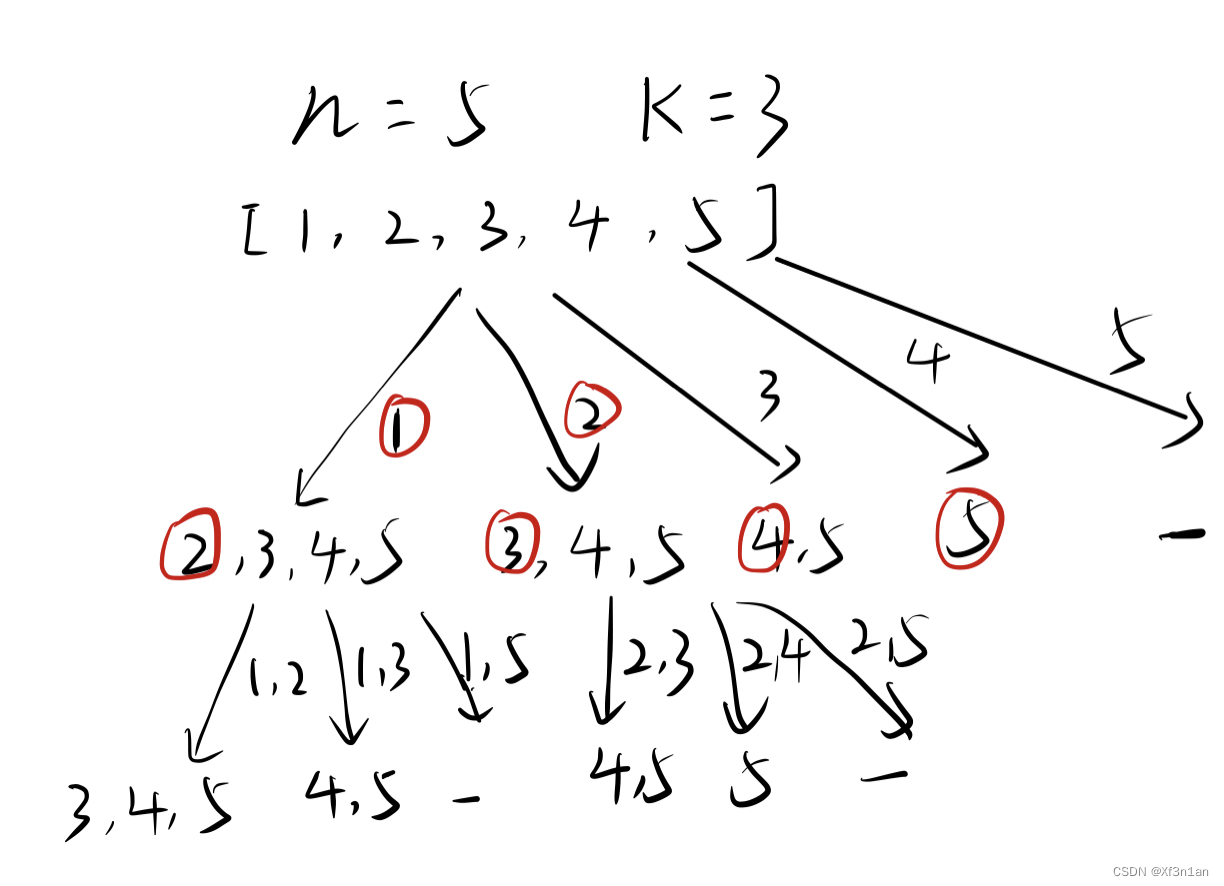
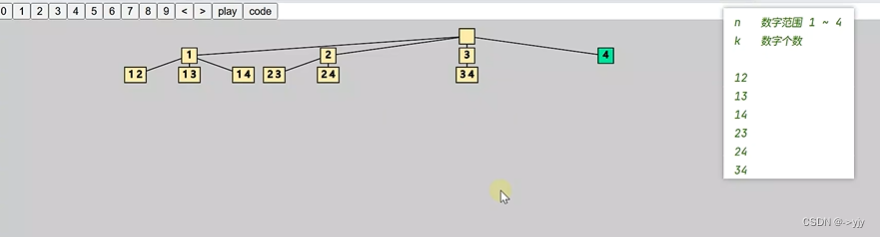
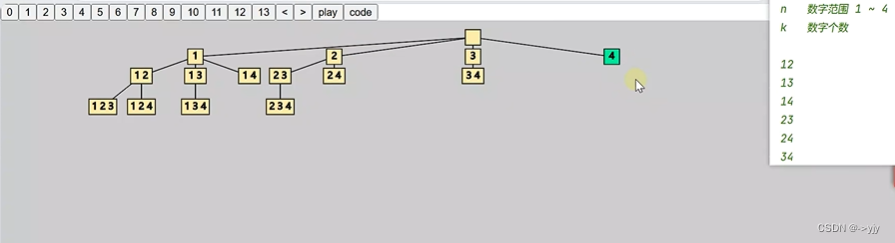
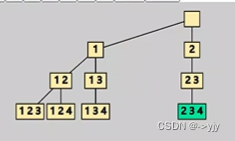
4) 组合-Leetcode 77

k=2
k=3
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer>stack = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(1,n,k,stack,result);
return result;
}
public void dfs(int start,int n,int k,LinkedList<Integer>stack,List<List<Integer>>result){
if(stack.size()==k){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for(int i = start;i<=n;i++){
stack.push(i);
dfs(i+1,n,k,stack,result);
stack.pop();
}
}
}

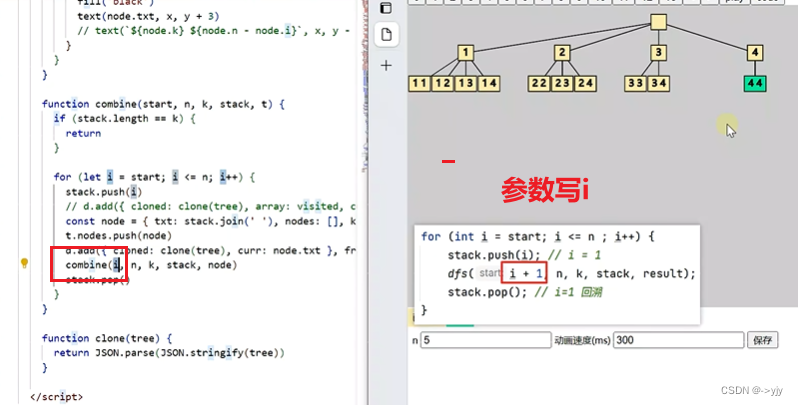
减枝
k- stack.length 还差几个能凑满
n - i +1 还剩下几个备用数字 if(k-stack.length >n-i+1) continue;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer>stack = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(1,n,k,stack,result);
return result;
}
public void dfs(int start,int n,int k,LinkedList<Integer>stack,List<List<Integer>>result){
if(stack.size()==k){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for(int i = start;i<=n;i++){
if(k - stack.size() > n-i+1){
continue;
}
stack.push(i);
dfs(i+1,n,k,stack,result);
stack.pop();
}
}
}
public class CombinationLeetcode77 {
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(n, k, 1, new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static int count = 0;
static void dfs(int n, int k, int start, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
count++;
if (k == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
System.out.println(stack);
return;
}
// if (k > n - start + 1) { return; }
for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) {
// System.out.printf("k-1=%d n=%d i=%d %n", k - 1, n, i);
if (k > n - i + 1) {
continue;
}
stack.push(i);
dfs(n, k - 1, i + 1, stack, result);
stack.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum(5, 4);
// for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
// System.out.println(list);
// }
System.out.println(count);
}
}
k 代表剩余要组合的个数
n - i + 1代表剩余可用数字剪枝条件是:剩余可用数字要大于剩余组合数
为啥放在外面不行?即这行代码:
if (k > n - start + 1) { return; }
因为它只考虑了 start 一种情况,而实际在循环内要处理的是 start,start+1 ... n 这多种情况
似乎 ArrayList 作为 stack 性能高一些,见下面代码,但是这道题在 leetcode 上执行时间不稳定,相同代码都会有较大时间差异(15ms vs 9ms)
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(k == 0 || n < k) return result;
dfs(n, k, 1, new ArrayList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int n, int k, int start, ArrayList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (k == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) {
if (k-1 > n - i) {
continue;
}
stack.add(i);
dfs(n, k - 1, i + 1, stack, result);
stack.remove(stack.size()-1);
}
}
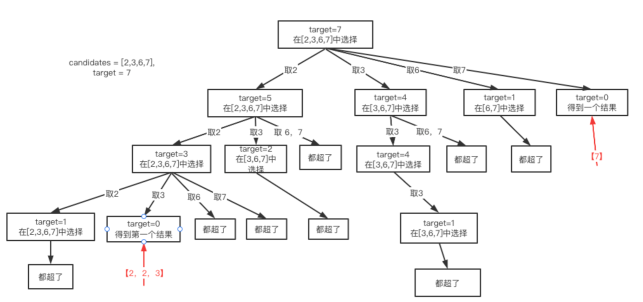
}5) 组合总和-Leetcode 39


class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> stack= new LinkedList<>();
dfs(0,candidates,target,stack,result);
return result;
}
public void dfs(int start,int[] candidates,int target,LinkedList<Integer>stack,List<List<Integer>>result){
if(target<0)
return ;
if(target==0){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for(int i = start;i<candidates.length;i++){
int candidate = candidates[i];
stack.push(candidate);
dfs(i,candidates,target-candidate,stack,result);
stack.pop();
}
}
} 
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> stack= new LinkedList<>();
dfs(0,candidates,target,stack,result);
return result;
}
public void dfs(int start,int[] candidates,int target,LinkedList<Integer>stack,List<List<Integer>>result){
if(target==0){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for(int i = start;i<candidates.length;i++){
int candidate = candidates[i];
if(target<candidate){
continue;
}
stack.push(candidate);
dfs(i,candidates,target-candidate,stack,result);
stack.pop();
}
}
}
与之前的零钱兑换问题其实是一样的,只是
本题求的是:所有组合的具体信息
零钱兑换问题求的是:所有组合中数字最少的、所有组合个数... [动态规划]
6) 组合总和 II-Leetcode 40

public class CombinationLeetcode40 {
static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(target, 0, candidates, new boolean[candidates.length], new LinkedList<>(), result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int target, int start, int[] candidates, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> stack, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
int candidate = candidates[i];
if (target < candidate) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && candidate == candidates[i - 1] && !visited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
stack.push(candidate);
dfs(target - candidate, i + 1, candidates, visited, stack, result);
stack.pop();
visited[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] candidates = {10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};
List<List<Integer>> lists = combinationSum2(candidates, 8);
for (List<Integer> list : lists) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}7) 组合总和 III-Leetcode 216

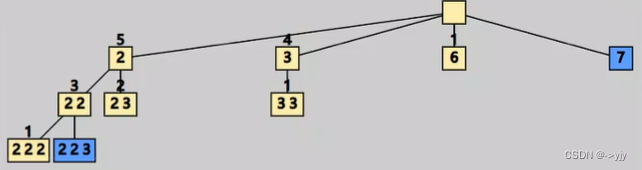
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int target ) {
List<List<Integer>>result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(1,target,k,new ArrayList<>(),result);
return result;
}
//static int count = 0;
static void dfs(int start,int target,int k,ArrayList<Integer>stack,List<List<Integer>>result){
// count++;
if(target==0&&stack.size()==k){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
for(int i = start;i<=9;i++){
// 还差几个数字 剩余可用数字
// if(k-stack.size() > 9-i+1){
// continue;
//} 这个减枝效率较低 设置一个count变量即可查看
if(target<i){
continue;
}
if(stack.size()==k){
continue;
}
stack.addLast(i);
dfs(i+1,target-i,k,stack,result);
stack.removeLast();
}
}
}
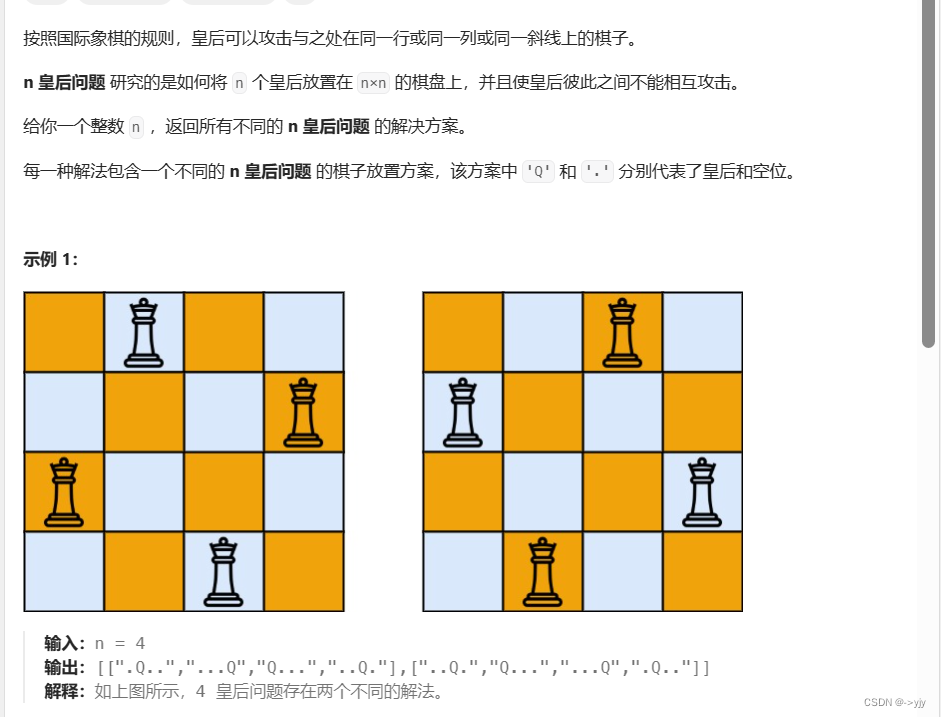
8) N 皇后 Leetcode 51
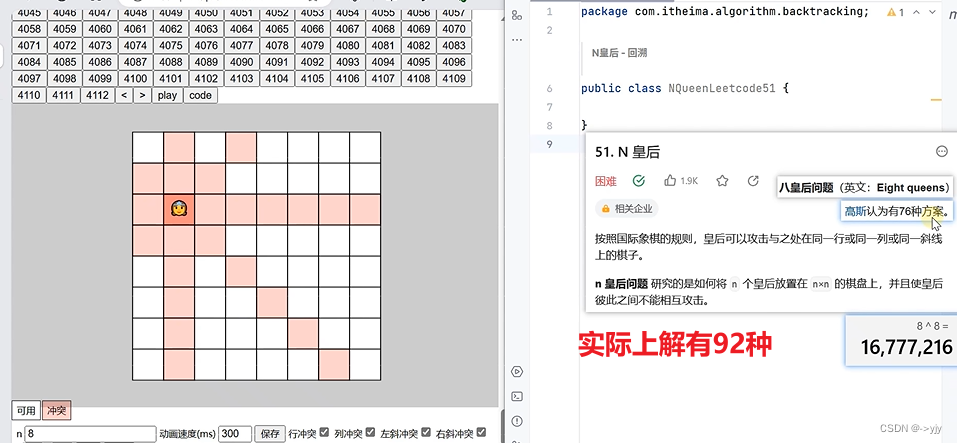
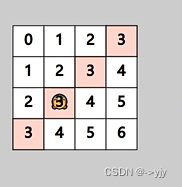 左斜线处理 i+j 相等
左斜线处理 i+j 相等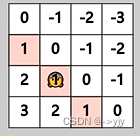 i - j
i - j
 n-1-(i-j)
n-1-(i-j)
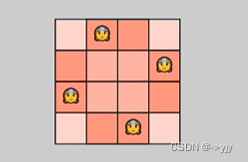 i== n 找到解
i== n 找到解
public class NQueenLeetcode51 {
static List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] table = new char[n][n];//'.' 'Q'
boolean[] va = new boolean[n];//列冲突
boolean[] vb = new boolean[2 * n - 1];//左斜线冲突
boolean[] vc = new boolean[2 * n - 1];//右斜线冲突
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(table[i], '.');
}
dfs(0, n, table, result, va, vb, vc);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int i, int n, char[][] table, List<List<String>> result, boolean[] va, boolean[] vb, boolean[] vc) {
if (i == n) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : table) {
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
result.add(list);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (va[j] || vb[i + j] || vc[n - 1-(i-j)]) {
continue;
}
va[j] = true;
vb[i + j] = true;
vc[n-1-(i-j)] = true;
table[i][j] = 'Q';
dfs(i + 1, n, table, result, va, vb, vc);
table[i][j] = '.';
va[j] = false;
vb[i + j] = false;
vc[i - j + n - 1] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for (List<String> table : solveNQueens(4)) {
for (String row : table) {
System.out.println(row);
}
count++;
System.out.println("--------------------- " + count);
}
}
}public class NQueenLeetcode51 {
static List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
char[][] table = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(table[i], '.');
}
dfs(0, n, table, result);
return result;
}
static void dfs(int i, int n, char[][] table, List<List<String>> result) {
if (i == n) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] chars : table) {
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
result.add(list);
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (notValid(table, i, j)) {
continue;
}
table[i][j] = 'Q';
dfs(i + 1, n, table, result);
table[i][j] = '.';
}
}
/*
. . . .
. . . .
. ? . .
. . . .
*/
static boolean notValid(char[][] table, int row, int col) {
int n = table.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (table[i][col] == 'Q') { // 上
return true;
}
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (table[i][j] == 'Q') {
return true;
}
}
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (table[i][j] == 'Q') {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for (List<String> table : solveNQueens(8)) {
for (String row : table) {
System.out.println(row);
}
count++;
System.out.println("--------------------- " + count);
}
}
}9) 解数独-Leetcode37
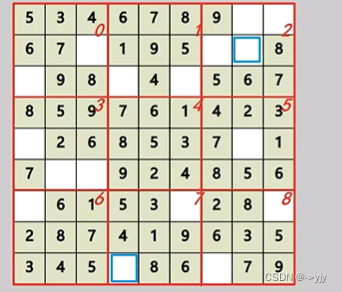 判断在那个九宫格 ==> i/3*3+j/3
判断在那个九宫格 ==> i/3*3+j/3
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
/*
1.不断遍历每个未填的空格
逐一尝试1~9 若行,列,九宫格内没有冲突,则填入
2.一旦1~9 都尝试失败,回溯到上一次状态,换数字填入
3.关键还是要记录冲突状态
*/
// 行冲突状态
boolean[][] ca =new boolean[9][9];
// ca[i] = {false,false,true,true,true,true...}
// 列冲突状态
boolean[][] cb = new boolean[9][9];
// cb[j] = {false,true,true....}
// 九宫格冲突状态
//i/3*3+j/3 = ..在几号九宫格
boolean[][] cc = new boolean[9][9];
//cc[i/3*3+j/3] = {...}
for(int i =0;i<9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
char ch = table[i][j];
if(ch!='.'){//初始化冲突状态
ca[i][ch-'1']=true; //'5'- '1' --> 4
cb[j][ch-'1']=true;
cc[i/3*3+j/3][ch-'1'] =true;
}
}
}
dfs(0,0,table,ca,cb,cc);
}
static boolean dfs(int i,int j,char[][] table,boolean[][] ca,boolean[][] cb,boolean[][] cc){
while(table[i][j]!='.'){ //查找下一个空格
if(++j>=9){
j=0;
i++;//到下一行
}
if(i>=9){
return true; //找到解了
}
}
//填空
for(int x = 1;x<=9;x++){
//检查冲突
if(ca[i][x-1]||cb[j][x-1]||cc[i/3*3+j/3][x-1]){
continue;
}
table[i][j] =(char)x+'0'; //1 -> '1'
//ca[0][0] = true; 第0行不能存储'1'
//cb[2][0] = true; 第2列不能存储'1'
//cc[0][0] = true; 第0个九宫格不能存储'1'
ca[i][x-1] = true;
cb[j][x-1] = true;
cc[i/3*3+j/3][x-1]=true;
if(dfs(i,j,table,ca,cb,cc)){
return true;
}
table[i][j] = '.';
ca[i][x-1] = false;
cb[j][x-1] = false;
cc[i/3*3+j/3][x-1]=false;
}
return false;
}public class SudokuLeetcode37 {
static void solveSudoku(char[][] table) {
int n = 9;
boolean[][] va = new boolean[n][n];//行冲突
boolean[][] vb = new boolean[n][n];//列冲突
boolean[][][] vc = new boolean[3][3][n];//九宫格冲突
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (table[i][j] != '.') {
int x = table[i][j] - '0' - 1;
va[i][x] = true;
vb[j][x] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(table, va, vb, vc, 0, 0);
}
static boolean dfs(char[][] table, boolean[][] va, boolean[][] vb, boolean[][][] vc, int i, int j) {
while (table[i][j] != '.') {
if (++j >= 9) {
j = 0;
i++;
}
if (i >= 9) {
return true;
}
}
int n = table.length;
for (int d = 0; d < n; d++) {
if (va[i][d] || vb[j][d] || vc[i / 3][j / 3][d]) {
continue;
}
char ch = (char) (d + '0' + 1);
table[i][j] = ch;
va[i][d] = true;
vb[j][d] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][d] = true;
boolean dfs = dfs(table, va, vb, vc, i, j);
if (dfs) {
return true;
}
table[i][j] = '.';
va[i][d] = false;
vb[j][d] = false;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][d] = false;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table = {
{'5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'},
{'6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'},
{'.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'},
{'8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'},
{'4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'},
{'7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'},
{'.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'},
{'.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9'}
};
solveSudoku(table);
print(table);
}
static char[][] solved = {
{'5', '3', '4', '6', '7', '8', '9', '1', '2'},
{'6', '7', '2', '1', '9', '5', '3', '4', '8'},
{'1', '9', '8', '3', '4', '2', '5', '6', '7'},
{'8', '5', '9', '7', '6', '1', '4', '2', '3'},
{'4', '2', '6', '8', '5', '3', '7', '9', '1'},
{'7', '1', '3', '9', '2', '4', '8', '5', '6'},
{'9', '6', '1', '5', '3', '7', '2', '8', '4'},
{'2', '8', '7', '4', '1', '9', '6', '3', '5'},
{'3', '4', '5', '2', '8', '6', '1', '7', '9'}
};
static void print(char[][] table) {
for (char[] chars : table) {
System.out.println(new String(chars));
}
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(table, solved));
}
}public class SudokuLeetcode37 {
record Pair(int i, int j) {
}
static void solveSudoku(char[][] table) {
int n = 9;
boolean[][] va = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][] vb = new boolean[n][n];
boolean[][][] vc = new boolean[3][3][n];
List<Pair> blanks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (table[i][j] != '.') {
int x = table[i][j] - '0' - 1;
va[i][x] = true;
vb[j][x] = true;
vc[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
} else {
blanks.add(new Pair(i, j));
}
}
}
dfs(0, blanks, table, va, vb, vc);
}
static boolean dfs(int p, List<Pair> blanks, char[][] table, boolean[][] va, boolean[][] vb, boolean[][][] vc) {
if (p == blanks.size()) {
print(table);
return true;
}
int n = table.length;
for (int d = 0; d < n; d++) {
Pair pair = blanks.get(p);
if (va[pair.i][d] || vb[pair.j][d] || vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d]) {
continue;
}
char ch = (char) (d + '0' + 1);
table[pair.i][pair.j] = ch;
va[pair.i][d] = true;
vb[pair.j][d] = true;
vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d] = true;
boolean dfs = dfs(p + 1, blanks, table, va, vb, vc);
if (dfs) {
return true;
}
table[pair.i][pair.j] = '.';
va[pair.i][d] = false;
vb[pair.j][d] = false;
vc[pair.i / 3][pair.j / 3][d] = false;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] table = {
{'5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'},
{'6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'},
{'.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'},
{'8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'},
{'4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'},
{'7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'},
{'.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'},
{'.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'},
{'.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9'}
};
solveSudoku(table);
print(table);
}
static char[][] solved = {
{'5', '3', '4', '6', '7', '8', '9', '1', '2'},
{'6', '7', '2', '1', '9', '5', '3', '4', '8'},
{'1', '9', '8', '3', '4', '2', '5', '6', '7'},
{'8', '5', '9', '7', '6', '1', '4', '2', '3'},
{'4', '2', '6', '8', '5', '3', '7', '9', '1'},
{'7', '1', '3', '9', '2', '4', '8', '5', '6'},
{'9', '6', '1', '5', '3', '7', '2', '8', '4'},
{'2', '8', '7', '4', '1', '9', '6', '3', '5'},
{'3', '4', '5', '2', '8', '6', '1', '7', '9'}
};
static void print(char[][] table) {
for (char[] chars : table) {
System.out.println(new String(chars));
}
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(table, solved));
}
}10) 黄金矿工-Leetcode1219

class Solution {
int[][] g;
boolean[][] vis;
int m,n;
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {
g = grid;
m = g.length;n = g[0].length;
vis= new boolean[m][n];
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){
if(g[i][j]!=0){
vis[i][j] = true;
ans = Math.max(ans,dfs(i,j));
vis[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int dfs(int x,int y){
int ans = g[x][y];
for(int[] d:dirs){
int nx = x+d[0],ny = y+d[1];
if(nx<0||nx>=m||ny<0||ny>=n)continue;
if(g[nx][ny]==0)continue;
if(vis[nx][ny]) continue;
vis[nx][ny] = true;
ans = Math.max(ans,g[x][y] + dfs(nx,ny));
vis[nx][ny] =false;
}
return ans;
}
}其它题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Leetcode 1219 | 黄金矿工 | |
| 无 | 马踏棋盘(The Knight’s tour problem) | |
| 无 | Rat in a Maze | 与 Leetcode 62 不同路径区别在于,该题问的是有多少种走法,而本题只是找到其中一种走法实现 |
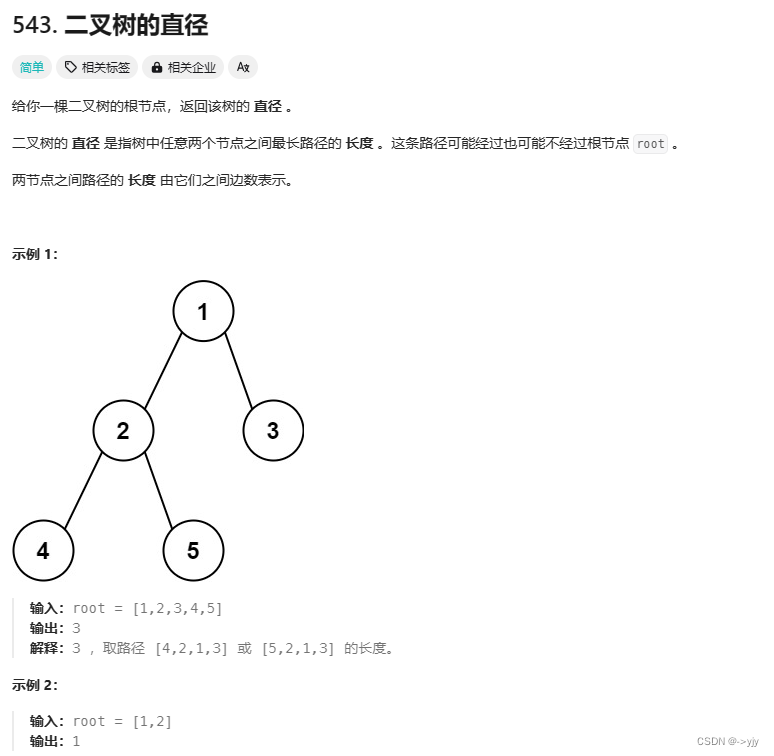
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
int dfs(TreeNode u){
if(u==null) return 0;
int l = dfs(u.left),r=dfs(u.right);
ans = Math.max(ans,l+r);
//返回最大深度
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
}
class Solution {
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int minMutation(String start, String end, String[] bank) {
backtrack(start, end, bank, new boolean[bank.length], 0);
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ans;
}
public void backtrack(String start, String end, String[] bank, boolean[] used, int t) {
if (t >= ans) return;
if (start.equals(end)) {
ans = Math.min(ans, t);
} else {
for (int i = 0, diff = 0; i < bank.length; i++, diff = 0) {
if (used[i]) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < start.length(); j++)
diff += start.charAt(j) != bank[i].charAt(j) ? 1 : 0;
if (diff == 1) {
used[i] = true;
backtrack(bank[i], end, bank, used, t + 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
}